- a
- b
- c
- d
- e
- f
- g
- h
- i
- j
- k
- l
- m
- n
- o
- p
- q
- r
- s
- t
- u
- v
- w
- x
- y
- z
- 3
- 7
Pump introduction
A pump is a machine that moves or pressurizes a fluid. It transfers the mechanical energy of the prime mover or other external energy to the liquid to increase the energy of the liquid. The pump is mainly used to transport liquids such as water, oil, acid and alkali liquid, emulsion, suspoemulsion and liquid metal, and can also transport liquid, gas mixture and liquid containing suspended solids. Pumps can usually be divided into three categories according to their working principles: positive displacement pumps, impeller pumps and other types of pumps.
Performance characteristics of Piston Pump
The piston pump is suitable for high pressure and small flow occasions, especially when the flow rate is less than 100m3/h and the discharge pressure is greater than 9.8 MPa, it shows its high efficiency and good operating performance.
It has good suction performance and can suck liquids of various media and viscosities. It can be used for water injection, oil injection and oil production in oil fields and coal seams. If the wetted parts are made of stainless steel, it can transport corrosive liquids. In addition, according to the different structural materials, it can also transport high-temperature tar, mineral slime, high-concentration mortar, high-viscosity liquid, etc.Piston pumps are widely used in petrochemical industry, machinery manufacturing industry, paper making, food processing, pharmaceutical production, etc.

Working Principle
The piston pump, being a positive displacement pump, generates high pressure by piston movement.
For piston motion, the pump is linked to a power supply.
The number of pistons required is determined by the application and pressure requirements.
To manage the flow as well as the state of the flow, a controlling device is required.
The piston pump working is similar to PD pumps. Because they work with the help of the pumping mechanism force to increase the volume of the liquid. These pumps can use the power from power sources.
These pumps include more than one piston with a set of control devices. The duplex pump includes two pistons as well as two controlling devices. Similarly, a triplex pump includes three pistons as well as three controlling devices. It is very important to check the controlling devices on both sides to ensure that the flow of liquid direction at both sides is flowing or not.
These pumps are single otherwise double acting pumps. Double acting pumps involve two sets of controlling devices & liquid on both ends. This lets the pump to complete a pumping cycle by flowing in one direction to other. When the piston is taking in one direction, then it will exhaust at another side. This pump needs solo action versions for flowing in both directions for completing a cycle.
Types of Piston pump
There are four different types of piston pumps: lift pumps, force pumps, axial pumps, and radial piston pumps. Lift and force pumps can be operated manually or with the assistance of an engine from these pumps.
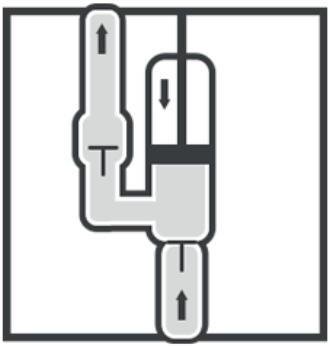
Lift Piston Pump
The piston can draw fluid into the lower section of the cylinder with the assistance of a control mechanism called a valve in this sort of pump. Fluid flows into the higher area of the cylinder through control mechanisms positioned in the piston on the below stroke. The fluid can then be expelled from the higher area of the cylinder through a spout on the upstroke.
This form of piston pump draws the fluid from the suction valve to the cylinder’s bottom part. The piston rises upward during the upward stroke, causing suction. The fluid enters the cylinder through the valve as a result of this.The piston now slides downward during the downward stroke, putting pressure on the fluid. In the piston, some valves allow the fluid to pass through to the opposite side. The fluid in the top portion of the cylinder is driven out during the upward stroke, while the fluid in the bottom half of the cylinder is sucked in. As a result, it takes three piston strokes to draw and distribute the fluid. The lift piston pump operates in this manner.
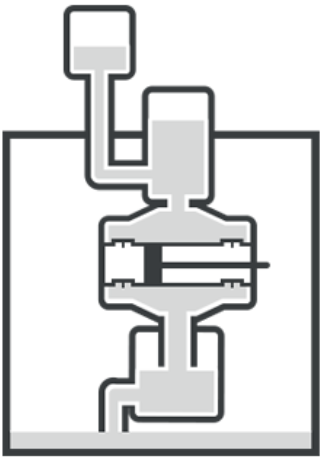
Force Piston Pump
The piston pump’s upstroke might pull fluid through an intake valve to the cylinder in this sort of pump (tube). The fluid level can be emptied into the output tube by an exit valve at the end of the downstroke. The force pump works similarly to the lift pump. The upward motion of the piston in this pump draws fluid into the cylinder through an inlet valve. The downstroke expels the fluid from the pump into the discharge pipe through an output valve after the compression operation.
