
The air conditioning system is a closed-loop working system, mainly composed of compressors, condensers, expansion valves, evaporators and other components. Now let's take a look at these components and what problems they are prone to.
1. AC Compressor
Common air conditioning compressors on cars are piston type and scroll type. The belt-driven compressors used in fuel vehicles are basically piston type.
1.1 Working Principle of Fixed Displacement Piston Compressor

As shown in the figure above: when the swash plate is tilted at 45 degrees, the piston 5 is in the intake stroke. At this time, the piston moves to the left, the intake valve opens, and the refrigerant enters.
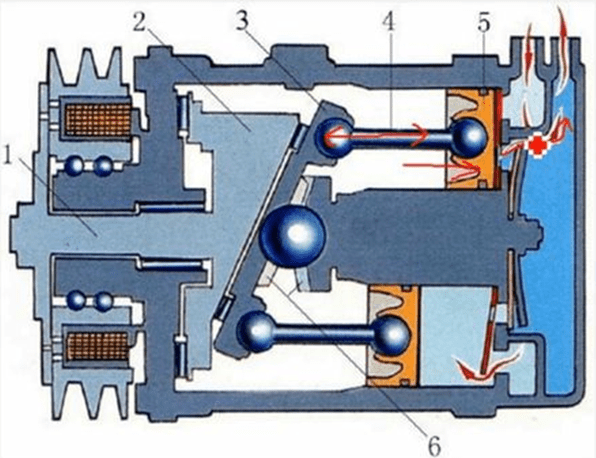
As shown in the figure: when the swash plate rotates, the piston moves to the right. At this time, it is a compression stroke, and the refrigerant in the chamber is compressed out.
1.2 Working Principle of Variable Displacement Piston Compressor
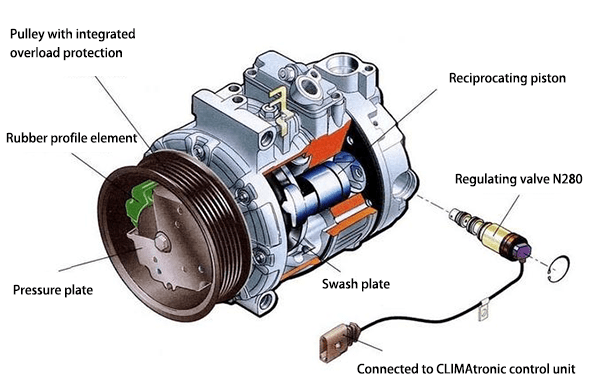
Based on the fact that ordinary compressors (fixed displacement compressors) will take away part of the engine power when working, if the engine power is insufficient, the compressor will be controlled to stop working. When the engine speed increases, the compressor will work again, so that the vehicle will jolt. Variable displacement compressors are a technology used to solve this problem.
The variable displacement compressor does not have an electromagnetic clutch. It relies on the belt pulley to drive the main shaft. The rotation of the main shaft drives the swash plate to rotate. The swash plate pushes the piston to do a reciprocating motion to complete the suction, compression, and discharge strokes.
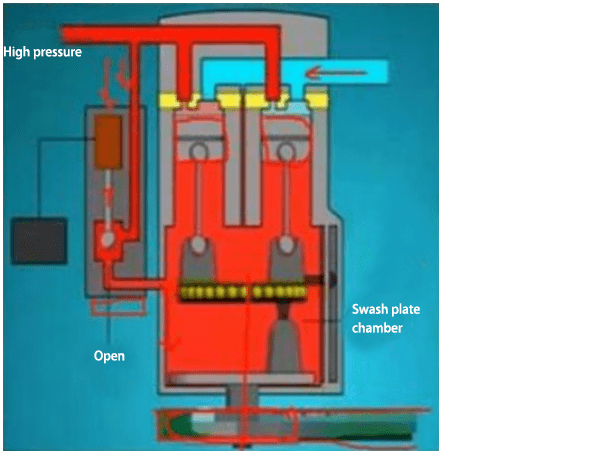
When the air conditioner is not turned on, the compressor belt pulley rotates with the engine. At this time, the control solenoid valve is not energized and is open. The refrigerant enters the swash plate chamber. Since the high-pressure chamber and the compressor swash plate chamber are connected, the pressure in the high-pressure chamber and the swash plate chamber reaches a balance, pushing the swash plate to change its angle to 90 degrees. At this time, the belt drives the swash plate to move, which is just only rotating, equivalent to idling.

