
Figure 1: Internal structure of low pressure screw air compressor.
Rotary screw air compressor (screw air compressor, screw type air compressor, rotary screw compressor), is a positive displacement air compressor, which compresses the volume of gas through the rotary motion of the rotor in the casing, and increases the density of gas molecules per unit volume to enhance the pressure of compressed air.
1. Components of Screw Air Compressor
The screw air compressor unit is composed of screw air compressor, electric motor, oil and gas separation barrel, cooling system,
air adjustment system, safety valve and control system.
The screw air compressor is the heart part of the unit. It is composed of a pair of male and female rotors meshing
with each other, bearings, shaft seals, etc. The air compression process is completed by the screw compressor.

Figure 2: Cutaway view of twin screw compressor.
2. How Does a Rotary Screw Air Compressor Work
The head of the screw air compressor is mainly composed of a pair of male and female screw rotors and a casing with
an inner cavity in the shape of "∞". The male and female screws are meshed with each other and can be driven by each
other under the action of lubricating oil.
Convex teeth, and grooves on the male and female screw rotors form a working chamber with casing. During the
rotation of the rotors, the volume of the working chamber formed by the tooth grooves and the casing changes from
large to small, thereby realizing the compression of gas.

Figure 3: Working process diagram of twin screw compressor.
3. Types of Screw Air Compressor
3.1 Single Screw and Twin Screw Air Compressors
Screw air compressors are divided into single-screw and twin-screw according to the number of screws.
The twin-screw air compressor is a new product in the air compressor. It came out more than ten years later than a
single-screw air compressor, and it is an optimized product based on single-screw type. It overcomes the
shortcomings of single-screw compressors such as short service life and high working noise, and with the maturity of
technology, it currently occupies an increasing share in the market.
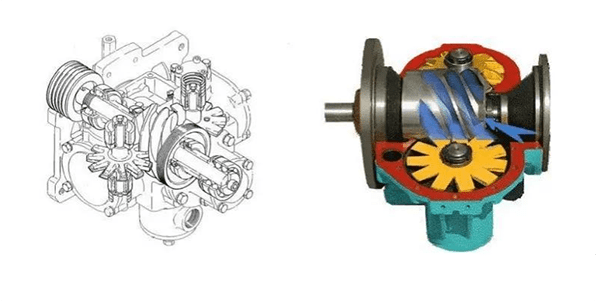
Figure 4: Structure diagram of single-screw compressor.
3.2 Oil-Free and Oil-Lubricated Screw Air Compressor
According to the lubrication method, it can be divided into oil-free and oil-lubricated screw air compressors.
If there is lubricating oil involved in the compression process, it is an oil-injected screw air compressor, and if
not, it is an oil-free screw air compressor. Oil-free screw compressors are divided into two types: dry screw
compressor and water-injected screw compressor.
Lubricating oil mainly has the following functions in oil-injected screw compressors: lubrication, sealing,
cleaning, anti-oxidation, anti-corrosion, cooling, and noise reduction.
The twin-screw compressor was invented by engineers from the Swedish SRM company in the 1930s. It was originally an
oil-free twin-screw air compressor. Oil-injected twin-screw compressors began to be introduced to the market in the
1960s. After decades of development, they have become the most widely used type of compressor.

Figure 5: Atlas AQ water-injected oil-free screw air compressor.
In addition, screw compressors can also be classified in the following ways:
According to different engines, it can be divided into electric motor drive mode and diesel engine drive mode air
compressor.
The large electric type is equipped with a power distribution cabinet, and the diesel-driven type is started by a
storage battery. Both types of screw air compressors have direct and side (that is, belt drive) types.
According to the cooling method, it can be divided into water-cooled and air-cooled air compressors.
The water-cooled type adopts cooling water open circulation cooling, and the air-cooled type adopts fan cooling.
According to the basic configuration of air compressors, it can be divided into stationary and mobile air
compressors.
4. Advantages of Screw Air Compressor
High performance and high efficiency
The male and female rotors, and the rotors and the casing are perfectly set, so that the leakage of gas backflow is
small, so the efficiency is high.
With efficient transmission system
Screw air compressors drive compression components at the optimum speed for the application through a highly
efficient drive system.
Low maintenance
It is completely maintenance-free during normal operation.
With built-in smart control
To reduce operating costs, precise operational control is essential. All screw air compressors are equipped with an
intelligent control system with an easy-to-use control menu.
Screw air compressors consistently provide high-quality compressed air for all walks of life with its advantages of
high efficiency, maintenance-free, and high reliability.

