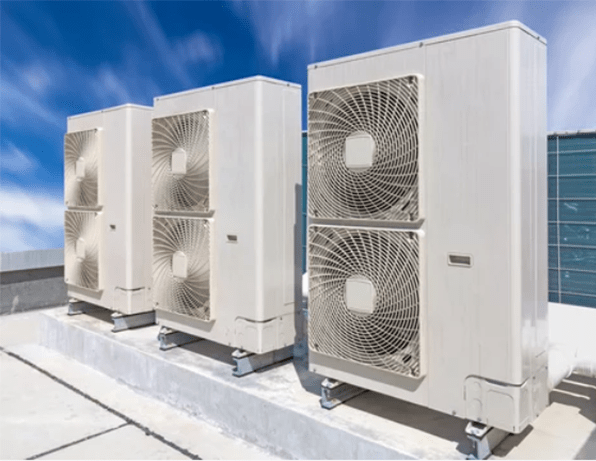

Figure 1: Heat pump outdoor units.
Are you considering a new heating and cooling system for your home or office? Have you heard about ducted heat pumps, but aren't sure what they are or how they work? If so, this article is for you.
In this ultimate guide, we will explore everything you need to know about ducted heat pumps, including what they are, how they work, their benefits and drawbacks, and more.
1. What is a Ducted Heat Pump?
A ducted heat pump is a type of HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) system that uses a single outdoor unit to provide both heating and cooling to your home through a network of ducts. The system consists of three main components: the outdoor unit, the central indoor unit, and the ductwork.
The outdoor unit contains the compressor and a heat exchanger. The central indoor unit, which is typically installed in the attic or a closet, contains the other heat exchanger and a blower fan.
The ducts in a ducted heat pump system distribute the conditioned air throughout the building. The air is pushed through the ducts by a fan in the indoor unit, which circulates the air and maintains a comfortable temperature in every room.

Figure 2: Heat pump ducts.
2. How Does a Ducted Heat Pump Work?
A ducted heat pump works by using refrigerant, which is a fluid that absorbs and releases heat as it cycles between the outdoor and indoor units.
During the heating season, the outdoor unit extracts heat from the outside air and transfers it to the central indoor unit via the refrigerant.
The refrigerant in the heat exchanger of the central indoor unit releases heat into the air that is blown by the blower fan, and then the heated air is distributed through the ductwork to the various rooms in your home.
During the cooling season, the process is reversed, with the central indoor unit extracting heat from the indoor air and transferring it to the outdoor unit.

Figure 3: Heat pump ducting systems.
3. Pros of Ducted Heat Pumps
There are several benefits to choosing a ducted heat pump system over other types of heating and cooling systems. Here are some of the most significant advantages:
Energy Efficiency: Ducted heat pumps are highly energy-efficient, making them an excellent choice for homeowners who want to reduce their energy bills and carbon footprint. These systems use less electricity than traditional heating and cooling systems, as they do not need to generate heat or cool air. Instead, they simply transfer heat from one place to another, making them more efficient.
Zoning: Ducted heat pumps can be zoned, which means that you can control the temperature in different parts of your home independently. This allows you to save energy by only heating or cooling the rooms that you are using, rather than the entire house.
Improved Air Quality: Ducted heat pumps filter the air as it circulates through the system, removing dust, pollen, and other allergens. This can improve the indoor air quality and make your home a healthier place to live.
Quiet Operation: Ducted heat pumps are quieter than traditional HVAC systems, as the outdoor unit is located outside the building. This means that you won't be disturbed by the noise of the system when it is running.

