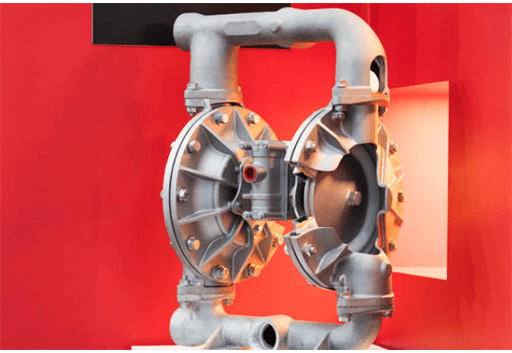
Figure 1: Diaphragm pump.
Diaphragm pump is a novel mechanical transportation equipment, which can absorb all kinds of corrosive liquids, liquids with particles, and liquids with high viscosity, volatile, flammable and highly toxic. Today, let's take a look at how it works.
1. Structure of Diaphragm Pump
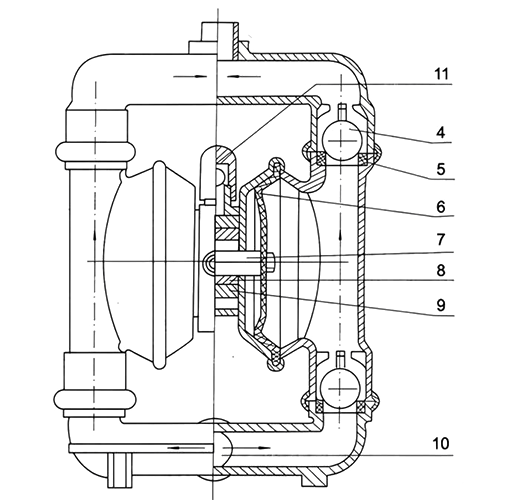
Figure 2: Structure of a diaphragm pump.
1 Air inlet 2 Valve body 3 Distribution valve 4 Valve Ball 5 Ball seat 6 Diaphragm 7 Connecting rod 8 Connecting rod copper sleeve 9 Intermediate support
10 Pump inlet 11 Exhaust port
2. Working Principle
The working principle of the pneumatic diaphragm pump is a positive displacement reciprocating pump that uses the air compressor to input compressed air into the air distribution valve of the diaphragm pump to drive the connecting shaft in the middle body of the diaphragm pump to drive the diaphragm in the medium chamber of the diaphragm pump body to make a horizontal stretching movement to achieve the effect of self-priming fluid. In the two symmetrical working chambers of the pump, each is equipped with an elastic diaphragm. The connecting rod integrates the two diaphragms. After compressed air enters the valve from the air inlet joint of the pump, it pushes the diaphragms in the two working chambers and drives the two diaphragms connected by the connecting rod to move synchronously. At the same time, the gas in the other working chamber is discharged out of the pump from the back of the diaphragm. Pneumatic diaphragm pump is composed of air flow structure and liquid flow structure, which are completely isolated by diaphragms on both sides.

Figure 3: How does it work.
The air supply pressure only needs to be greater than two kilograms per square centimeter to work. Under the working pressure of 5 to 8 kg, the high-pressure gas in the air valve chamber drives the connecting rod shaft to move back and forth through the air flow dredging system. At the same time, the consumed low-pressure gas is quickly discharged through the exhaust port. Under the alternating action of high and low pressure gases on both sides, the connecting rod shaft drives the diaphragms on both sides to move left and right, so that the air pressure in the volume chambers on both sides changes alternately, so as to realize the continuous suction and discharge of liquid.
The valve mechanism automatically introduces compressed air into another working chamber and pushes the diaphragm to move in the opposite direction, thus forming the synchronous reciprocating motion of the two diaphragms. Each working chamber is equipped with two one-way ball valves. The reciprocating motion of the diaphragm changes the volume of the working chamber, forcing the two one-way ball valves to open and close alternately, so as to continuously suck and discharge the liquid.
When the fluid passes through the diaphragm pump, the soft seal ball core and valve seat are opened and closed, which makes each outer diaphragm chamber fill and discharge alternately, and the ball core and valve seat respond to the passing pressure difference. And because of the soft sealing form of the ball core and valve seat, it can also pass through some fluids containing small particles.
3. Where can I use diaphragm pump?

Figure 4: Diaphragm pumps are common in many industries.
Diaphragm pumps are common in many industries. There are a large number of building materials that can be used to produce configurations to adapt to difficult fluids, such as:
1. Corrosive chemicals
2. Volatile solvent
3. Viscous liquid
4. Cutting sensitive food and pharmaceutical products
5. Dirty water and abrasive slurry
6. Smaller solids
7. Face cream, gel and grease
Related Info
What is Diaphragm PumpsCommon Types of Diaphragm Pump
What is a Gear Pump
Classification of Gear Pump


