Video: Central Air Conditioning System: Types, Components, and Brands (including Mitsubishi, Daikin, etc.)

Figure 1: Household central air conditioners.
The various parameters of the central air conditioning system are basically outperformed by various wall-mounted units and cabinet units, but they have incomparable advantages in terms of space and appearance. In other words, if your home has a relatively large space and you care more about cost-effectiveness and functional parameters than aesthetics, then there is no need to purchase a central air conditioning system.
1. What is Central Air Conditioning System?
Central air conditioning is an air conditioning system used to regulate indoor temperature, humidity, and air quality, usually in large buildings and residences. A central air conditioning system is a centralized system that cools or heats air through a central unit and then distributes the treated air to various rooms or areas of a building through ducts or air channels.
Central air conditioning uses refrigerant under the action of a compressor to regulate the temperature and humidity of indoor air without exchanging air with the outdoors. If you want the central air conditioning system to achieve the exchange of indoor and outdoor air, it is needed to install a fresh air system.
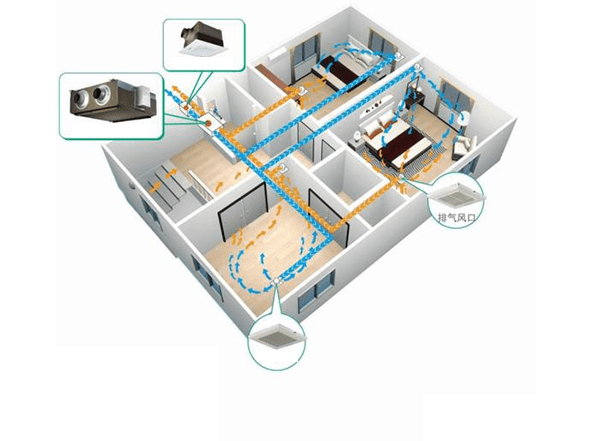
Figure 2: Fresh air system diagram.
2. Types of Central Air Conditioning System
According to the different cooling media, it is divided into water systems and fluorine systems (Freon). This article mainly introduces the fluorine central AC system represented by Japanese brands (such as Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Toshiba, Hitachi, and Daikin) and the water central AC system represented by American brands (such as Trane, York, and Carrier).
2.1 Fluorine System
Speaking of fluorine system machines, we have to mention Japan's home appliance technology. Japan has few natural resources, so everything starts with energy conservation. In terms of cooling and refrigeration, R&D personnel hope to be more efficient and save energy. Daikin, Hitachi, and Mitsubishi have all invested heavily in R&D. Each has explored and developed their own air conditioning systems.
The United States mainly relies on water central air conditioning systems. At first, there was no central air conditioning with a fluorine system in the United States, but later, with the market demand developing, the technology was also expanded.
VRV system
The main implementation method of central air conditioning is the VRV system (Variable Refrigerant Volume System), which is an air conditioning system that controls the flow volume of refrigerant and realizes cooling or heating through direct evaporation or direct condensation of the refrigerant.
VRV is a variable refrigerant volume system invented by Daikin in the 1980s and has been registered by Daikin. Since the VRV system only transports refrigerant to the extension units in each room, there is no need to design independent air ducts (separate air ducts are arranged for the fresh air system), achieving miniaturization and quietness of the equipment.

Figure 3: VRV system diagram.
VAV system
In addition to the VRV system, the Variable Air Volume (VAV) System is also an air conditioning method of the all-air system.
The VAV system controls and adjusts the temperature of a certain air-conditioned area by changing the air supply volume, rather than the air supply temperature, so as to adapt to changes in the load of the air-conditioned area. The VAV system usually consists of air treatment equipment, supply (return) air system, terminal device (variable air volume box), air supply outlet and automatic control instrument.
Generally, the VAV system should be used in the following systems:
1) In the same air-conditioning system, each air-conditioning zone has large heat and cold load differences and changes, and long low-load operation time, and the temperature of each air-conditioning zone needs to be controlled separately.
2) The inner area of the building needs to be supplied with cold air throughout the year.

