
Figure 1: AC compressor.
For the electrical product—— the air conditioner, the air conditioner compressor (AC compressor) is an indispensable structure for the normal use of the air conditioner. It can be said that it is precisely because of the air conditioner compressor that the air conditioner can perform cooling work in summer.
So, how does an ac compressor work? In order to let everyone have a more comprehensive understanding of the air conditioning compressor, the following introduces the basic knowledge about it.
1. Refrigeration Cycle
Before understanding the working principle of the air conditioner compressor, it is necessary to understand what is the refrigeration cycle system and its components.
The refrigeration cycle consists of four basic components: compressor, condenser, evaporator, and throttling device (expansion valve).
The working process of the general refrigeration cycle system is as follows:
●The compressor sucks the lower-pressure refrigerant vapor from the evaporator, raises its pressure and sends it to the condenser.
●The refrigerant condenses into a higher pressure liquid in the condenser.
●After throttling, the refrigerant becomes a liquid with a lower pressure and is sent to the evaporator.
●The refrigerant absorbs heat and evaporates in the evaporator to become vapor with a lower pressure, and then is sent to the inlet of the compressor to complete the refrigeration cycle.

Figure 2: Air conditioning system diagram.
1.1 Compressor
The compressor sucks the vapor from the evaporator and compresses it into high-pressure and high-temperature vapor.
[The higher the pressure, the higher the boiling point; the lower the pressure, the lower the boiling point]. Only by increasing the pressure of the refrigerant to make the freezing point (boiling point) of the refrigerant higher than the outdoor temperature, can the refrigerant dissipate heat to the outside, lower the temperature, and condense into a liquid.
1.2 Condenser
The condenser cools the high-temperature and high-pressure vapor discharged from the compressor into liquid, and the released heat is taken away by water or air. Condensers can be divided into three types: water-cooled, air-cooled, and combined air- and water-cooled (evaporative condenser).
Most air conditioning condensers adopt a finned coil-type structure. In order to improve heat exchange efficiency, aluminum alloy fins are often pressed into various shapes to increase the heat exchange area.
1.3 Throttling Device
The main function of the throttling device is to achieve the purpose of reducing the pressure and regulating the flow.
1.4 Evaporator
The evaporator evaporates the refrigerant liquid into a gas state and absorbs heat.
Other components include dry filter, gas-liquid separator, sight glass, axial fan, oil separator, solenoid valve, etc.
2. Working Principle and Structure of AC Compressor
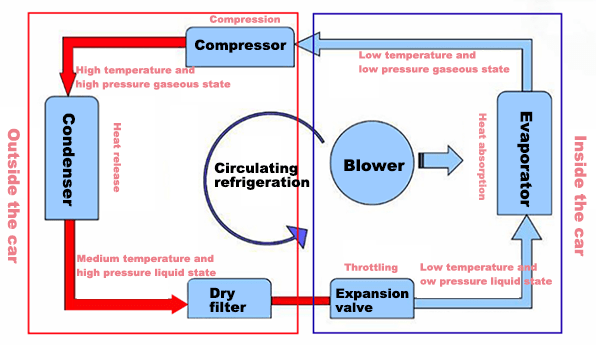
Figure 3: Refrigeration cycle diagram of car AC.
The air conditioner compressor plays the role of compressing and driving refrigerant in the air conditioning refrigerant circuit. The air conditioner compressor is generally installed in the outdoor unit.
The air conditioner compressor sucks the refrigerant from the low-pressure area, compresses it, and then sends it to the high-pressure area for cooling and condensation. The heat is released into the air through the heat sink, and the refrigerant also changes from gaseous to liquid, with increasing pressure.
The indoor unit and outdoor unit of the air conditioner belong to the low-voltage area and high-pressure area respectively. The refrigerant flows from the high-pressure area to the low-pressure area, and is sent into the evaporator through the capillary tube. After entering the evaporator, the pressure drops suddenly, and the liquid refrigerant immediately becomes gaseous, and absorbs a large amount of heat in the air through the cooling fins.
The air conditioner compressor keeps working, and it continuously absorbs the heat at one end of the low-pressure area into the refrigerant, and then sends it to the high-pressure area for releasing heat into the air, which plays a role in regulating the temperature.
The essence of the working principle of the air conditioner compressor is to use the principle of liquid absorbing heat to turn into gas, and the principle of gas releasing heat to turn into liquid. The former will cause the surrounding air to cool down, and the latter will cause the surrounding air to expand, thus causing the air to heat up.
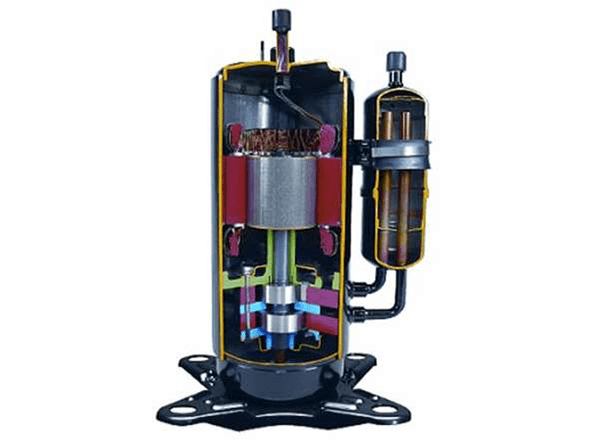
2.1 Structure of AC Compressor

