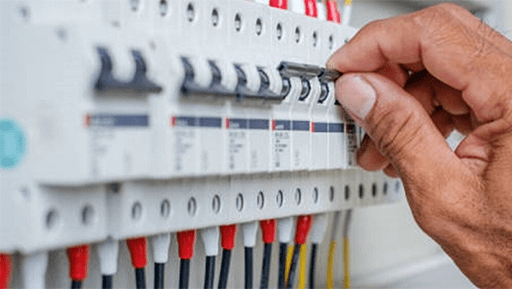
Figure 1: perating a circuit breaker.
The circuit breakers is a very common safety component in the circuit. It can break the circuit at the proper time to protect the circuit and other equipment. To better learn about how it works, we’d better figure out some key concepts.
Electric Arc
Electric arc, or arc discharge is a gas discharge phenomenon, an instantaneous spark created by the passage of an electric current through some insulating medium, such as air. An electric arc is a self-sustaining gas conduction (electrical conduction in an ionized gas) where most of its charge carriers are electrons generated by one-time electron emission.
Electrons escape from the metal surface of the contact due to one-time electron emission (thermionic emission, field emission or photoemission), and gas atoms or molecules in the gap will generate electrons and ions due to ionization (collision ionization, photoionization and thermal ionization).
In addition, bombardment of the emitting surface with electrons or ions can in turn cause second-time electron emission. When the ion concentration in the gap is large enough, the gap is electrically broken down and arcing occurs.

Figure 2: Electric arc generated during operation.
The electric arc is a free gas with high temperature and high conductivity, which not only has a great destructive effect on the contacts, but also prolongs the time of breaking the circuit.
When an electric arc occurs in the dynamic and static contacts of the circuit breaker, the electromagnetic thrust can blow the arc into the arc chute space. When the arc enters the arc extinguishing hood, an equal amount of near-cathode effect is formed immediately in these multiple intervals, coupled with the cooling of the arc gas on the metal sheet, and finally the arc is extinguished.
Electric Breakdown
The electrical breakdown is cause by the fact that the free electrons in the solid dielectric are accelerated in a strong electric field and accumulate a large kinetic energy. These kinetic energies are sufficient to disrupt the molecular structure of the medium. When a chain reaction of collision and dissociation occurs, a penetrating conductive channel will be generated in the dielectric, and the solid medium will lose its insulating properties, resulting in electrical breakdown.

Figure 3: Breakdown voltage in junction.
The characteristics of electrical breakdown are: the voltage action time is short; the breakdown field strength is closely related to the uniformity of the electric field, and has almost nothing to do with the ambient temperature.
Contact Clearance
Contact clearance, also called contact gap, refers to the minimum distance between the dynamic and static contacts of the switch/circuit breaker in the off position. With the improvement of the voltage level of the vacuum circuit breaker, the distance of the vacuum circuit breaker will increase accordingly to meet the requirements of dynamic and static insulation.

Figure 4: Electric breakdown experiment.
The purpose of the distance is to ensure that there is no electrical breakdown of the air between the dynamic and static contacts in the open state.
Related Info
4 Common Types of Circuit BreakersHow do Circuit Breakers Extinguish Electric Arc?
Top Circuit Breaker Brands
What are the Main Parameters of a Molded Case Circuit Breaker?
How to Calculate the Breaking Capacity?


