Video: Defrosting of Cold Storage Air Coolers (with 9 Other Common Faults of Air Cooler)

Figure 1: Cold room air cooler.
The air cooler for a cold room is also called a cold room evaporator, air cooled evaporator, unit cooler,
refrigeration evaporator, etc. The air cooler is the main heat exchange component in the cold storage equipment,
mainly composed of an evaporation tube group and a ventilation unit (a fan). It relies on the forced air supply of the fan to make the
air in the warehouse flow through the evaporation tubes of the air cooler at a certain speed to reduce the
temperature of the warehouse.
When the air cooler works at a temperature below 0°C and below the air dew point, frost will begin to form on the
surface of the evaporator. As the operating time increases, the frost layer will become thicker and thicker.
A thicker frost layer will cause two main problems: one is the increase in heat transfer resistance, and the cold
energy in the evaporator coil cannot be effectively transferred to the cold storage through the tube wall and frost
layer. The other problem: thicker frost layer forms a large wind resistance for the fan motor, resulting in a reduction in the air volume
of the air cooler, and also reduces the heat transfer efficiency of the air cooler.
The following is a brief analysis of the causes of frost on the air cooler (evaporator):
1. Why Does the Air Cooler Freeze / Frost?
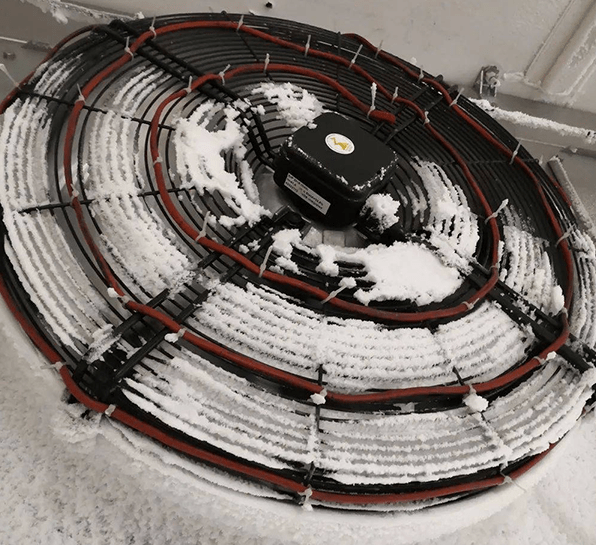
Figure 2: Frost on air cooler fan.
1. Insufficient air supply, including blockage of the outlet and return air ducts, blockage of the filter, blockage
of fin gaps, non-rotating fans or reduced fan speed, etc., resulting in insufficient heat exchange, reduced
evaporation pressure, and reduced evaporation temperature.
2. Problems with the heat exchanger (evaporator) itself. When the heat exchanger is used for a long time, the heat
exchange performance decreases, which reduces the evaporation pressure.
3. The external temperature is too low, and the environment temperature requirement for civil refrigeration
application is generally not lower than 20℃. Refrigeration in low-temperature environments will cause insufficient
heat exchange and low evaporation pressure.
4. The expansion valve is blocked or the pulse motor
system that controls the opening is damaged. After the system has been running for a long time, some debris may
block the expansion valve port and prevent it from working properly, reducing the refrigerant flow rate and the
evaporation pressure. Abnormal opening control will also result in reduced flow and reduced pressure.
5. Secondary throttling. The evaporator pipes inside are bent or blocked by debris, causing secondary throttling,
and dropped pressure and temperature.
6. The system is poorly matched. To be precise, the evaporator is too small or the working condition of the compressor is too high. In this case, even if the
evaporator performance is fully exerted, due to the high working condition of the compressor, the suction pressure
will be low and the evaporation temperature will drop.
7. Lack of refrigerant, causing low evaporation pressure and low evaporation temperature.
8. The relative humidity in the warehouse is high, or the evaporator is installed in the wrong position, or the cold
storage door is opened and closed frequently.
9. The frost is not removed completely. Due to the insufficient defrost time and the unreasonable position of the
defrost probe, the system begins to run when the frost on the evaporator is not cleaned completely. The local frost
layer of the evaporator turns into ice-like form after multiple cycles and the accumulation becomes larger.