Figure 4: Cutaway view of AC compressor.
AC Compressors currently used mainly include piston, rotary, scroll and large screw types. Although their structure is different and the main components are different, there are generally the following major components:
1. Motor coil: There are two types of coil windings: single-phase (capacitor start required) and three-phase.
2. Bearing: that is, the rotor, which is the crankshaft used for rotation and compression, also called the eccentric bearing.
3. Compression chamber: Piston type includes piston and piston chamber, rotary type includes rolling piston and vane, scroll type includes fixed scroll and orbiting scroll, and screw type achieves compression through the meshing between gears.
3. Air Conditioning Compressor Types
The compressor is the heart of the refrigeration and air conditioning system and consists of a motor part and a compression part. The motor runs after being energized to drive the compression part to work, so that the low-temperature and low-pressure refrigerant gas sucked through the suction pipe becomes high-temperature and high-pressure gas. There are several types of common air conditioner compressors.
3.1 Piston Compressor (Reciprocating Compressor)
The application of piston compressors is relatively early, the power is relatively large, and the temperature resistance requirements of the motor coils are not very high, so most cabinet air conditioners at home and abroad use this type of compressor.
Its disadvantages are large volume, complex structure, low efficiency, relatively large noise and vibration, and it will be gradually eliminated.

Figure 5: Piston compressor.
3.2 Rolling Piston Compressor
The rolling piston compressor has a simple structure, small size, light weight and fewer parts. Compared with the reciprocating piston compressor with the same cooling capacity, the volume is reduced by 60%, the weight is reduced by 35%, and the parts are reduced by 50%. This kind of compressor only performs rotary motion, and does not need to convert rotary motion into piston reciprocating motion, so it runs smoothly, with little vibration and low noise.
Since the suction and discharge of rotary compressors are continuous, no suction valve is required. In order to prevent high-pressure gas from returning to the cylinder after shutdown, only a discharge valve is provided.
Since there is no suction valve, the loss of suction pressure is reduced, and the volumetric efficiency and energy efficiency ratio are increased, but the machining precision of the parts is very high, and the service life is shorter than that of the piston compressor.
This kind of compressor has only one roller and is arranged eccentrically, and the vibration is relatively large when rotating, so a twin rotary compressor appears. The two rollers of this type compressor are symmetrically distributed, so the dynamic balance is improved.

Figure 6: The structure of the twin rotary compressor.
3.3 Scroll Compressor
Compared with the reciprocating compressor, the scroll compressor has the characteristics of 40% smaller volume, 15% lighter weight, 10% higher efficiency and lower noise. Its main components are only 5 while the reciprocating compressor has more than 30 main components.
Moreover, the scroll compressor has no suction valve and discharge valve, and the torque changes little during operation. The overall performance is better than that of the piston rotary compressor, but the processing precision is high, the shape is complicated, and the service life is not as good as the piston reciprocating compressor.

Figure 7: The structure of the scroll compressor.
3.4 Inverter Compressor
The inverter compressor is different from ordinary compressors, it can operate at high or low speed arbitrarily, so that the displacement of the compressor can be effectively changed and controlled.
This kind of compressor mostly adopts scroll compressor, twin rotary compressor, and also uses reciprocating type compressor. The motor coil is three-phase, and the adjustable frequency range is 30-130Hz.
4. How do You Know If the AC Compressor is Bad
What are the symptoms of a broken air conditioner compressor?
1. The main manifestation of compressor damage is that the air conditioner does not cool and cannot operate.
2. The circuit is damaged and the motor coil is short-circuited.
3. The noise and vibration of the compressor become louder, and the performance decreases.
If the compressor is damaged, it is difficult to see the problem just by looking at the appearance, so you need to open the outdoor unit and test the compressor to make an accurate judgment.
Related Info
Why is My Central AC Running but Not Blowing Air?Why is My AC Not Cooling? (Detailed Reasons and Solutions)
Why is My AC Freezing up? How to Fix [With Pictures]
Why is My AC Compressor Not Turning on and What to Do?
What is an AC Compressor? Everything You Need to Know