Figure 6: Screw type air compressor working system diagram.
5. Application of Screw Air Compressor
1. Gas pipeline transportation: such as coal gas, natural gas transportation, etc. This use may not be understood by
most people, but it is inseparable from our lives. Most people are familiar with tire inflation, and air compressors
also play an irreplaceable role in tire inflation.
2. Power source: The common use of screw air compressors is as a power source, which is widely used in
pharmaceutical, textile, food and beverage, industrial automation and other fields. Compared with other energy
sources, compressed air has the advantages of cleanness, free pollution and easy control.
Common traditional aerodynamic applications: pneumatic tools, pneumatic picks, pneumatic sandblasting, rock drilling
machines, bottle blowing machines, painting, etc.
3. Gas separation: In the artificial refrigeration industry, the gas can be compressed, cooled, expanded and
liquefied by the air compressor, so as to achieve the effect of refrigeration and air conditioning. In addition, for
the mixed gas, the air compressor can separate gases of various components through the separation device to obtain
gases of various colors and concentrations.

Figure 7: KAISHAN 132KW screw air compressor for tunnel.
6. How to Choose a Screw Air Compressor
First of all, you should first understand the basic knowledge related to the screw air compressor.
6.1 Working Pressure of Air Compressor
Here we introduce the pressure units commonly used in screw air compressors.
Working pressure (exhaust pressure) refers to the highest pressure of exhaust gas of the air compressor. Commonly
used working pressure units are: bar or Mpa, 1 bar = 0.1 Mpa. Generally, users may also refer to the pressure unit
as: Kg (kilograms), 1 bar = 1 Kg.
6.2 Volumetric Flow Rate of Air Compressor
Volumetric flow rate (displacement volume) refers to the volume of gas discharged by the air compressor per unit
time under the required exhaust pressure, so that the amount of the intake state can be estimated.
Volume flow unit is: m³/min (cubic/minute) or L/min (liter/minute), 1m³ (cubic) = 1000L (liter). The commonly used
flow unit is: m³/min (cubic/minute).
6.3 Power of Air Compressor
Generally, the power of the air compressor refers to the nameplate power of the matching drive motor or diesel engine. The unit of power is: KW (kilowatt) or HP (horsepower), 1KW ≈ 1.333HP.
6.4 Selection Guide for Rotary Screw Air Compressor
Working pressure:
When users are going to purchase an air compressor, they must first determine the required working pressure at the
gas-consuming end, plus a margin of 1-2 bar, and then select the pressure of the air compressor.
The margin is to consider the pressure loss of the distance from the installation site of the air compressor to the
actual gas-consuming end pipeline, and the pressure margin should be properly considered between 1-2 bar according
to the actual distance.
Of course, the size of the pipeline diameter and the number of turning points are also factors that affect the
pressure loss. The larger the pipeline diameter and the fewer the turning points, the smaller the pressure loss;
otherwise, the greater the pressure loss.
Therefore, when the distance between the air compressor and each gas-consuming end pipeline is too far, the diameter
of the main pipeline should be appropriately enlarged. If the environmental conditions meet the installation
requirements of the air compressor and the working conditions permit, it can be installed near the gas-consuming
end.

Figure 8: Connection diagram of air compressor and other equipment.
Volumetric flow rate:
When selecting the volume flow rate of the air compressor, you should first understand the calculation method of the
volume flow rate of all gas-consuming equipment: multiplying the total flow rate by 1.2 (that is, enlarging the
margin by 20%).
Right selection is beneficial to both the user and the air compressor equipment. Too large selection is wasteful,
and too small selection may cause the air compressor to be in a loaded state for a long time, or the air pressure is
insufficient.
Occasions and conditions of using rotary screw air compressor
If the space for gas use is narrow (for ships and vehicles), vertical type should be selected;
If there is a long-distance change (more than 500 meters), mobile type should be considered;
If there is no power supply, the diesel engine drive type should be selected;
If there is no running water, an air-cooled type can be chosen.


