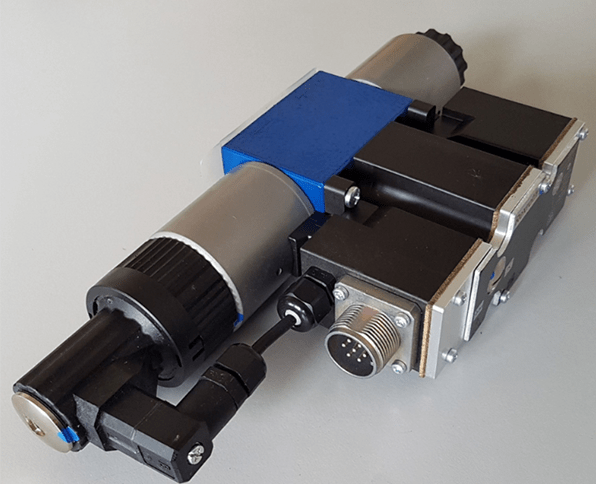
A proportional solenoid valve is a device that controls the opening degree of a valve by changing the input current to the electromagnet (solenoid coil). It acts on the valve through the magnetic field of the electromagnet, making the opening degree of the valve proportional to the input current of the electromagnet. The specific working principle of proportional valve is as follows:
1. How the Proportional Solenoid Valve Works
1. Electromagnetic actuation: Proportional solenoid valves are usually actuated by electromagnetic components, which include electromagnetic coils and magnets. When an electric current passes through an electromagnetic coil, it creates a magnetic field that changes the position of the magnet. This electromagnetic actuation mechanism allows the opening and closing degrees of the valve to be precisely controlled.
2. Valve structure: Proportional solenoid valves usually have a valve core and a valve seat. The gap (the valve opening degree) between the valve core and the valve seat can be adjusted according to changes in the magnetic field, thereby controlling the flow of fluid.
3. Feedback sensor: In order to ensure precise control, proportional solenoid valves are usually equipped with feedback sensors. These sensors monitor the flow or pressure of the fluid and send feedback information back to the control system.
4. Control signal: The control system of the proportional solenoid valve sends control signals to the electromagnetic components through the electronic controller. These signals tell the solenoid how to adjust the opening and closing of the valve to achieve the desired flow or pressure.
5. Fluid flow: When the electromagnetic element adjusts the position of the valve according to the control signal, the fluid can pass through the valve and enter or leave the system. By changing the opening degree of the valve, the speed and amount of fluid flow can be controlled.
6. Feedback control: Feedback sensors continuously monitor fluid flow or pressure and compare the actual value with the required value. The control system will continuously adjust the operation of the electromagnetic components based on this feedback information to keep the system in the desired state.
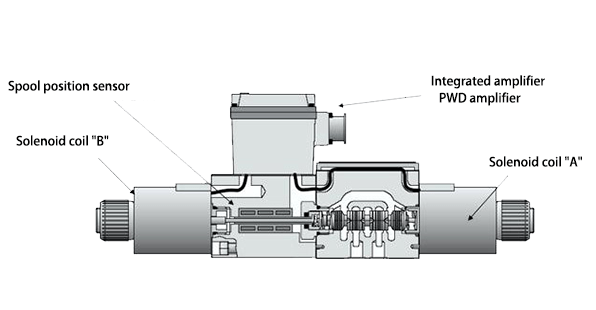
1.1 Proportional Solenoid Valve Working Principle Block Diagram
The figure below shows the working principle block diagram of the proportional solenoid valve.
The proportional amplifier amplifies the command signal and outputs current to the proportional electromagnet of the proportional solenoid valve in proportion. The proportional electromagnet outputs force and moves the position of the valve core proportionally, thereby controlling the flow rate of the liquid flow and changing the liquid flow direction to achieve the position or speed control of the actuator.
In some applications that require high position or speed accuracy, the displacement or speed of the actuator can also be detected to form a closed-loop control system.

