Video: A Guide to Fresh Air Ventilation System: Working Principle, Functions & Types
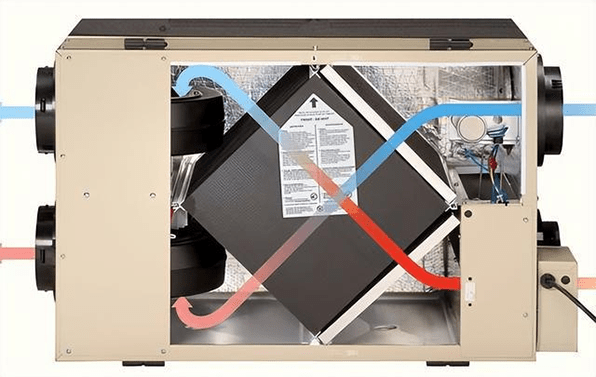
Figure 1: Heat recovery ventilator.
Fresh air ventilation system, also known as "house breathing system", is a type of indoor exhausting and ventilation
system. It can discharge the dirty indoor air to the outside while also pulling fresh outdoor air into the room.
It is an open circulation system that provides fresh, filtered outdoor air indoors 24 hours a day, allowing people
to breathe fresh, clean, high-quality air indoors. Fresh air ventilation system is a pursuit of high-quality life in
modern society.
1. How Does a Fresh Air Ventilation System Work?
The fresh air ventilation system mainly consists of fresh air ventilators, air ducts, filters, regulating valves,
etc. Here's how it works:
First, the fan of the fresh air supply system draws fresh outdoor
air into the system.
Secondly, the fresh air is filtered through the filter. The filter can effectively filter out harmful substances
such as particles, dust, pollen, and bacteria in the air to ensure good quality of the air entering the room.
Fresh air is delivered through ducts to various indoor spaces. Then, the indoor dirty air is discharged outside
through the exhaust fan.
The regulating valve can adjust the fresh air volume according to actual needs. In winter, the fresh air volume can
be appropriately reduced to keep the room warm; in summer, the fresh air volume can be appropriately increased to
keep the room cool.
To sum up, the working principle of the fresh air ventilation system is to pull in fresh air through the fresh air
ventilator, and then the fresh air is filtered and transported to various indoor spaces through the air duct. At the
same time, the indoor dirty air is discharged to the outside through the exhaust fan, and the regulating valve
controls the fresh air volume. This can achieve indoor air circulation and renewal, providing a comfortable and
healthy indoor environment.

Figure 2: Working principle diagram of a heat recovery ventilator.
2. Main Functions of Fresh Air Ventilation Systems
In addition to the ventilation function, the fresh air ventilation system also has the functions of deodorization,
dust removal, moisture removal, room temperature adjustment, and formaldehyde removal.
1. Ventilation Function
It provides fresh air for people, exhausts polluted air, and keeps the room comfortable 24 hours a day.
2. Deodorizing Function
Ventilation fans can quickly discharge unpleasant odors caused by various reasons and create a comfortable
environment.
3. Dust Removal Function
The dust floating in the air contains many bacteria that are invisible to the naked eye, so it is necessary to drive
away the dust in the home and workplace to create a comfortable environment.
4. Moisture Removal Function
Moisture in the room mostly comes from the bathroom. Regularly removing indoor moisture can keep the room
comfortable and people healthy.
5. Adjust Room Temperature
On summer nights, use a fresh air ventilation system to drive away the indoor hot air and replace it with cool
outside air. In winter, use a total heat exchange to reduce indoor temperature loss and improve the heating effect.

Figure 3: 3D diagram of heat recovery ventilator.
3. Basic Types of Fresh Air Ventilation Systems
3.1 One-Way Flow Fresh Air Ventilation System (Exhaust or Supply Ventilation System)
One-way flow fresh air ventilation systems are divided into positive pressure (supply) and negative pressure
(exhaust) fresh air ventilation systems.
The supply ventilation system pulls in fresh outdoor air through a fan and sends the fresh air into
the room from the air supply vent, forming a positive pressure indoors. Under the action of the pressure field, the
dirty air in the room is discharged through the air outlet and exhaust duct.

Figure 4: Supply ventilation system diagram.
The exhaust ventilation system uses a fan to extract indoor turbid air to form a negative pressure in the room. At the same time, outdoor air flows into the room through gaps in doors, windows, etc. or negative pressure air inlets to complete the ventilation needs.

Figure 5: Exhaust ventilation system diagram.
3.2 Balanced Ventilation
The fresh air system integrates the exhaust and supply ventilation systems, and can pull in and discharge air at the same time. According to the position setting of the fresh air inlets and outlets and the arrangement of the ducts, the indoor air is completely replaced to achieve the goal of purifying the indoor air.

Figure 6: Balanced ventilation system diagram from hvi.org.
3.3 Energy Recovery Ventilation
This system mainly adds a full heat exchange device based on the above fresh air system. The function of this device is to exchange energy between the incoming and outgoing air.

Figure 7: Energy recovery ventilation system diagram.
When the outdoor ambient temperature is lower than the indoor temperature, the fresh air entering the room can be
preheated by absorbing the heat from the dirty air discharged indoors, so that the temperature difference between
the air entering the room and the indoor temperature is smaller, reducing the energy consumption of the indoor
heating system.
When the outdoor ambient temperature is higher than the indoor temperature, the dirty air discharged indoors can
take away part of the heat in the fresh air, so that the temperature of the air entering the room is close to the
indoor temperature, reducing the energy consumption of the indoor air conditioning system.
The outdoor air passes through the total heat exchanger, which can be pre-cooled and dehumidified in summer, and
pre-heated and humidified in winter.
In addition, the fresh air system also has wall-mounted and cabinet-type fresh air ventilators for old houses and
renovated houses. The fresh air ventilators can be installed on the wall or placed on the indoor floor, reducing the
difficulty of installing a fresh air system in old houses and avoiding damaging the ceiling.

Figure 8: Wall-mounted fresh air ventilation system diagram.



