1. Main Reasons for Heat Pump Compressor Burnout
1.1 Frequent Start-Up of Heat Pump Compressor
If the heat pump temperature is improperly set -- the cooling temperature is too low, or the heating temperature is too high, the heat pump compressor will be frequently turned on and off, which will shorten the life of the compressor.
1.2 Unstable Heat Pump Power Supply Voltage
Poor power supply voltage quality, such as too high or too low voltage, will have adverse effects on the heat pump compressor motor. It is especially inappropriate to use the heat pump compressor beyond the rated voltage range. Long-term operation will cause the heat pump compressor motor to be in an inefficient overheating state, resulting in poor insulation and motor winding burnout.
In addition, unbalanced three-phase voltage or current will also cause increased motor loss (iron loss and copper loss), and too high temperature of the heat pump compressor motor coil, improper overheating protection, and burnout of the heat pump compressor motor insulation, will result in short circuit and burnout of the heat pump compressor motor coil.

1.3 Stuck Rotating Parts of Heat Pump Compressor
When this happens, if the motor protection fails, the heat pump compressor motor may be overloaded and burned.
1.4 Faulty Contactor for Starting Heat Pump Compressor
Contactor contact resistance is too large or sintered, causing the heat pump compressor motor to short-circuit and burn, or poor line contact, and large starting current can easily burn the heat pump compressor.
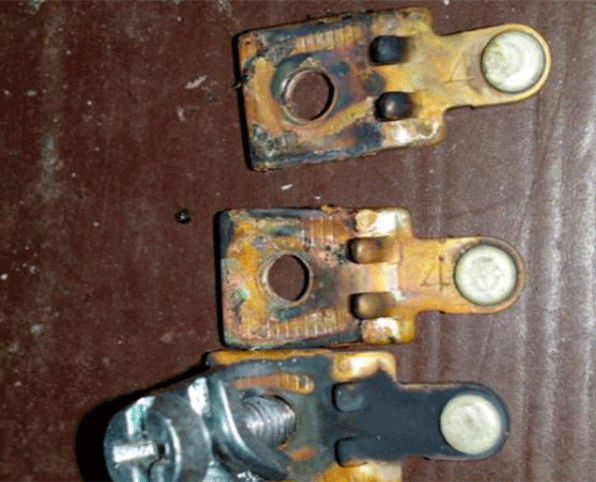