Figure 4: VAV system diagram.
Other
VRF is a variable refrigerant flow central air conditioning system. VRF means the same thing as VRV. Since VRV is registered by Daikin, other brands call this technology VRF.
Other names such as MDV (Midea, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries), GMV (Gree), TVR (Trane), etc. are all names given to central air conditioners by different companies.
2.2 Water System
Unlike the Japanese fluorine system, most central air conditioning systems in the United States are based on water systems. Using water as the cooling medium, the temperature of the outlet air is more comfortable, but the temperature changes slowly, which is more suitable for situations where the house area is large and the door is continuously opened. York, Trane, McQuay and Carrier are the four major brands of central air conditioning in the United States.
Advantages of water central air conditioning system:
1. Compared with the fluorine system, the water system absolutely beats it in terms of comfort. The water system uses water as the medium, and the air outlet temperature is uniform and soft, generally around 15-18°C. The humidity in the rooms is also relatively high, which will not give people a dry feeling and is highly comfortable for the human body. The air outlet temperature of the fluorine system is low, with the air outlet temperature around 7-12°C. The air temperature is uneven, and it also removes all the humidity (condensed water) from the air, giving people a dry mouth feeling.
2. The investment in purchasing a water system central air conditioning is low.
3. The service life of a water system is generally longer than that of a fluorine system.
4. The water system has strong scalability and can be equipped with floor heating. The later cost of floor heating is much cheaper than that of a boiler with floor heating.
Disadvantages of water central air conditioning system:
1. The outdoor unit of water central air conditioning is larger in size, and is more troublesome to install than the fluorine system and requires large space.
2. The temperature changes slowly, and the change is not obvious in a short period of time.
3. The noise is relatively loud.
4. The energy consumption of the entire heat exchange process, from air to refrigerant to water and finally to air, is relatively high.

Figure 5: Water central air conditioning system diagram.
3. Central Air Conditioning Components
Here we will use the fluorine system as a representative to introduce the composition of the central air conditioning system. Household central air conditioning systems are mainly composed of outdoor units, indoor units, branch boxes/branch pipes, pipes and other parts.
3.1 Outdoor Unit
The outdoor unit is often referred to as the air conditioning main unit. A central air conditioning system generally has only one air conditioning main unit, which mainly include a compressor, fan, condenser tube, etc.
Among them, the compressor in the outdoor unit is the heart of the air conditioning system and plays a decisive role in the quality of the system. Air conditioning mainly achieves heat exchange by compressing the refrigerant into high-temperature and high-pressure gas through a compressor.
What is the difference between a single fan and double fan of an air conditioning outdoor unit?
A single fan will be slightly weaker than a double fan in terms of working conditions, energy efficiency, and capabilities. However, in terms of price, dual fans will be much more expensive than single fans because the technology of dual fans is more complex. Dual fans are generally used in main units above 5P.

Figure 6: Heat pump outdoor units.
3.2 Indoor Unit
Indoor units are usually called terminal equipment of central air conditioning systems and come in many types.
There are various types of indoor units for multi-split central air conditioning systems.
● The air duct of the duct-type indoor unit is combined with the indoor decoration, which is completely concealed, takes up no space, and has a wide range of applications;
● Ceiling cassette indoor units are usually installed on the ceiling and have excellent cooling (heating) effects, but have higher requirements for room height;
● Wall-mounted and cabinet-type indoor units are more used in small-scale family spaces. They have good control functions and cooling effects and have no requirements on room height.
Let’s take a look at the appearance and structure of these indoor units.
(1) Duct type indoor unit
▲ The duct type indoor unit is usually embedded in the corresponding wall of the room during house decoration. Its interior mainly consists of a dust screen, air outlet baffle, air outlet, cross-flow fan, motor, evaporator, electric auxiliary heat, water outlet pipe, control circuit, wiring terminals, etc.

Figure 7: Duct type indoor unit.
(2) Ceiling cassette indoor unit
▲ The interior of the ceiling cassette indoor unit is mainly composed of a centrifugal fan motor, a centrifugal fan, an evaporator, a water tray, a control circuit, a drainage pump, a front panel, a filter screen, a filter screen housing, etc.

