
Figure 1: Vane pump.
A vane pump is a self-priming positive displacement pump providing constant flow at varying pressures. Operation is via a motor connected to a gearbox as typically the maximum rpm is 900. The pump is fitted with a relief valve to prevent the pump from building to a pressure which may damage the pump.
The pump head contains a slotted rotor which contain vanes. The vanes create segmented chambers within the pump head, partitioning the pump head between the rotor and outer casing which enable the vane pump to be self-priming as the chambers operate similar to valves. Vane pump head with vanes in rotor.
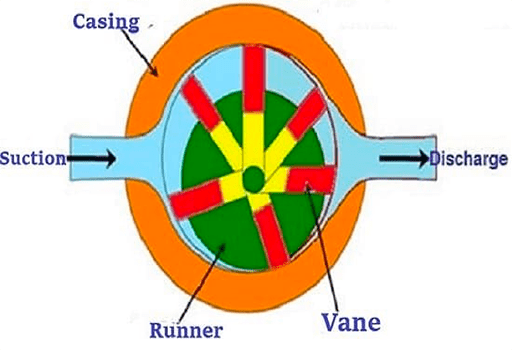
Figure 2: Structure of vane pump.
The pump head is circular for the most part but has a flat portion as the vanes move in and out of the main rotor. The vanes will push out towards the casing due to the centrifugal force when the pump is in operation with forces exerting outwards keeping the vanes tight against the casing. When the vanes reach the outlet of the pump the casing is flatter and tighter against the rotor causing the vane to be pushed into the rotor and the fluid to expel through the outlet of the pump.
2. How it Works

Figure 3: Working principle of the vane pump.
When the rotor of vane pump rotates, the tip of the vane is close to the inner surface of the stator under the action of centrifugal force and pressure oil. In this way, the working volume formed by the two blades, the rotor and the inner surface of the stator first absorbs oil from small to large, and then discharges oil from large to small. When the blades rotate for one cycle, they complete oil absorption and drainage once.
3. What are the Advantages of A Vane Pump?
Vane pumps are ideal for pumping low to medium viscosity liquids, including those with entrained gases, and can give an accurate, smooth, low pulsation output. With a varying feed pressure, a vane pump will continue to provide a constant flow. They are especially noted for their dry priming, ease of maintenance, and good suction characteristics over the lifetime of the pump. There is no internal metal-to-metal contact and the pumps self-compensate for wear through vane extension. Vane pumps can handle thin liquids at relatively high pressures and can run dry for short periods. They are also reversible so can be used to load and unload a vessel and also ensure liquid is fully recovered from delivery hoses.

Figure 4: Vane pumps of Okmarts.
4. What are the Disadvantages of A Vane Pump?
The efficiency of a vane pump decreases with increasing fluid viscosity so they are not suitable for high viscosity liquids. The maximum differential pressure for vane pump operation is about 15 bar. Flexible vane pumps can be used to pump liquids containing solids but sliding vane pumps are more suitable for clean liquids. Flexible vane pumps can be used with slurries but it may be necessary to limit pump speed to restrict wear. Vane pumps are prone to damaging wear when used with feeds containing abrasives and usually require protection by a suction-side filter.
Unless the pump uses a magnetic coupling, the drive will require a shaft seal of some type and this can be a source of leaks. Mechanically, vane pumps are complex with many parts but any maintenance to replace worn vanes or shaft seals is generally straightforward and inexpensive. As with most positive displacement pumps, some form of pressure relief is necessary in case of a downstream blockage. Vane pumps with multiple vanes will give essentially pulse-free flow but pulsation may be problem at low speeds with pumps fitted with only one or two vanes.
Related Info
How to Choose A Water PumpHow to Prime a Water Pump
Installation Knowledge of Water Pumps
4 Common Causes of Water Pump