When the air conditioner is turned on and a large cooling capacity is required, at this time, the solenoid valve is energized and the valve body is closed. Since the swash plate chamber is not connected to the high-pressure chamber, the pressure in the swash plate chamber will decrease. At this time, the angle of the swash plate is tilted to about 45 degrees and it starts to work.
Note: The angle between the swash plate and the pulley is changed through controlling the opening degree of the solenoid valve, then changing the stroke of the piston.
In addition, the pressure relief valve and the low-pressure chamber are connected.
1.3 How to Distinguish Variable Displacement Piston Compressors from Fixed Displacement Piston Compressors
Variable swash plate compressors usually have a control solenoid valve behind the compressor, which is the main difference.
The other way is to check whether there is an electromagnetic clutch. But this method is not necessarily accurate, because some automobile variable displacement compressor pulleys are also equipped with electromagnetic clutches during the development process.
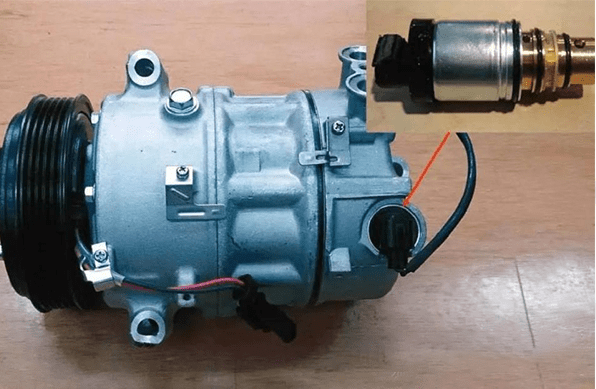
2. AC Compressor Control Valve

The function of the air conditioning control solenoid valve (regulating valve) is to change the pressure difference between the high and low pressure chambers.
The control valve can control the pressure change of the low and high pressure chambers by changing the opening degree of the valve, that is, the displacement of the piston when working.
If the failure of the AC compressor control valve causes the air conditioning to cool slowly, not cool, and fluctuate between hot and cold, you can try to replace the solenoid valve. Note that only variable displacement piston compressors have this control valve.
3. AC Condenser

Its function is to dissipate heat, and the refrigerant changes from gas to liquid here.
Common problems are as follows:
1. Dirty and blocked, resulting in poor heat dissipation and reduced refrigeration effect.
Detection method: Use a pressure gauge to check, and the pressure will be found too high.
Solution: Clean the condenser. It is recommended to clean it once a year in summer.
2. Leakage. Some leakage can be repaired by repair welding, while if it is natural aging leakage, the condenser can only be replaced.
4. AC Expansion valve
The opening degree of the valve is automatically adjusted according to temperature of the evaporator outlet, which is sensed by the temperature sensor (sensing bulb), and it is only a slight adjustment. Its function is to control the flow rate of high-pressure liquid refrigerant into the evaporator and divides the refrigerant system into high-pressure and low-pressure areas.
The flow rate of the expansion valve is adjusted according to the actual working conditions, and the adjustment methods include mechanical and electronic types. Electronic control is definitely more accurate, but it is also relatively more prone to failure.

Common faults are as follows:
1. Dirty blockage. Once it works, it will stop due to excessive high pressure.
Solution: Clean the entire pipeline and replace the receiver drier (it has a filtering function). If the problem persists, the expansion valve should be replaced.
2. Ice blockage. It is caused by excessive moisture content in the refrigerant. The phenomenon is that the AC will stop working after a while and work again after a while. It is generally caused by the incomplete vacuuming during the last maintenance.
Solution: Evacuate the system and replace the receiver drier. The evacuation time must be more than fifteen minutes.
5. AC Evaporator

Its function is to allow the high-pressure liquid refrigerant to release pressure here, changing from liquid to gas, thereby cooling the surrounding air. At this time, the hot air blown in by the air conditioner blower flows through the low-temperature evaporator fins and absorbs the heat, and then the cool air is blown out.
Common faults are as follows:
1. When the outside is dirty and blocked seriously, the low-pressure pipe (from the evaporator to the compressor) will freeze on the outside, resulting in insufficient cooling capacity.
Solution: Clean with detergent. Keep the habit of cleaning it once a year in summer.

2. Leakage. Replace it. The car dashboard needs to be removed, and the amount of work is relatively large.
6. Conclusion
The above is only an introduction to some components of the automotive air-conditioning system. In order to ensure the normal operation and intelligence of the air conditioning, there are many various sensors and control valves. Later, we will introduce the maintenance knowledge of the automotive air-conditioning system.


