Keeping servo motors running in optimal condition is crucial for any industrial business, especially for industries such as robotics or CNC machine tools, as the cost of downtime caused by servo motor failure can be very expensive, both financially and in terms of time.
Next, let’s take a look at some of the most common servo motor component failures and their potential causes so you can try to avoid them.
1. Servo Motor Parts May Break: Causes and Solutions
1.1 Bearing
Usually there is a bearing on the drive side and the non-drive side of a servo motor respectively to connect and support the motor shaft. The drive-side bearing must bear the axial and/or radial loads of the external mechanical connection and usually has a larger dimension and shaft load.
Ball bearings for servo motors generally feature double protection and permanent lubrication, and do not require maintenance under normal use conditions.

Signs of Bearing Fault
Bearing failure is one of the most common motor failures. As the most important wearing part in servo motors, more than half of servo motor failures are usually attributed to the bearing. Its specific manifestations are various, ranging from jitter and abnormal noise when the motor rotates to motor shaft stuck.
It is worth noting that if bearing failure is not handled in time, it will usually cause secondary damage. For example, debris from bearing corrosion flying into the brake or motor encoder will cause more serious losses.

Possible Causes
Factors that affect the life of motor bearings include: axial load and radial load acting on the bearing, motor speed, operating temperature and bearing rated parameters. There are many reasons for bearing failure:
●Inappropriate mechanical load (such as overload, radial misalignment, axial thrust, belt tension problems).
●Excessive vibration and shock.
●Overspeed operation.
●Shaft current.
●Overheating (resulting in loss of lubrication).
●Moist or liquid intrusion.
●Contaminants (e.g. incompatible grease, water condensation, dust/dirt).
How to Prevent
●When using the servo motor, do not operate it beyond the rated load for a long time.
●For applications with shaft current, add conductive brushes or use a motor with insulated bearings.
●Perform preventive maintenance on servo motors.

1.2 Shaft Seal
For applications where the motor (especially the connection between the motor shaft and mechanical equipment) is exposed to polluted environments, servo motors often need to be equipped with oil seals. The industrial-grade framework oil seal of the motor shaft can keep pollutants (oil, impurities) out to extend the life of the motor. Shaft seals are prone to wear and require regular inspection and replacement.
2. How to Help Your Motor Keep Cool

Signs of Shaft Seal Fault
●Shaft seal wear.
Possible Causes
●Accidental damage.
●Normal wear and tear.
How to Prevent
●Preventive maintenance.
●Depending on usage, it is recommended to replace it every 3 months, up to 12 months.
1.3 Stator Winding
Winding problems are the second most common failure of servo motors.

Signs of Stator Winding Fault
When a winding fails, part of the motor shorts out, causing the inside of the motor to burn.
Possible Causes
●Overload.
●Overvoltage.
●Lack of phase.
●Wrong wiring.
●Inappropriate drive parameter settings.
●Too high ambient temperature.
●Cooling device failure.
●Physical damage.
How to Prevent
●When using the servo motor, do not operate it above the rated load for a long time.
●Monitor current and current accumulation over time.
●Monitor winding temperature.
1.4 Rotor and Shaft
Unlike asynchronous motors, the rotor of a servo motor usually consists of permanent magnets. The permanent bar magnets are fixed on the rotating shaft of the motor by being pasted on the surface of the rotor or embedded in the rotor.

Signs of Rotor and Shaft Fault
●The rotating shaft is broken or deformed.
●The bar magnet falls off.
Possible Causes
●Excessive vibration.
●Too much starting or reversing of the motor, or too short an interval between starting/reversing.
● Overheating (e.g. high ambient temperature, overload or locked rotor).
●Unexpected collision.
How to Prevent
●Run under rated load.
●Avoid accidental collisions.
1.5 Motor Feedback Device (Resolver or Encoder)
The motor feedback device feeds back the position signal to the drive, so that the drive emits precise current for precise position control.