Figure 8: Ceiling cassette indoor unit.
(3) Wall-mounted indoor unit
The wall-mounted indoor unit can be hung on the wall of the room according to the user's needs. From the outside, you can find the air inlet, front cover, air suction grille (air filter part), display and remote control panel, air deflector, air outlet and other parts. The interior has parts such as evaporator, air guide plate assembly, cross-flow fan assembly, control circuit board, remote control receiving circuit board, temperature sensor, etc. (basically the same as a mini split air conditioner).
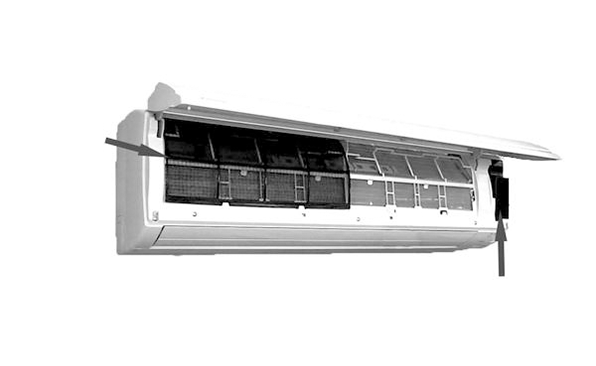
Figure 9: Wall-mounted indoor unit.
(4) Others
In addition to the types introduced above, central air conditioners also include vertical cabinet type and floor air supply type (divided into concealed floor air supply and exposed floor air supply).
3.3 Branch Box/Branch Pipe/Multi-Pipeline
In the central air-conditioning system, the branch pipe and the branch box both play a role in controlling and distributing refrigerant. However, due to their different structures, there is a big difference in cost, use and maintenance.
(1) Branch pipe
The branch pipe is actually a pipe with one input and multiple outputs. It is mainly used in the pipeline installation of the central air-conditioning VRV system. It can distribute the refrigerant in the central air-conditioning multi-split pipeline to the indoor unit, which can play a role of distributing the flow.
The branch pipe technology is mostly used in products of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Haier, Hitachi and other brands, and the high-end series products of Daikin, Mitsubishi Electric and Toshiba also use branch pipe connections.

Figure 10: Branch pipes.
(2) Branch box
The branch box is also a way to distribute refrigerant. It is a box that stores refrigerant, and all indoor refrigerant pipes will be connected to it. It will distribute refrigerant according to the size of each indoor unit and the required amount.
Each two upper and lower ports on the branch box are a group, which are the refrigerant liquid port and the refrigerant gas port respectively. Major brands rarely use this technology, and the representative brand using this technology is Mitsubishi Electric.

Figure 11: Branch box.
(3) Multi-pipe connection
In addition to using branch pipes and branch boxes, there is another way to connect internal and external units - multi-pipe connection.
Multi-pipe household central air conditioning systems refer to the separate pipe connections between the outdoor unit and each indoor unit. That is, as many indoor units as there are, the outdoor units need to have corresponding sets of refrigerant pipe ports. This connection method is mainly used in the products of Daikin MX series, Toshiba DI-IMS series, etc.
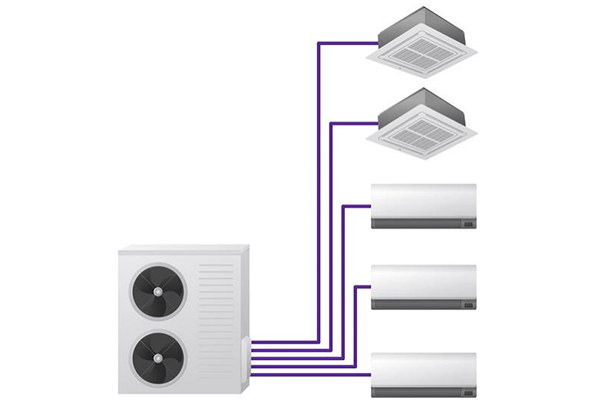
Figure 12: Multi-pipe connection.
3.4 Pipe Material
Pipe materials are also very important in the entire central air-conditioning system. Because when the central air conditioning system is working, the refrigerant in the pipes changes between high-pressure gas and liquid, so the pipes need to be leak-free and high-pressure resistant.
(1) Refrigerant pipe
For pipes that convey refrigerant, copper pipes that can withstand high pressure need to be selected, and the connection method is welding.

Figure 13: Refrigerant pipe.
(2) Condensate pipe
The best choice for condensate pipes is UPVC pipes (also called "hard PVC pipes"), which are affordable, safe and stable. Those who are not short of money can choose PEX pipes.



