Video: Air Purifier: Components, and Principle of Dust Removal & Purification

Figure 1: The structure of an air purifier.
Air purifiers are a common household appliance in modern life. It can remove various air pollutants and effectively improve air cleanliness. Air purifiers are mainly used in homes, offices, medical institutions and commercial places, with various types and different shapes and structures.
The development of modern technology has led to a wide variety of air purifiers. Different purification technologies have different emphases in the effect of purifying the air. So, do you know the basic structural components and purification principles of air purifiers? Don’t worry, the relevant content will be introduced in detail below.
1. Main Components of Air Purifier
1.1 Air Filter/Dust Filter for Air Purifier
In an air purifier, a device that can effectively capture, adsorb, filter, and transform dust and harmful substances (bacteria and odors, etc.) in the air is the filter, which is the core component of the air purifier.
The basic filtration system consists of 3 parts: primary filter PP cotton, HEPA fine filtration, and activated carbon adsorption.

Figure 2: Basic filtration system schematic diagram of an air purifier.
Primary filter: It may be composed of common filter materials such as PP cotton to filter large particles such as dust mites, dust, hair, and pollen.
HEPA filter: It is a high-efficiency filter that can filter out particles above 0.3 microns, including bacteria, viruses, pollen, dust mites, etc., with a purification efficiency of over 99.97%.
Activated carbon filter: It can remove odors and harmful gases in indoor air, such as formaldehyde, benzene, etc.
The above are the most basic parts of an air purifier. Common air purifiers on the market generally include these three parts. In addition, there are some new technologies to deal with pollutants: First, take a look at the schematic diagram of the advanced air purifier. On the premise of the three basic filter layers of PP cotton, HEPA filter, and activated carbon mesh, more filter layers are added.

Figure 3: structure of a 9-in-1 purification system diagram of an air purifier.
The advanced filter layers mainly include:
Electrostatic air filter: It mainly uses electrode discharge to charge solid particles, and the particles can be adsorbed to the dust collecting plate, so its function is to remove dust.
Note: This method will produce ozone. Ozone itself has a purifying effect, but too high a concentration will be harmful to the human body and the environment. Therefore, when buying this type of air purifier, you should pay attention to whether it has an ozone reduction device or the ozone release is within the safe range.
Ionizer: It releases negative ions into the air to charge small particles suspended in the air, thereby these particles converge into large ones and settle on the ground. Negative ion technology has a good removal effect on second-hand smoke, dust, etc., and is very helpful in the treatment of respiratory diseases.
Photocatalyst: It is an optical semiconductor material with photocatalytic effects such as nanoscale titanium dioxide. It must function under ultraviolet irradiation, otherwise it will not be effective. The main function is to degrade toxic and harmful gases in the air, kill bacteria and fungi, etc. It can also remove formaldehyde and deodorize.
Cold catalyst filter: It is also a new type of air purification technology. It uses catalytic oxidation and chemical adsorption to decompose harmful gases at room temperature, such as formaldehyde, benzene, ammonia, etc., and converts them into carbon dioxide and water. The cold catalyst itself does not participate in the reaction, so it can be used for a long time.
Ultraviolet UV lamp and ozone: It can destroy the molecular structure of microorganisms and play a role in sterilization and disinfection. However, ultraviolet rays are harmful to the human body. Check whether there is any possibility of exposure to ultraviolet lamps (It's okay to be exposed to ultraviolet light for a short time, but don't stay under ultraviolet light frequently or for a long time).
The picture below shows the air filter layers of Daikin MCK70 air purifier.

Figure 4: The air filter layers of Daikin MCK70 air purifier.
Daikin MCK70 purifier adopts four air filter layers.
1. The front filter is used to capture and intercept larger particles of dust.
2. The electrostatic filter is used to adsorb positively charged dust particles.
3. The titanium photocatalyst filter can oxidatively decompose odors and pollutants, and is close to the electrostatic filter. It can self-restore its purification function after decomposing dirt.
4. Photocatalyst and deodorizing catalyst mainly decompose and eliminate the harmful substances of fine particles to improve the dust removal and filtration effect.
1.2 Air Circulation System of Air Purifier
The air circulation system of the air purifier is mainly composed of a fan and air duct. The fan consists of fan blades and a motor, and is used to make the air to form airflow. The air duct is composed of an air inlet channel and an air exhaust channel.
The motor drives the fan blades to rotate at high speed, pushing the air to form a strong airflow, allowing the indoor air to pass through the dust filter and circulate. During the circulation process, dust and mold in the air are intercepted, captured and decomposed by the dust filter. Continuous cycle work purifies all the air in the room. The position of the air purifier in the room and the air flow formed are shown in the figure below.

