
Figure 1: FlexSim’s programmable logic controller.
When a programmable logic controller (PLC) is put into operation, its working process is generally divided into three steps, namely input scan, executing program(s), and output scan. They compose a scan cycle. During the entire operation period, the central processing unit (CPU) of the PLC repeatedly executes the above three steps at a certain scanning speed.
Input Scan
The PLC sequentially reads all input values, and stores them in the corresponding units in the I/O image table. After this step is over, it goes to the steps of executing program and output scan.
In these two stages, even if the input state and data change, the state and data of the corresponding unit in the I/O image table will not change. Therefore, if the input is a pulse signal, the width of the pulse signal must be greater than one scan period to ensure that the input can be read in any case.
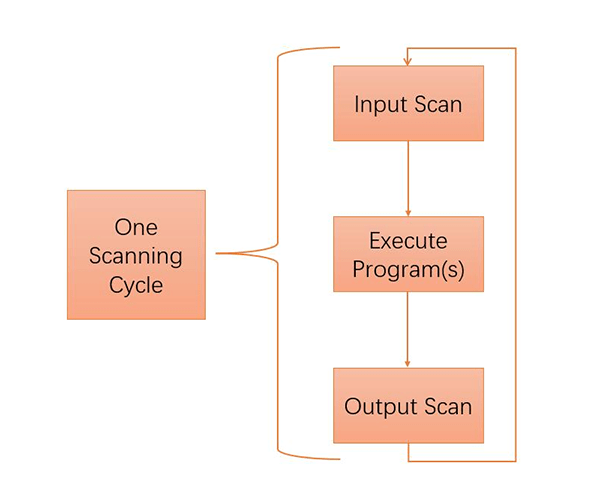
Figure 2: Three steps of one PLC scanning cycle.
Executing Program(s)
The PLC always scans the user program sequentially from top to bottom. In the ladder diagram, the control circuit formed by the contacts on the left side of the ladder diagram is always scanned first, and the logic algorithm is performed on the control circuit formed by the contacts in the order of first left, then right, first up and down.
Then, according to the result of the logic algorithm, the state of the corresponding point of the logic coil in the system random access memory (RAM) storage area is updated; or the state of the corresponding bit of the output coil in the I/O image table is updated; or whether to execute the special function instruction specified by the ladder diagram is determined.
In a nutshell, during the execution of the user program, only the state and data of the input point in the I/O image table will not change. The state and data of other output points and soft devices may change in the I/O image table or the system RAM storage area. And the program execution result of the upper ladder diagram will affect all the ladder diagrams that use these coils or data in the lower row. On the contrary, for the ladder diagrams arranged below, the status or data of the logic coils to be updated can only take effect on the programs arranged above it until the next scan cycle.
Output Scan
When the scanning user program ends, the PLC comes to the output scan. During this step, the CPU updates all output latch circuits according to the corresponding state and data in the I/O image table, and then drives the corresponding peripherals through the output circuit. At this time, it is the real output of the PLC.
Conclusion
According to the description of the above process, the characteristics of the PLC working process are summarized as follows:
1) The PLC adopts the working mode of centralized sampling and centralized output, which reduces the influence of external interference.
2) The working process of PLC is the process of cyclic scanning. The length of the cyclic scanning time depends on the instruction execution speed, the length of the user program and other factors.
3) The effect of the output on the input has a lag. PLC adopts the working mode of centralized scanning and centralized output. When the scanning period is over, the change of the input state will not be accepted until the next sampling period. Therefore, the length of this lag time mainly depends on the length of the cycle period. In addition, the factors that affect the lag time include the input filter time, the lag time of the output circuit, and so on.

Figure 3: A PLC at work.
Related Info
What is an Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier?What is an Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier?
How do Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers Work?
What is a Programmable Logic Controller?
Classifications and Features of Optical Fiber Amplifiers