Figure 3: Cold storage warehouse.
2. Various Methods for Defrosting an Air Cooler
The frost on the surface of the cold storage evaporator hinders the conduction and dissipation of cold energy in the
refrigeration evaporator (pipeline) and affects the refrigeration effect. When the thickness of the frost layer (ice
layer) on the evaporator surface reaches a certain level, the refrigeration efficiency even drops below 30%,
resulting in a large waste of electrical energy and shortening the service life of the refrigeration system.
Therefore, it is necessary to perform the defrosting operation for the cold storage air cooler within an appropriate
cycle.
The defrosting methods for cold storage air coolers include the following: electric defrosting, water defrosting,
and hot gas defrosting.
2.1 Electric Defrosting
In small Freon refrigeration systems, electric heating can also be used to defrost. The evaporator coils of an air
cooler that uses electric defrosting have an electric heating tube inserted.
When defrosting, it is necessary to stop the air cooler, close the liquid supply valve, and then turn on the power
of the electric heating tube to defrost the air cooler. After the frost layer melts, turn off the power of the
electric heating tube, start the compressor, open the liquid supply valve appropriately, and resume the operation of
the air cooler.
This defrosting method is convenient, simple to operate, and easy to realize automatic control.
However, it consumes more electricity and the temperature of the cold room fluctuates greatly, so it is generally
only used in very small refrigeration systems, such as some small Freon cold storages and some commercial
refrigeration equipment.
2.2 Hot Gas Defrosting
Hot gas defrosting is to guide the high-temperature refrigerant gas discharged from the refrigeration compressor
into the evaporator after being separated by the oil separator, and use the heat released by the superheated vapor
to melt the frost layer on the outer surface of the evaporator. The superheated vapor turns into liquid after
releasing heat, and is discharged into the drain bucket or low-pressure circulation reservoir together with the
previous oil in the evaporator.
This method has a good defrosting effect, short defrosting time, and low labor intensity, but the system is complex.
Especially in large cold storages with multiple warehouses, the system is particularly complex, the operation is
complicated, and the temperature of the storage changes greatly, so this method is not suitable when there is a
large amount of inventory in the warehouse.
 defrost system-min.png)
Figure 4: Four-way reversing valve hot fluorine defrost system.
2.3 Water Spray Defrosting
Water defrost is a method that uses a water spray device to spray water on the outer surface of the evaporator, so
that the frost layer is melted and falls off by the heat of the water. It is suitable for defrost of air coolers in
direct refrigeration systems.
Water spray defrosting is more effective than refrigerant hot gas defrosting, and it takes less time, is simple to
operate, and easy to manage. However, this method consumes a lot of water. Therefore, its scope of application is
limited to air coolers with discharge pipes.
3. How to Troubleshoot Common Air Cooler Failures?
3.1 Insufficient Air Volume
Cause Analysis:
1. The valve in the pipeline is not open.
2. The air suction duct is not large enough.
3. The power supply voltage is low or reversely connected.
4. The air suction duct is too long, has too many elbows or the air volume of the fan is too small.
5. The impeller is too oily.
6. The air duct connector is leaking.
Solution:
1. Open the valve.
2. Replace the air suction duct.
3. Check the power supply and exchange the two-phase wiring.
4. Replace the fan with a large air volume.
5. Clean the impeller.
6. Seal the duct connector with adhesive tape or glass glue.

Figure 5: Air coolers.
3.2 Violent Vibration of the Fan
Cause Analysis:
1. The impeller is deformed or unbalanced.
2. The bearings are severely worn and the impeller coaxiality deviation is too large.
3. The anchor bolts are loose, causing resonance.
4. The impeller positioning bolt or the impeller retaining bolt is loose.
Solution:
1. Replace the impeller.
2. Replace the bearings and adjust the coaxiality.
3. Tighten the anchor bolts.
4. Tighten the positioning bolts or retaining bolts.
3.3 Too High Motor Temperature
Cause Analysis:
1. The density of the air delivered by the fan is too high, which increases the pressure and overloads the motor.
2. The input voltage is too high or too low.
3. The flow rate is too large or the negative pressure is too high.
4. The cross-sectional area of the power supply line wires is too small.
Solution:
1. Increase the motor power.
2. Install overload protection device.
3. Redesign and install the air duct.
4. Replace the power supply line wires.
3.4 Motor Temperature Rise is Too High
Cause Analysis:
1. The flow rate exceeds the rated value.
2. There is a problem with the motor or power supply.
Solution:
1. Close the valve a little.
2. Look for motor and power supply related causes.

Figure 6: The back of the air cooler.
3.5 Too High Bearing Temperature
Cause Analysis:
1. Not enough lubricating oil (grease).
2. The lubricating oil (grease) is of poor quality.
3.The fan shaft and the motor shaft are not concentric.
4. Bearing damage.
Solution:
1. Add enough.
2. After cleaning the bearings, replace the previous lubricating oil with the qualified lubricating oil (grease).
3.Adjust the concentricity.
4. Replace the bearing.
3.6 Too Much Noise
Cause Analysis:
1. The impeller rubs against the air inlet or casing.
2. The bearing parts are worn and the clearance is too large.
3.The speed is too high.
Solution:
1. See the related entry below.
2. Replace or adjust.
3.Reduce the speed or replace the fan.

Figure 7: Air cooler fan.
3.7 Excessive Vibration
Cause Analysis:
1. The nuts of anchor bolts or other connecting bolts are loose.
2. The bearings are worn or loose.
3.The fan shaft and the motor shaft are not concentric.
4. The connection between the impeller and shaft is loose.
5. The blade weight is not the same or some blades are worn or corroded.
6.There are uneven attachments on the blades.
7. The weight or position of the balance block on the impeller is wrong.
Solution:
1. Tighten.
2. Replace or tighten.
3.Adjust the concentricity.
4. Fasten.
5. Adjust balance or replace blades or impeller.
6. Clean.
7. Perform the balance correction.
3.8 The Impeller Rubs against the Air Inlet or Casing
Cause Analysis:
1. The bearing is loose in the bearing seat.
2. The center of the impeller is not at the center of the air inlet.
3.The connection between the impeller and shaft is loose.
4. Impeller deformation.
Solution:
1. Fasten.
2. Find out the cause and make adjustments.
3.Fasten.
4. Replace.
3.9 Too Small Air Volume
Cause Analysis:
1. The impeller rotation direction is reversed.
2. The valve is not opened enough.
3. The speed is not enough.
4. The air inlet or outlet is blocked.
5.The connection between the impeller and shaft is loose.
6. The gap between the impeller and the air inlet is too large.
7. The fan has manufacturing quality issues and cannot reach the rated air volume marked on the nameplate.
Solution:
1. Exchange any two wiring positions of the motor.
2. Open to a suitable opening degree.
3. Check voltage, bearings.
4. Clear the blockage.
5.Fasten.
6. Adjust to the appropriate gap.
7. Replace the fan with a suitable one.



