
Figure 1: Air Compressors.
There are two methods of achieving air compression: positive and dynamic displacement. Each method has several sub-categories which we cover below. The outcomes are relatively similar, but the processes to achieve them vary.
1. Positive Displacement Air Compressor
Positive displacement air compressors force air in a chamber where the volume is decreased to compress the air.
Positive displacement is an umbrella term that describes different air compressors that are power through positive air displacement. Although the internal systems vary among different machines, the method of providing the power is the same.
Some types of positive displacement compressors are better equipped for industrial workloads while others are better for hobbyists or private projects. Here are the three main types of air compressors that use positive displacement.
1.1 Rotary Screw Air Compressor
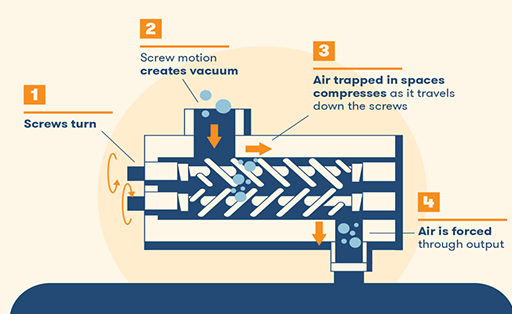
Figure 2: How rotary screw compressors work.
Rotary screw compressors have two internal “screws" that rotate in opposite directions, trapping and compressing air between them. The two screws also generate constant movement as they rotate around.
This is a common type of air compressor and is one of the easiest to take care of. The engines are typically industrial-sized and are great for continuous use.
1.2 Rotary Vane Air Compressor

Figure 3: How rotary vane compressors works.
Rotary vane compressors are like rotary screw compressors, but instead of screws, vanes are mounted on a rotor and rotated inside the cavity. The air compresses between the vane and its casing and is then pushed out at a different exhaust port.
Rotary vane compressors are very easy to use, making them very popular for private projects.
2. Dynamic Displacement Air Compressor
Dynamic displacement compressors utilize a rotating blade powered by an engine to generate airflow. The air is then restricted to create pressure, and the kinetic energy is stored within the compressor.
These are mainly designed for large projects, like at chemical plants or steel manufacturers, so it’s unlikely you’ll be able to find one at your local mechanic.
Just like with positive displacement compressors, there are two distinct types of dynamic displacement: axial and centrifugal.
2.1 Axial Air Compressor
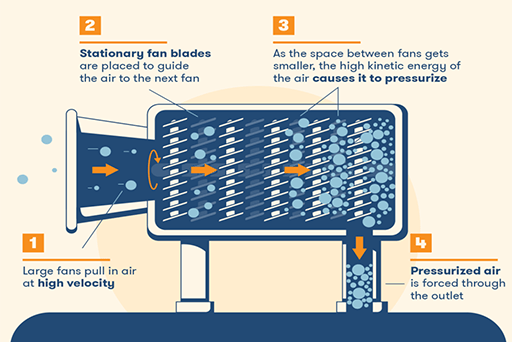
Figure 4: How axial compressors work.
Axial compressors use a series of turbine blades to generate air, forcing it through a small area. Although similar to other bladed compressors, axial compressors operate with stationary blades which slow airflow, increasing pressure.
These types of air compressors aren’t very common and have limited functionality. They’re used mainly in aircraft engines and in large air separation plants.
2.2 Centrifugal Air Compressor
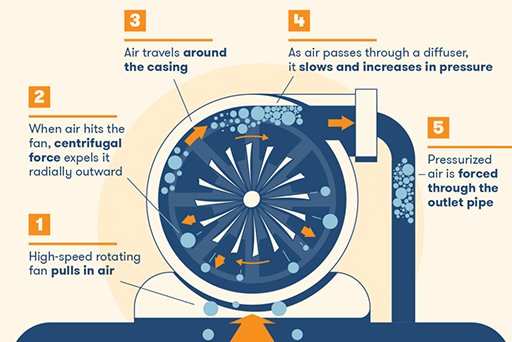
Figure 5: How centrifugal air compressors work.
Centrifugal, or radial compressors, work by bringing air into the center through a rotating impeller, which is then pushed forward through centrifugal, or outward, force. By slowing the flow of air through a diffuser, more kinetic energy is generated.
Electric high-speed motors are typically used for these kinds of compressors. One of the more common uses of centrifugal compressors is through HVAC systems.
Related Info
How to Choose an Air CompressorHow to Use an Air Compressor
How to Set Air Compressor Pressure
What is Air Compressor


