Video: Types of RV Refrigerators and Their Working Principles

Figure 1: RV refrigerator.
Recreational Vehicles (RVs) have become a popular means of travel and adventure, allowing individuals to explore the great outdoors while enjoying the comforts of home. One crucial component that ensures a smooth and enjoyable RV experience is the refrigerator. This article introduces 4 main types of RV refrigerators, including: absorption refrigerator, compressor refrigerator, thermoelectric refrigerator, and residential refrigerator.
1. Absorption Refrigerator
1.1 What Is an Absorption Refrigerator?
Absorption refrigerators are prevalent in RVs due to their propane-powered functionality. These refrigerators
operate using a combination of heat, ammonia, and hydrogen gas. The process begins with a propane flame heating a
solution of ammonia and water in the absorption unit. As the solution evaporates, it absorbs heat from the
refrigerator's interior, creating a cooling effect.
Absorption refrigerators are versatile, capable of running on propane, electricity, or both, making them suitable
for various camping scenarios.

Figure 2: Small absorption refrigerator.
1.2 How Does an Absorption Refrigerator Work?
The working principle of absorption refrigerators relies on a continuous cycle of evaporation, absorption, and
condensation.
The propane flame heats a mixture of ammonia, water, and hydrogen in the boiler. The ammonia vapor rises, and as it
reaches the condenser, it releases heat, causing it to condense back into a liquid. The liquid ammonia then flows to
the evaporator, absorbing heat from the refrigerator's interior, and the cycle repeats.
The versatility of absorption refrigerators allows RVers to switch between power sources depending on their camping
conditions.

Figure 3: Absorption refrigerator operating principle diagram.
2. Compressor Refrigerator
2.1 What Is a Compressor Refrigerator?
Compressor refrigerators in RVs operate similarly to residential refrigerators. They use a compressor to compress a refrigerant gas, which then
circulates through coils and an expansion valve to produce cooling.
Unlike absorption refrigerators, compressor models rely on electricity as their primary power source. This type is
often found in larger, more luxurious RVs with ample power supply options. Compressor refrigerators are known for
their efficiency and ability to cool rapidly, making them ideal for extended stays in RV parks or locations with
reliable electrical hookups.
2.2 How Does a Compressor Refrigerator Work?
Compressor refrigerators follow the traditional vapor compression cycle. A compressor pressurizes a refrigerant gas,
causing it to become hot. The hot gas flows through a condenser where it releases heat and turns into a
high-pressure liquid. This liquid passes through an expansion valve, where it undergoes a sudden drop in
pressure, turning it into a low-pressure gas. As the gas moves through the evaporator coils, it absorbs heat from
the refrigerator's interior, causing it to evaporate. The cycle then repeats.
Compressor refrigerators offer rapid cooling and maintain consistent temperatures, making them suitable for larger
RVs.

Figure 4: Compressor refrigerator refrigeration schematic diagram.
3. Thermoelectric Refrigerator
3.1 What Is a Thermoelectric Refrigerator?
RV thermoelectric refrigerators (thermoelectric coolers) are a less common but viable option. These units use the
Peltier effect, employing a thermoelectric module to create a temperature difference across its surfaces. When a
direct current (DC) passes through the module, it absorbs heat on one side and releases it on the other.
While thermoelectric refrigerators are energy-efficient, they are generally less powerful than absorption and
compressor models. They are suitable for smaller RVs or situations where power consumption is a critical concern.

Figure 5: 3D diagram of thermoelectric refrigerator.
3.2 How Does a Thermoelectric Refrigerator Work?
Thermoelectric refrigerators operate based on the Peltier effect. When a direct current passes through a thermoelectric module, it creates a temperature difference. One side of the module absorbs heat, and the other side releases it. The absorbed heat is then moved away from the interior of the refrigerator.

Figure 6: Working principle of thermoelectric refrigerator.
4. Residential Refrigerator
An RV residential refrigerator is completely a household fridge. These fridges offer advantages like precise
temperature control, efficiency, and larger storage space. These residential-style units have become increasingly
popular in modern RVs, especially in larger and more luxurious models.
But the shaking of the vehicle while driving will affect the service life of the refrigerator. Moreover, this type
of refrigerator can only use AC power, and an inverter is required to power it when used in the RVs.

