- a
- b
- c
- d
- e
- f
- g
- h
- i
- j
- k
- l
- m
- n
- o
- p
- q
- r
- s
- t
- u
- v
- w
- x
- y
- z
- 3
- 7
Peripheral Pump
A peripheral pump has an impeller with many radial vanes on the outside edge and is a close-coupled centrifugal pump. The impeller rotates within a concentric channel of the casing with liquid flowing between the vanes and casing, which transfers large amounts of energy leading to an increase in pressure inside the pump. As pressure increases along the circumference of the casing, fluid moves from its inlet to its outlet. In the casing channel, the stripper is positioned between the outlet and the inlet to prevent a hydraulic short circuit between the high- and low-pressure sides.
A thin clearance between the impeller vanes and the pump casing means that any solids would stop the impeller, so they are generally designed for clean media. Peripheral pumps can be relatively small given the large increase in energy.
Applications that use peripheral pumps are typically those where a medium to the high-pressure transfer of low viscosity liquid is required, such as for hydrocyclone feed, filtration, fluid transfer across long distances, jetting, and display fountains.

Working Principle of Peripheral Pump
In essence, peripheral pumps are niche products that sit between displacement pumps and centrifugal pumps. In many applications in the industry, the medium is pumped in a peripheral channel, which is why we call it that. This pump works as a volume displacer by sucking the liquid through the suction flange. The liquid is then directed into an annular channel.
A peripheral impeller rotates within this channel, centrifugally transforming the liquid. Peripheral impellers are special impellers that have a large number of small radial vanes arranged around their perimeter. The blades in the impeller impart great kinetic energy onto the liquid as it exits the pump via the discharge flange after passing through the annular channel.
Peripheral pumps contain impellers with many small radial blades (with dual inputs) arranged along their peripheral area. Within the rotor, centrifugal forces create a circulation of the flow between the impeller and casing channel. A fluid and an impeller have essentially the same peripheral speeds, but the fluid in the casing channel has a significantly lower speed. Thus, the fluid flows spirally from the casing channel to the impeller, which occurs several times along the perimeter.
As more vortices form, more energy is transferred, and the produced pressure is higher. With a reduced flow, the number of spirals increases, so there is a greater transfer of energy and a higher amount of power absorbed in partial-load conditions.
Types of Peripheral Pump
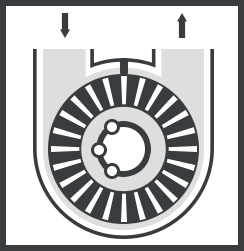
Closed Peripheral Pump
Closed peripheral pump adopts closed impeller and open runner structure. Closed impeller refers to the blade part is provided with a middle partition, the blade is relatively short impeller. The suction and discharge of the pump are separated in addition to the tongue. Through the runner. The runner directly connected with the suction and outlet is called the open runner.
The runner directly connected with the suction and outlet is called the open runner. Closed peripheral pump must be equipped with open runner.The blade and flow channel of Closed peripheral pump are more. Generally, the flow of rectangular section channel is larger, but the head and efficiency are lower. The semicircular section runner has higher head and efficiency, but smaller flow. Therefore, the middle and low specific revolution vortex pump mostly uses semicircular section flow channel, while the middle and high specific revolution vortex pump mostly uses rectangular section flow channel. Blade shape is the most widely used radial straight blade, in low specific revolution vortex pump also has the use of rear Angle blade.
In a closed peripheral pump, the liquid flow enters the pump from the outer edge of the impeller with a larger circular velocity. Therefore, cavitation performance is poor and cavitation allowance must be large. And because the outlet of the closed peripheral pump is located at the outer edge of the flow passage. When aggregated, the gas at the root of the piece is not easy to discharge. Therefore, without special measures, closed vortex pump has no self-priming capacity, and can not pump the aspirated liquid mixture. The efficiency of closed vortex pump is higher than that of open vortex pump, which can reach 35% ~ 45%.
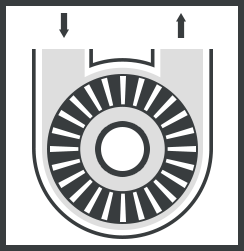
Open Peripheral Pump
Open peripheral pump with open impeller, closed flow structure. Open impeller refers to the blade without a middle partition, the blade is relatively long impeller. Closed runner refers to the runner whose suction and outlet cannot be directly communicated. The suction and discharge of open peripheral pump are generally opened in the side cover of the pump near the root of the blade, so on the one hand, the gas is easy to discharge, which is conducive to improving the ability of the pump self-priming and pumping the gas liquid mixture; On the other hand. The inlet circumference velocity is relatively small, so the cavitation resistance is better than the closed vortex pump. However, the efficiency of open peripheral pump is low. If the closed runner with the worst efficiency is used, the efficiency is only 20% ~ 27%. Even if the centripetal open runner with small hydraulic loss is used, the efficiency can only be improved to 27% ~ 35%.
In addition to the above two types of peripheral pumps, there is another type of peripheral pump, called centrifugal-peripheral pump, as follows:
Centrifugal-peripheral Pump
Compared with centrifugal pump, peripheral pump has higher head, easier to achieve self-priming, but poor cavitation performance, while centrifugal pump has lower head, but relatively good cavitation performance. Centrifugal peripheral pump is the combination of these two pumps, that is, the first stage for the centrifugal impeller, in order to reduce the pump necessary cavitation allowance; The second stage for the vortex impeller, improve the pump head. This is not only good cavitation performance, but also higher pump head.
Common Applications of Peripheral Pumps
Peripheral pumps are also widely used in many sectors of the national economy, such as:
1. In the chemical industry to transport acid, alkali and other corrosive liquids, the pump is required to have a small flow, high head, slow chemical reaction speed and high corrosion resistance. Because the working parts of the vortex pump are simple, it is easy to achieve the above requirements.
2. Pumping medium density small liquid (such as gasoline, alcohol, etc.). Because these liquids are easy to volatilize, they are often mixed with steam and liquid when pumped, such as airports, automobile fuel distribution stations, and even aircraft refueling. Vortex pump can carry out steam liquid mixed transport, in the above circumstances, the general time is short, so, low efficiency is not the main problem.
3. Pumping liquid containing gas, pumping liquid containing highly elastic gas (such as propane, butane, etc.). Pump the partially evaporated liquid from the suction tube.
4. For small automatic pump station, agricultural water supply.
5. For urban public construction, such as booster auxiliary pump, household water, etc.
6. Replace liquid ring pump as true rate pump and low pressure compressor.
7. Used for steam extraction and Marine washing, drinking water, fire and other auxiliary equipment.
8. For small boiler auxiliary equipment, for water supply.
Advantages of Peripheral Pumps
Among the advantages of peripheral pumps are:
Gas-entrained fluids can be handled without cavitation risk. Moreover, they have versions with the ability to self-prime up to 6m and handle any air ingress without trouble. When fitted with a foot valve, the standard models offer manometric suction lifts up to 8m.
The flow rate is extremely low at high pressures, similar to gear pumps, without the use of gear boxes. Additionally, they are compact, and with low axial thrust, they have a long lifespan.