Signs of Motor Feedback Device Fault
●The zero position (the number of turns) is lost.
●Resolver or encoder wear.
●The glass encoder disk is broken.
●Encoder electrical failure.
Possible Causes
●For encoders using backup batteries, the zero position may be lost as the battery power is exhausted during use.
●As a secondary damage to the aforementioned motor bearing failure, motor bearing problems can also cause mechanical wear of the encoder or resolver.
●The motor shaft current may not only act on the bearing of the motor itself, but also harm the bearing built into the encoder, causing burning and damage to the encoder bearing.
●Shock and vibration during motor transportation or installation can easily cause the glass encoder disk of the optical encoder to break. Especially when adding key pins, pulleys or couplings to the motor shaft, be sure not to knock the motor shaft.
●In addition to incorrect wiring of the encoder, electromagnetic interference caused by improper wiring is also one of the main causes of electrical failure of the encoder.
How to Prevent
●Depending on the specific application environment, the battery life is usually one or several years. Regular battery replacement can reduce the risk of such accidents. Or, more permanently, switch to a mechanical multiturn absolute encoder.
●After installation, the motor must be reliably grounded. In the case of shaft current, it is necessary to consider using an insulated bearing and insulated encoders or installing a motor shaft grounding device.
●During the installation of the motor, such as when adding a pulley or coupling, if knocking is unavoidable, consider removing the encoder first, and then install the encoder after all mechanical installation is completed. In this case, the phase angle of the encoder needs to be readjusted in the servo drive.
●Another way to prevent encoder disk failure is to use metal encoder disks that have become popular in recent years. Compared with glass encoder disks, the vibration and impact resistance of metal encoder disks are much improved, and their resolution and accuracy are comparable to those of glass encoder disks.
1.6 Braking Device
The motor brake is used to brake the motor shaft to prevent rotation when the power is turned off. When the brake is powered on, the brake is in a released state.
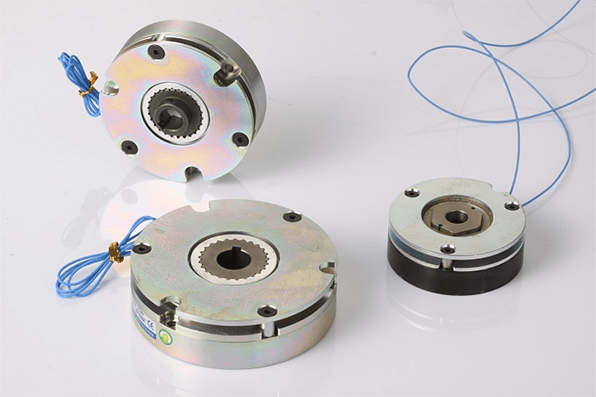
Signs of Braking Device Fault
●Abnormal noise.
●Unable to release.
●Unable to brake (locked).
Possible Causes
●The intrusion of foreign matter from faulty bearings is a common main cause of abnormal brake noise.
●Secondly, the brake is forced to operate in a power-off state due to a fault in the brake drive circuit, which may also cause damage to the brake.
How to Prevent
It is worth noting that as a static holding device for the motor, the brake should not be used as a motor deceleration device when the motor is powered on, as this will accelerate the wear of the brake.
1.7 Cooling Device
Most small and medium-power servo motors use self-cooling. For servo motors with larger power or special applications, air cooling or liquid cooling is also common.
Signs of Cooling Device Fault
●Fan shaking or locked rotor.
●Coolant leakage.

Possible Causes
●The culprit of most fan failures is dust. This is because dust will accumulate on the fan blades over time. Increased load on the blades can lead to vibration and subsequent damage.
●Most coolant leaks occur at connections, and seal failure is usually the key to the problem.
●Physical damage caused by accidental impact.
How to Prevent
●Add a filter to the fan and replace it regularly.
●Inspect the cooling device regularly.
1.8 Electrical Connection Device
This includes the terminal box and socket.

Signs of Electrical Connection Device Fault and Possible Causes
As a non-wearing part, the failure of the connecting device is mostly due to mechanical damage.
How to Prevent
Be careful when using it and try to avoid accidents.
1.9 Coupling and Pulley
A torsion resistant rigid coupling or reinforced belt is required to connect the motor shaft. After the motor has been running for a period of time, frequent acceleration and deceleration may cause the coupling or belt to become loose or slip.

Signs of Coupling and Pulley Fault and Possible Causes
If the shaft is subjected to severe impact during the installation of the coupling and pulley, fatal damage to the motor bearings and/or encoder may occur.
How to Prevent
Therefore, it is strictly prohibited to use tools to knock the shaft, coupling or pulley during installation or disassembly. When attempting to remove any equipment from the motor shaft, a hydraulic device should be used to eject it from the shaft end.