Table 1. Comparison of 4 types of RV refrigerators.
5. Choosing the Right RV Refrigerator
Choosing the right RV refrigerator depends on various factors, including the size of the RV, power sources available, and individual preferences. Here are some considerations:
5.1 Size and Layout
Consider the available space in your RV and the layout that best suits your needs. Compressor refrigerators are available in various sizes and configurations, making them adaptable to different RV interiors. Absorption refrigerators are often more flexible in terms of installation due to their venting requirements.
5.2 Power Sources
Evaluate the power sources available during your travels. If you plan to boondock or camp in locations without electrical hookups, an absorption refrigerator with propane capability may be more suitable. Compressor refrigerators are ideal for RVs with consistent access to electricity.
5.3 Energy Efficiency
If energy efficiency is a priority, thermoelectric refrigerators may be a good option, especially for smaller RVs or weekend trips. However, they may not provide the same level of cooling performance as absorption or compressor models.
5.4 Climate Considerations
Consider the climate of the regions you plan to explore. Absorption refrigerators can struggle in extremely hot conditions, while compressor models excel in maintaining consistent cooling even in high temperatures.
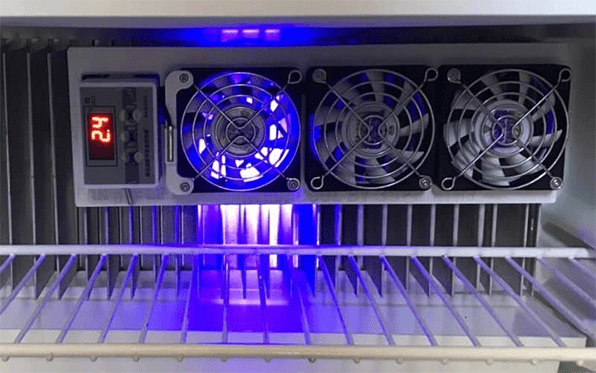
Figure 7: Fan set for absorption refrigerator from rvingknowhow.com.
6. Why Choose an RV-specific Refrigerator instead of an Ordinary Household Refrigerator?
Compared with household refrigerators, the main advantages of RV refrigerators are:
▶More Functions: Because of usually being used in an outdoor environment, product functions need to
be more complete, for example, the low voltage protection function.
▶High Requirements on Material: The exterior of the RV refrigerator is made of high-quality
engineering plastics, which can be used in humid environments; the interior materials are more strictly selected and
are all environmentally friendly materials.
▶Variable Power Sources: RV-specific refrigerators can work using two or more different types of
energy, namely: AC power, DC power, and propane gas.
▶Good Vibration Resistance: For ordinary household refrigerators, they rarely have the opportunity
to move since they are bought home. The RV refrigerator may encounter some complex road conditions while the RV is
running, and must be able to withstand high-intensity shaking and vibration.
In addition, RV refrigerators must maintain good performance in harsh climates and multiple environmental changes.
Therefore, products must undergo more stringent performance testing during the development process.

Figure 8: A new RV refrigerator.
7. Maintenance Tips of RV refrigerators
Regardless of the type of RV refrigerator you choose, proper maintenance is crucial for longevity and efficient
operation:
1. Regular Cleaning: Clean the interior and remove any expired or spoiled items regularly.
2. Leveling: Ensure your RV is level when parked to assist absorption refrigerators in the proper circulation of the
refrigerant.
3. Ventilation: Keep the refrigerator vents and coils clean and free of obstructions to facilitate optimal heat
exchange.
4. Power Source Check: Before each trip, verify that your RV refrigerator is set to the correct power source and
that it's operating as expected.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the types and working principles of RV refrigerators empowers RV enthusiasts to make
informed choices based on their travel preferences and needs.
Whether opting for the reliability of absorption refrigerators, the efficiency of compressor models, or the energy
conservation of thermoelectric units, selecting the right RV refrigerator enhances the overall comfort and
convenience of the RV lifestyle. Regular maintenance ensures that these essential appliances continue to provide
reliable service throughout your journeys.