Figure 4: Air conditioning ventilation duct.
4. Cons of Ducted Heat Pumps
While ducted heat pumps offer many benefits, there are also some drawbacks to consider before investing in this type of system. Here are some of the most significant disadvantages:
Upfront Cost: Ducted heat pump systems can be expensive to install, as they require both an outdoor and indoor unit, as well as ductwork throughout the building. However, these costs can be offset by the energy savings over time.
Ductwork Requirements: Ducted heat pumps require ductwork to distribute the conditioned air throughout the building. If your home does not already have ducts installed, this can add to the cost of the system.
Maintenance Requirements: Like all HVAC systems, ducted heat pumps require regular maintenance to keep them running efficiently. This can include cleaning the filters, checking the refrigerant levels, and inspecting the ductwork for leaks.
5. Choosing the Right Ducted Heat Pump System
If you are considering a ducted heat pump system for your home or office, there are several factors to consider when choosing the right system. Here are some of the most important considerations:
Size: The size of the system you choose will depend on the size of your building and the heating and cooling needs of your space. A professional HVAC contractor can help you determine the right size system for your needs.
Efficiency Rating: Look for a ducted heat pump system with a high efficiency rating, as this will help you save money on energy bills over time.
Zoning Capability: If you want to be able to control the temperature in different parts of your home independently, look for a system that offers zoning capabilities.
Brand and Warranty: Choose a reputable brand and look for a system with a good warranty, so you can have peace of mind knowing that your investment is protected.
6. Installation and Maintenance of a Ducted Heat Pump
Installation of a ducted heat pump typically involves several steps, including the installation of the outdoor unit, the indoor unit, and the ductwork. It is important to have a professional HVAC contractor handle the installation to ensure that everything is done correctly and safely.
Once the system is installed, regular maintenance is important to keep it running smoothly and efficiently. This includes tasks such as changing the air filters, cleaning the coils, and checking the refrigerant levels. It is recommended to have a professional perform an annual maintenance check to ensure that the system is operating at peak efficiency.

Figure 5: Check the heat pump outdoor unit.
7. FAQs
7.1 Can a Heat Pump Use Existing Ducts?
Yes, a heat pump can use existing ducts in your home, provided that they are in good condition and properly sized for the heat pump.
When installing a ducted heat pump, a professional HVAC contractor will evaluate your existing ductwork to determine if it is suitable for use with the new system. If the ducts are in good condition and properly sized, they can be used with the heat pump.
However, if the ducts are damaged or undersized, they may need to be repaired or replaced in order to work with the new system. Properly sized and sealed ducts are important for efficient operation and optimal performance of a heat pump.
7.2 Are Ducted Heat Pumps Efficient?
Yes, ducted heat pumps are generally very efficient. They are designed to transfer heat from the outside air to the inside of your home, rather than generating heat through combustion or resistance heating. This means that they can provide the same amount of heating as traditional systems while using less energy.
Additionally, ducted heat pumps often have a high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) ratings, which indicate their energy efficiency. Properly installed and maintained ducted heat pumps can provide significant energy savings and reduce your carbon footprint.
Figure 6: Ventilation system on the ceiling of a large building.
7.3 How Good Are Ducted Heat Pumps?
Ducted heat pumps are generally considered to be very good heating and cooling systems due to their high energy efficiency and quiet operation. They are designed to transfer heat from the outside air to the inside of your home, which can be done more efficiently than generating heat through combustion or resistance heating.
In addition, by using zoned heating and cooling, ducted heat pumps can provide customized comfort while saving energy. Properly installed and maintained ducted heat pumps can provide reliable, consistent heating and cooling for your home while offering energy savings over time.
7.4 Are Ducted Heat Pumps Expensive to Run?
Ducted heat pumps are generally not expensive to run compared to other heating and cooling systems. They are designed to be highly energy efficient, using less energy to provide the same amount of heating or cooling as traditional systems. This means that they can help you save money on your energy bills over time.
Additionally, by using zoned heating and cooling, which allows you to heat or cool only the rooms that are in use, you can further reduce your energy consumption and save money.
However, the exact cost of running a ducted heat pump will depend on several factors, including the size of your home, your local climate, and your energy usage patterns.
Related Info
Heat Pump vs Mini Split: Which is Better for Your Home?How Do I Know If I Have a Heat Pump or an AC? A Comprehensive Guide
Heat Pump Not Turning On: Troubleshooting Guide
Heat Pump vs Central Air: Which One is Right for You?
Heat Pump vs Conventional HVAC: Which is Better for Your Home?