2. Types of Proportional Solenoid Valves
Classified by controlled parameters
The parameters controlled by the proportional valve can be pressure, flow, direction, etc. There are proportional valves that control one parameter (single parameter, single function), and that control two parameters or more parameters (multiple parameters, multifunction).
① Proportional pressure control valves, such as proportional pilot pressure valves, proportional relief valves, proportional pressure reducing valves, proportional sequence valves, etc., are proportional valves that control the pressure parameter (single parameter) of the hydraulic system through the input electrical signals.
② Proportional flow control valves, such as proportional throttle valves, proportional speed control valves, proportional one-way speed control valves, etc., are also single-parameter control valves.
③The proportional directional control (direction and flow) valve is a multi (two)-parameter control valve that simultaneously controls the flow rate and flow direction of the liquid flow according to the magnitude and direction of the input electrical signal.
④ The proportional combination valve is a multi-parameter control valve, which combines a pressure compensator and a pressure control valve on the basis of a proportional directional control valve.
⑤ The proportional pressure and flow control valve is also a multi-parameter proportional control valve, which combines pressure and flow control. Through the balance valve (pressure compensation valve), it keeps the pressure at both ends of the throttle port unchanged.

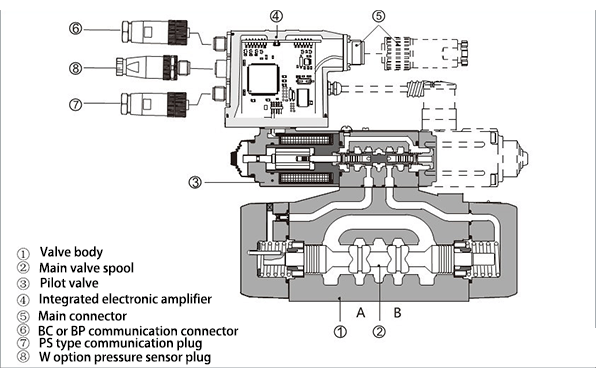
According to the installation position of electronic amplifier and proportional valve body
①Separate type: The proportional valve body is separated from the electronic amplifier;
②Integrated type: The electronic amplifier is integrated on the proportional valve body.
3. Difference between Proportional Solenoid Valve and Other Valves
3.1 Difference between Proportional Solenoid Valve and Ordinary Valve
Ordinary valves are single-action on-off valves, either fully open or fully closed, with maximum or minimum flow, and no intermediate state, such as ordinary direct-acting solenoid valves, solenoid operated directional control valves, and electro-hydraulic directional control valves.
The proportional valve performs continuous step control in proportion, and performs automatic compensation control on the target based on the information collected from changes in actual conditions. The valve opening direction, opening degree or spring setting force are all changeable to achieve a series of continuously controllable and follow-up movements.

3.2 Difference between Proportional Solenoid Valve and Servo Valve
The valve opening degrees of the servo valve and the proportional valve are both electrically controlled, and can be opened to the degree as needed, thereby controlling the flow rate.
Their differences:
Different actuation devices: The driving device of the proportional valve is a proportional electromagnet, and that of the servo valve is usually a torque motor.
Different performance parameters: The servo valve has no deadband, while the proportional valve has.
Different application scenarios: Servo valves and servo proportional valves are mainly used in closed-loop control systems, while proportional valves with other structures are mainly used in open-loop control systems and closed-loop speed control systems.
4. Common Applications of Proportional Solenoid Valves

Proportional solenoid valves are widely used in the field of fluid control in industrial automation control systems. Here are some common application areas:
1. Hydraulic system: In the hydraulic system, the proportional solenoid valve is used to control the flow and pressure of hydraulic oil to achieve precise control of the actuator. The use of proportional solenoid valves can improve the stability and response speed of the hydraulic system.
2. Petrochemical industry: In the petrochemical industry, proportional solenoid valves are used to adjust the flow and temperature of various media. For example, in a distillation tower, proportional solenoid valves are used to adjust the liquid level and temperature between different trays to control the distillation process.
3. Sewage treatment: The flow of different media needs to be precisely controlled during the sewage treatment process. The proportional solenoid valve can adjust the position of the valve disc according to actual needs, thereby adjusting the flow of the medium and achieving precise control of the sewage treatment process.
4. Industrial field: Proportional solenoid valves can be used in various types of industrial equipment, such as automated machine tools, fluid delivery systems, textile machinery, metallurgical equipment, etc. It can control the flow, pressure, temperature and other parameters of gas or liquid to achieve refined management in the production process.
5. Use in daily life: Proportional solenoid valves are also widely used in daily life, such as water flow control in washing machines, refrigerant flow control in air conditioners, and adjustment of fuel injection quantity in automobile engines. In addition, they also have important applications in medical equipment, food machinery and other fields.


