
Figure 1: PLCs of different producers and models.
The programmable logic controller (PLC) is a digital operation controller with microprocessor for automatic control, which can load control instructions into memory for storage and execution at any time. With the wide application of PLC in industry, different types of PLC appear to meet different needs. According to different component structures, and total input/output (I/O) points, PLC can be divided into the following categories:
1. According to the Component Structures
1) The compact PLC. It installs central processing unit (CPU), memory, I/O interface, power supply and other hardware in one case. It can also be composed of a module (called a host) with a certain number of I/O points and external I/O cards. This kind of PLC has the advantages of compact structure, small size and low price, but it is not very convenient to maintain. PLCs with this structure are more common in micro and small PLCs.
2) The modular PLC. It divides each part of PLC into several independent modules, such as the controller composed of CPU and memory, the power supply module, the input (I) module composed of several input points, and the module composed of several output points. Output (O) modules, and specific functions specially made into a function module.
Modular PLCs consist of modules selected by the user. This kind of PLC has the advantages of flexible configuration, convenient assembly, diversified and personalized combination, easy expansion and maintenance. And mostly used for medium and large PLC.

Figure 2: Modular PLC XC300 EATON Industries France.
Recently there has also been a PLC that combines the advantages of the compact and modular PLCs, the so-called stackable PLC. Its CPU, memory, power supply, I/O and other units are still independent modules, but connected by cables, so they can be stacked on top of each other. It has not only the flexible configuration of the modular PLC, but also the advantages of compact PLC.
2. According to the I/O Points
According to the number of I/O devices that can be controlled by PLCs, there are the micro PLC, the small PLC, the medium PLC, and the large PLC.
1) The micro PLC: limited numbers of input and outputs; can control up to 32I/O devices, very compact; applicable to simple machine level control;
2) The small PLC: can control 32 to 128 I/O devices; has memory up to 2 Kbytes; applicable to simple to advance level machine control;
3) The medium PLC: can control 128 to 2048 I/O devices; has memory up to 32 Kbytes; more expensive; applicable to complex advance machine control;
4) The large PLC: can control 2048 to 8192 I/O devices; most sophisticated in PLC family; used in supervisory control and data acquisition system (SCADA).
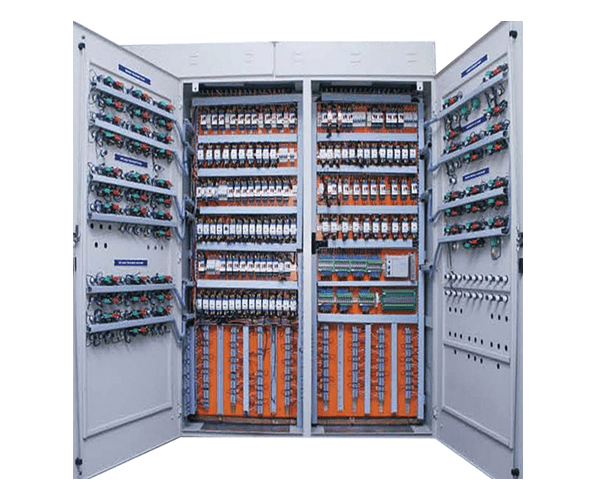
Figure 3: The panel of the large PLC.
Related Info
What is an Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier?What is an Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier?
How do Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers Work?
What is a Programmable Logic Controller?
How do Programmable Logic Controllers Work?