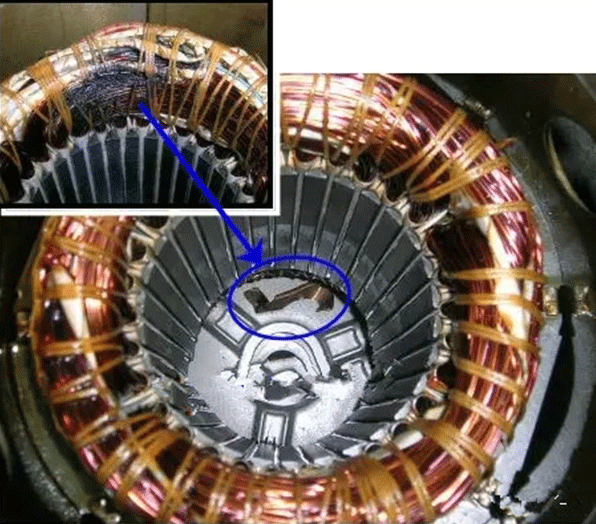
1.5 Insufficient Cleanliness of Heat Pump Copper Pipe System
If there is water in the copper pipe, the water will cause poor insulation of the heat pump compressor motor.
Water, refrigerant and refrigeration oil circulate in the system, and after state changes under high and low temperatures, acidic substances will be produced, which will damage the insulation layer of the motor. After a long time of working, the heat pump compressor motor will burn.
1.6 The System Is Not Cleaned Completely After the Heat Pump Compressor Burnt
There have been cases where the air conditioning compressor burned out again because the system was not cleaned after the compressor burned out. Therefore, the refrigeration system must be cleaned thoroughly.
When the heat pump compressor motor burns out, strong acid will be produced and stay in the system. If it is not cleaned completely, when the new heat pump compressor motor is running, the residual acidic substances will corrode its insulation layer, causing the new heat pump compressor to burn out.
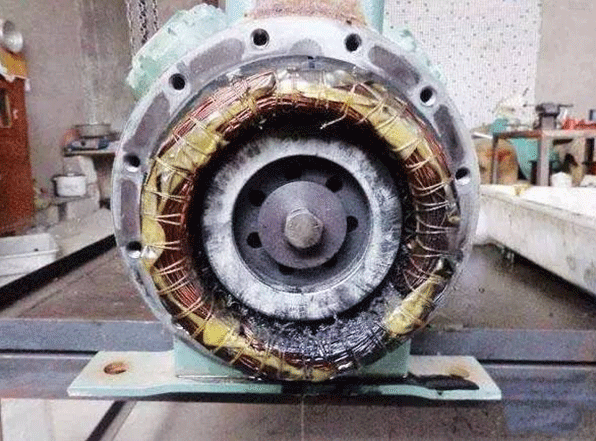
1.7 Poor Cooling of Heat Pump Compressor
Poor superheat control of return gas in the heat pump system -- too high return gas temperature or low return gas volume, results in insufficient cooling of the compressor motor coil.
This problem happens in air-cooled heat pump units more commonly, and too high return gas temperature will also lead to too high discharge temperature, causing a series of heat pump compressor problems.
1.8 Manufacturing Process Defects of Heat Pump Compressor Itself
Generally, if the heat pump compressor motor burns out after a short period of use, it may be a problem with the heat pump compressor manufacturing itself.
1.9 Liquid Return of Heat Pump Compressor
Liquid return can easily cause liquid slugging accidents. Liquid return will dilute or wash away the lubricating oil on the sliding surface, aggravating wear.
Liquid return will dilute the lubricating oil in the oil pool. Lubricating oil containing a large amount of liquid refrigerant has low viscosity and cannot form enough oil film on the friction surface, resulting in rapid wear and even jamming of moving parts.
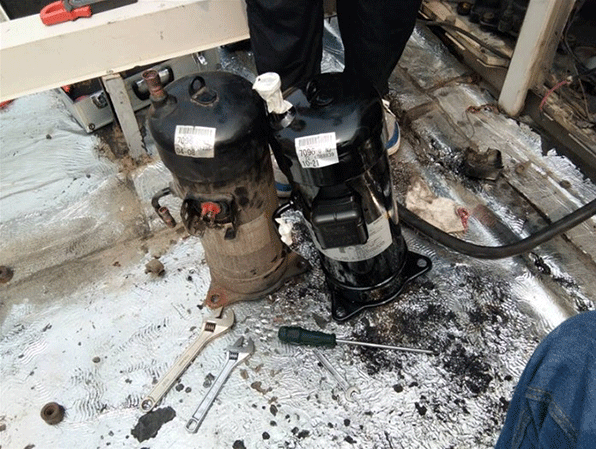

1.10 Heat Pump Compressor Burnout due to High Temperature
It is not uncommon for air conditioning compressors to burn due to high temperature and overheating. Common fault are:
●Discharge or compressor top temperature is too high;
●Compressor cavity temperature is too high;
●High pressure protection (when the system is blocked);
●Current protection or circuit breaker tripping.
Common reasons for air conditioning compressors to burn due to high temperature and overheating include:
●Too little refrigerant added or refrigerant leaks, resulting in too high discharge / return temperature.
●Refrigeration oil leakage or refrigerant oil quality problems.
●The system is dirty-blocked or ice-blocked, resulting in high discharge or compressor top temperature.
●The system vacuum is not enough. The compressor compresses air, and the pressure ratio is too large, causing too high temperature.
●The system air duct is blocked, and the return air is poor. Besides, the heat exchanger is dirty, resulting in high condensation pressure and continuous rise in discharge temperature.
●The connecting pipe is too long or the pipe diameter is too small, and the system resistance increases, resulting in increased discharge temperature and pressure.

2. Suggestions for Avoiding Compressor Burnout
7 suggestions to prevent air conditioning compressor burnout:
Copper pipes should be dustproof and waterproof before installation to prevent impurities and moisture from entering the refrigerant pipeline and compressor.
Use special tools (cutters) to cut copper pipes and avoid using hacksaws or other tools which will cause copper chips to enter the pipeline.
Use nitrogen protection when welding pipes to avoid welding slag and oxide scale entering the refrigerant pipeline.
The indoor units of the same system are powered uniformly to avoid refrigerant liquid slugging caused by direct power failure of some indoor units.
The indoor units of multi-split units shall not be used as precision air conditioning, and avoid long-term low-load operation or frequent start-stop of the outdoor unit, which will cause the compressor to lack oil.
Clean the filter regularly to avoid reduced air volume and incomplete evaporation of refrigerant due to the filter being too dirty.
Calculate the additional amount of refrigerant according to the standard, and use an electronic scale to add to avoid liquid slugging or excessive refrigerant temperature caused by too much or too little refrigerant respectively.
Standardize the power supply voltage and power wiring of the air conditioning system to avoid large current in the compressor due to unstable power supply voltage, unbalanced three-phase voltage, and phase loss.