Figure 5: Air circulation in a room with an air purifier.
The figure below is a schematic diagram of the fan and air duct structure of the air purifier. The fan is small and efficient and can achieve large air volume. It is composed of a motor and fan blades. When the motor rotates, the indoor air is sucked in from the axial direction of the motor. Under the guidance of the air duct, the air flow is discharged from the upper part of the air duct to form a circulation of indoor air.

Figure 6:The fan and air duct structure diagram of an air purifier.
The picture below shows the structure of the fan blades and the motor. When the air purifier is working, the motor drives the fan blades to rotate to form airflow. The greater the speed of the motor, the faster the dust removal speed.

Figure 7:The structure of the fan blades and the motor of an air purifier.
1.3 Humidification Mechanism of Air Purifier
In order to improve the sterilization ability, many manufacturers have added humidification mechanisms to indoor air purifiers and use ionized water for anti-mildew and antibacterial purposes.
The humidification mechanism is composed of a water storage tank, water wheel and ion generator. The humidification filter is installed in the water wheel. The ion generator ionizes the water. When the water wheel rotates, the filter is soaked by water. The air passes through the dust filter with ionized water for further anti-mold and antibacterial treatment and is humidified at the same time.
The humidification and dust removal mechanism used in the air purifier with dual humidification filter is shown in the figure below.

Figure 8:Air purifier with dual humidification filter.
2. What is the Purification Principle of Air Purifier?
How many steps does the purification process of an air purifier have?
Step 1: Suck in air into the body.
Step 2: Purify the air in the machine.
Step 3: Release the purified air.
There are three main working principles of air purifiers on the market: physical filtration, chemical adsorption, and biological sterilization. Next, we will explain in detail the purification principles of different air purification technologies.
Physical Filtration
This is mainly achieved through filters such as HEPA filters and activated carbon filters. This filtration method often causes harmful substances such as bacteria and viruses to accumulate in the filter itself. The filter is easily saturated or even releases harmful substances, causing secondary pollution, so it needs to be replaced regularly.
Chemical Adsorption
Use chemical technology to catalyze, oxidize, neutralize and adsorb air pollutants. For example, photocatalyst air purification technology uses photocatalytic reactions for purification. Its oxidation ability can cut off the chemical bonds that make up organic molecules and decompose them into harmless water and carbon dioxide.
Biological Sterilization
Short-wave ultraviolet UVC with a wavelength in the range of 200~280nm can destroy the molecular structure of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) or RNA (ribonucleic acid) in bacteria and viruses, causing growth cell death and/or regenerative cell death, to achieve the effect of fundamentally killing bacteria and viruses.
However, it is worth noting that short-wave ultraviolet rays have certain harm to the human body. When purchasing an ultraviolet purification device, choose one device that can coexist with humans, so that you can use it more safely at home.
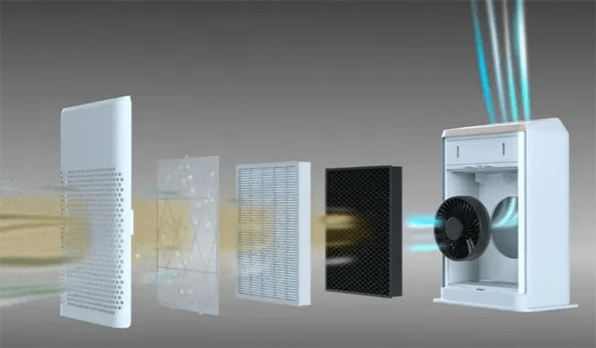
Figure 9:Working principle diagram of an air purifier.
Generally speaking, the working principle of an air purifier is to filter particulate matter and harmful gases in the indoor air through filters, thereby achieving the purpose of purifying the air. The principle of filter filtration mainly includes three methods: physical filtration, chemical adsorption and biological sterilization. Regular replacement of the primary filter can ensure the purification effect.














