
Figure 1: Heat pump units.
Heat pumps are a popular alternative to traditional heating and cooling systems. They work by transferring heat from one location to another, providing both warmth in the winter and coolness in the summer.
However, like any technology, there are both advantages and disadvantages to using a heat pump. In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of heat pumps.
Before introducing heat pump pros and cons, it is necessary to understand the basic knowledge about heat pumps
1. Heat Pumps Basics
1.1 What are heat pumps?
Heat pumps are devices that can both heat and cool a building by transferring heat from one location to another. They are similar to air conditioners in that they use refrigerant to absorb and release heat, but they can also reverse the process to provide heating instead of cooling. Heat pumps can be used in a variety of settings, including residential homes, commercial buildings, and industrial facilities.

Figure 2: Heat pump external unit structure diagram.
1.2 Types of Heat Pumps
There are several types of heat pumps available, including air-source, ground-source, and water-source.
Air-Source Heat Pumps: Air-source heat pumps are the most common type of heat pump. They work by transferring heat between the indoor air and outdoor air, and are typically less expensive to install than other types of heat pumps.
Ground-Source Heat Pumps: Ground-source heat pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, transfer heat between the indoor air and the ground. They are more expensive to install than air-source heat pumps, but can be more efficient in colder climates.
Water-Source Heat Pumps: Water-source heat pumps transfer heat between the indoor air and water, such as a lake or pond. They are typically more efficient than air-source heat pumps, but can be more expensive to install.
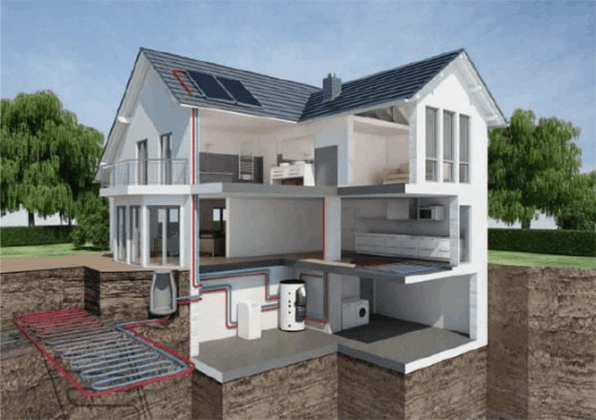

Figure 3: Ground-source heat pump diagram.
1.3 How Do Heat Pumps Work?
Heat pumps work by transferring heat from one location to another using refrigerant. When the heat pump is in heating mode, it absorbs heat from the outside air or ground and transfers it inside the building. In cooling mode, the heat pump absorbs heat from inside the building and releases it outside.
The process of transferring heat is accomplished through the use of a compressor, evaporator, condenser, and expansion valve.

Figure 4: Working principle diagram of heat pump.
2. 5 Pros of Heat Pumps
2.1 Energy Efficiency
One of the main advantages of heat pumps is their energy efficiency. Unlike traditional heating systems that generate heat by burning fuel, heat pumps simply transfer heat from the outside to the inside of a building. This means that they use less energy to heat a space, which can result in significant cost savings on energy bills.
2.2 Versatility
Another benefit of heat pumps is their versatility. They can be used for both heating and cooling, making them a great all-in-one solution for homeowners. Additionally, some heat pumps can even be used to heat water, further increasing their usefulness.
2.3 Long Lifespan
Heat pumps have a longer lifespan than traditional heating systems. They can last up to 15 years or more with proper maintenance. This means that you can enjoy the benefits of your heat pump for a long time without worrying about costly repairs or replacements.
2.4 Environmentally Friendly
Heat pumps are also more environmentally friendly than traditional heating systems. Because they don't burn fuel to generate heat, they don't produce emissions that contribute to air pollution or climate change.
Additionally, because they use less energy to heat a space, they reduce the overall demand for energy, which can help to conserve natural resources.
2.5 Consistent Temperature
Heat pumps provide consistent temperatures throughout your home, which can be more comfortable than traditional heating systems that often produce hot spots and cold spots. This can improve indoor air quality and reduce the risk of respiratory issues caused by temperature fluctuations.

Figure 5: Heat pump outdoor unit.
3. 5 Cons of Heat Pumps
3.1 Upfront Cost
One of the main disadvantages of heat pumps is their upfront cost. Heat pumps can be more expensive to install than traditional heating systems, which can be a barrier for some homeowners or businesses. However, it's important to note that the cost of a heat pump can be offset by energy savings over time.
3.2 Temperature Limitations
Heat pumps are most effective when outdoor temperatures are moderate. When temperatures drop below freezing, heat pumps may struggle to keep up with heating demands. However, this limitation can be overcome by installing a backup heating system, such as a furnace.
3.3 Noise
Heat pumps can be noisy, especially when they are operating at full capacity. This can be a problem for homeowners who value peace and quiet. However, newer models of heat pumps have been designed to operate more quietly than older models.
3.4 Installation Challenges
Installing a heat pump can be more complex than installing a traditional heating system. Heat pumps require an outdoor unit to be installed, which can be difficult in areas with limited space or where zoning regulations are strict.
Additionally, because heat pumps rely on refrigerants to transfer heat, they require specialized training and certification to install.
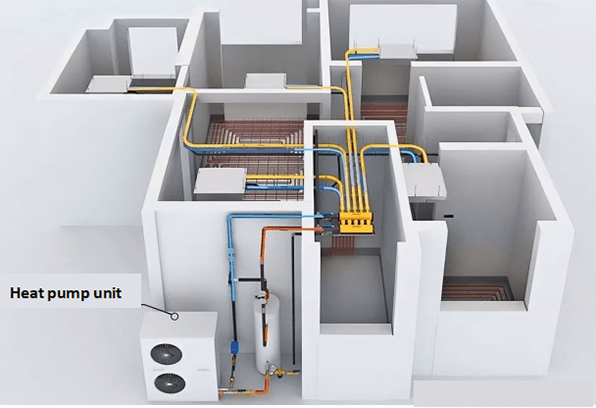
Figure 6: Installation diagram of heat pump system.
3.5 Maintenance Requirements
Heat pumps require regular maintenance to operate effectively. This can include cleaning the outdoor unit, replacing filters, and checking refrigerant levels. Failure to maintain a heat pump can result in reduced efficiency and increased energy costs.
4. Conclusion
Overall, heat pumps are an energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solution for heating and cooling homes and businesses. They offer versatility, quiet operation, and cost savings on energy bills.
However, they also have some disadvantages, including upfront cost, installation challenges, and maintenance requirements.
When considering whether to install a heat pump, it's important to weigh the pros and cons and consult with a qualified HVAC professional to determine if a heat pump is the right solution for your needs.
Related Info
Are Window Heat Pumps Efficient? (Window Heat Pump: Everything You Need to Know)How to Defrost a Heat Pump: A Comprehensive Guide
Why is My Heat Pump Icing Up? Understanding the Causes and Solutions
Heat Pump Not Working in Cold Weather: Causes and Solutions
How Does a Heat Pump Work in Winter?


