Video: Difference between AC, DC and EC Fans

Figure 1: Backward-inclined centrifugal EC fan.
AC fans, DC fans and EC fans are classified according to their power supply type and motor type respectively. They differ in drive method, performance and application range. The choice of fan type has an important impact on cooling effect, energy consumption and noise.
This article introduces in detail the basic knowledge about these three types of fans and the differences between them. Hope it can help you distinguish these three types of fans and provide assistance for your fan selection.
1. Introduction to AC, DC and EC Fans
1.1 AC Fan
AC (Alternating Current) fans refer to fans driven by AC power, and their motors are usually single-phase or three-phase asynchronous motors. Since the voltage and frequency of the AC power supply are relatively stable, the output power and mechanical efficiency of the AC fan are very high.
At the same time, its rotation speed is stable, the torque stability is good when the load changes, and the reliability is high. Usually AC fans are widely used in industrial ventilation, cooling, HVAC, agriculture, transportation and other fields.

Figure 2: AC fan.
AC Fan Basics:
Drive Method: AC fans are powered by AC power, usually connected to the power grid or a generator.
Structure and Working Principle: An AC fan includes a motor, rotor and stator, and they generate rotational force through the voltage and frequency provided by AC power to create fan flow.
Advantages: AC fans have simple design and structure, a wide range of applications, and are usually used in low-cost and simple applications, such as household electric fans.
Disadvantages: The speed of AC fans is usually constant and cannot be adjusted. An inverter is required to adjust the frequency and speed. They also consume more energy and are noisier.
1.2 DC Fan
DC (Direct Current) fans refer to fans driven by DC power, and their motors are usually brushed or brushless DC motors. The voltage and current of the DC power supply fluctuate greatly, so the output power and mechanical efficiency of the DC fan are relatively low, but it can achieve higher rotation speed and smaller size.
At the same time, DC fans have good torque performance and control performance when operating at low speed and low load, and are widely used in computers, communication equipment, power tools, small household appliances and other fields.

Figure 3: DC fan.
DC Fan Basics:
Drive Method: DC fan is powered by DC power supply, which can be provided by battery or adapter.
Structure and Working Principle: DC fans consist of motors, rotors and stators, similar to AC fans. However, they use DC power and the rotational speed can be regulated by changing the voltage or using a speed controller.
Advantages: It has good starting and speed regulation characteristics. The DC fan has an adjustable speed function, and the fan speed can be adjusted as needed. They are also relatively efficient, consuming less energy. Additionally, their noise levels are relatively low. These make DC fans very useful in applications that require precise control and adjustable speed capabilities, such as computer radiators, server cooling, and some industrial and automotive applications.
Disadvantages: A controller is required to output DC power for the DC fan, and the electromagnetic radiation is large. DC fans may cost slightly more than AC fans.
1.3 EC Fan
EC (Electrical Commutation) fans refer to fans that use permanent magnet motors driven by electronic controllers. They achieve the small size and high efficiency of DC fans while having the high reliability and better control performance of AC fans.
The EC fan achieves precise control of parameters such as speed, air volume and pressure through an electronic controller, which can effectively reduce energy consumption and noise, and improve the efficiency and life of the fan. EC fans are currently used in air treatment, ventilation, refrigeration, fresh air systems and other fields.
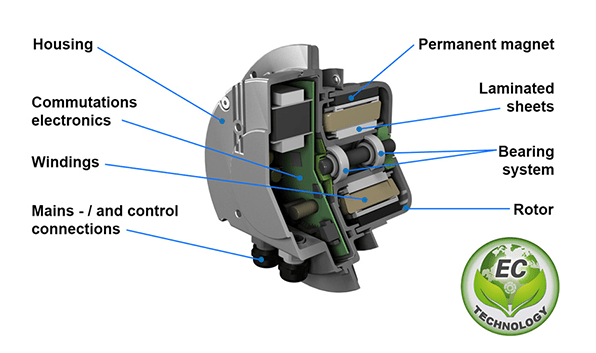
Figure 4: EC fan motor
EC Fan Basics:
Drive Method: An EC fan adjusts the speed of the motor through an Electronic Control Unit (ECU), and is usually powered by a DC power supply.
Structure and Working Principle: EC fans adopt advanced electronic speed control technology and combine the advantages of AC and DC fans. EC fans have dedicated motor controllers and sensors that can adjust the speed accurately according to demand.
Advantages: EC fans provide precise fan speed control which can be dynamically adjusted according to needs. They feature high performance and low energy consumption, providing optimal performance under varying loads. In addition, EC fans also have the advantages of low noise and long life. They are widely used in building ventilation, HVAC systems, data centers and other applications that require efficient and intelligent control.
Disadvantages: EC fans may cost more than AC and DC fans.
2. Comparison between AC Fan and EC Fan
EC fans have the following advantages over AC fans:

Figure 5: EC fan vs. AC fan.
1. It can realize constant voltage, constant current, constant power and other control modes, making the mechanical load small and the work efficiency high.
2. Able to adjust the power supply output voltage in real time according to load changes, and automatically adjust the fan speed when the power supply voltage fluctuates to maintain stable operation.
3. The starting torque is small, the starting time is short, the transient response is fast, and the air volume can be changed quickly.
4. In long-term operation, EC fans consume less energy than AC fans and have lower maintenance costs.
5. EC fans do not need to use additional electrical components such as frequency converters and capacitors. The system is simpler and more reliable, with lower noise and longer life.
3. Comparison between DC Fan and EC Fan
Both DC fans and EC fans are actually DC powered, but there are certain differences between them. To summarize briefly: a DC fan works with direct current, and an EC fan also works with the direct current converted from alternating current.
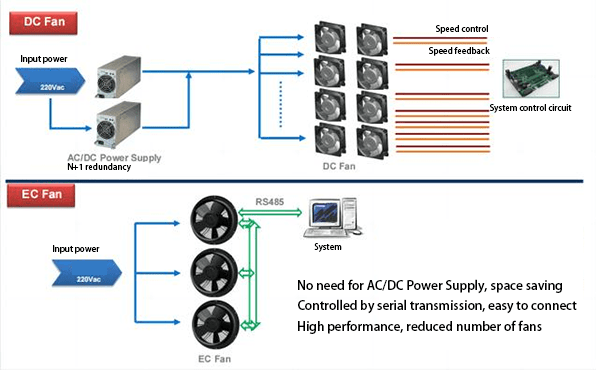
Figure 6: DC fan system vs. AC fan system.
1. Different motor control methods: EC fans control the motor speed and current through electronic circuits, while DC fans need to use an external speed regulator or PWM controller to adjust the motor speed and current.
2. Different speed adjustment ranges: EC fans have more diverse speed adjustment methods, supporting 0-10V/4-20mA analog speed adjustment, PWM control, RS485 communication, etc.; while DC fans usually only support PWM/0-10V speed adjustment.
3. Different electrical noise: The control method of the EC fan electronic circuit reduces the control noise and current noise existing in traditional DC fans.
4. Efficiency: EC fans are more efficient than traditional DC fans.

Figure 7: EC fan signal control.
In general, EC fans have better characteristics in terms of speed range, control method and noise, and are more efficient. DC fans are generally cheaper and allow simple speed regulation by directly adjusting the voltage when fine control is not required. When more advanced fine control, increased efficiency and reduced noise are required, EC fans may be a better choice.











/SKF-Oil-Seal-35X72X7-HMS5-RG-(NBR).jpg)