The major distinction between a forced pump and a lift pump is that a lift pump requires an additional upstroke to release the fluid, whereas a force pump does not.
To suction the fluid, the force pumps require only one upward stroke and one downward stroke. To fill the power pump with water, all it takes is one upstroke and one downstroke. The fluid is discharged by the lift pumps on the second upstroke, while the fluid is discharged by the force pumps on the first downstroke. A sort of force piston pump is the well-known “hand pump.”
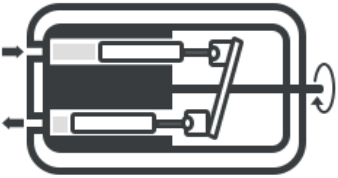
Axial Piston Pump
This is a positive displacement (PD) pump with many pistons arranged in a circular array within a tube block. With an essential shaft connected to the pumping pistons, this block may be operated to spin its symmetry axis. These pumps can be used as a compressor for an automobile, as a standalone pump, or as a hydraulic motor.
The pistons of this pump are arranged in a row parallel to the driving crankshaft. Axial pumps can be used for both constant and variable displacement applications. The cylinder and pistons alternate around the central vertical axis of these pumps. As they move on a fixed swash plate with a changeable angle, the shoe and pistons reciprocate inward and outward in the cylinder.
The piston switches between suction and discharge valves as it rotates. The liquid is injected into the piston chamber when the piston passes through the suction valve. It drains liquid from the piston chamber when it passes past the discharge valve.
The piston’s rotation speed is controlled by the crankshaft’s mechanical rotation input. The swash block angle controls the quantity of liquid sucked into the compression cylinder during piston motion. Axial piston pumps are further divided into the following categories:
Straight axis piston pump
Bent axis piston pump
The pistons of Bent axis piston pump are angled to the driving shaft and Thrust Plate. A universal connection, not visible, connects the piston block shaft to the driving shaft. All of the components of the driveshaft, thrust plate, piston block shaft, and piston block rotate. Unlike a swash plate pump, where the piston rods glide past a stationary swash plate, the connecting rods are linked to the thrust plate and rotate with it.
The outlet ports are semi-circular holes in the Valve Plate, which can be seen on the edge on the far right of the system and in a head-on view below, right. Half of the pistons suck in fluid as they pass over the intake port while the pump rotates. The fluid from the other pistons is discharged through the output port. The radial piston pump, swash plate pump, and wobbling pump should all be compared to this pump.
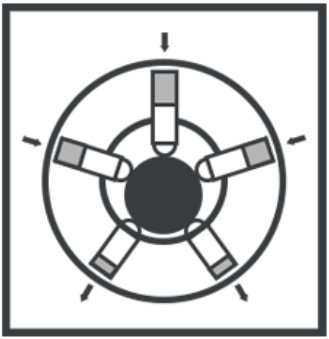
Radial Piston Pump
This pump is a type of hydraulic pump in which the working pistons expand in a radial track symmetrically in the vicinity of the driving shaft, in contrast to the axial piston pump’s direction of expansion. Some pistons are housed in a cylindrical block that surrounds the rotor hub in radial piston pumps. A shaft, a piston, and a rotor make up the cylinder. The fluid is moved in and out of the cylinder by the pintle.
The pump housing is eccentrically linked to the rotor. Hydraulic oil is taken into the cylinder cavity and drained from the cylinder cavity as the piston moves in and out of the cylinder. The valve on the middle shaft houses the pump’s input and outflow. When a piston expands, it connects to the inlet, and when it shrinks, it connects to the outlet.Radial piston pumps are used in high-pressure applications (working pressures ranging from 400 to over 700 bar), such as presses, plastics processing machines, and machine tools for sustaining oil pressure. They provide a variety of benefits, including high efficiency, high-pressure capacity up to 1,000 bar (14,000 psi), low flow and pressure fluctuations, minimal noise development, extremely high load at low speed, excellent dependability, and more.
Because of its huge radial dimensions, it is more significant than an axial pump and so is not always available in situations with restricted space.
Applications of Piston Pump
Piston pumps are used to manage extremely low flow rates at high pressure.
These pumps are used to convey fluids with a high viscosity.
They used to be in charge of pumping hydraulic oil.
High-pressure cleaning is also done using the piston pump.Pumps like this are used in industrial processing equipment.
Advantages of Piston Pump
Following are some benefits of piston pumps:
Suitable for fluids with a high viscosity.
The pace is slow.
High productivity.
There is a large pressure range.
The Head has no influence on pump discharge.
Pumps for metering are widely used.
When there is no flow, it is normally exceptionally difficult to regulate the force.
The pressure of the liquid or gas has no influence on pump performance.
It can handle abrasives, slurries, and other abrasive materials with ease.


