
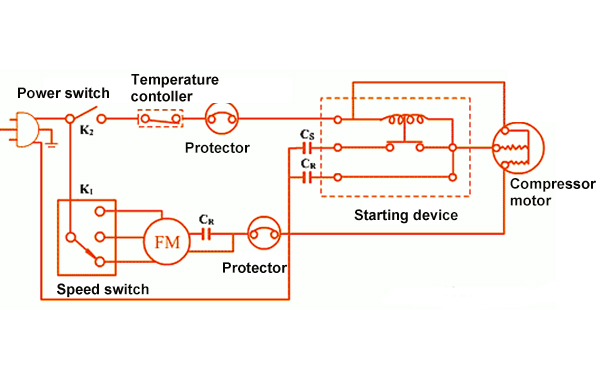
The compressor overheat protection is designed to prevent the motor from being damaged by high temperature. When the motor temperature or the compressor temperature itself exceeds a certain value, the compressor's power supply is disconnected through some built-in or external protection devices, thereby protecting the compressor.
After the refrigeration compressor sucks in low-temperature and low-pressure gaseous refrigerant from the system, the refrigerant directly enters the cavity of the compressor, first cools the motor, and then is compressed.
Therefore, the superheat degree of the sucked refrigerant vapor is an important factor in determining whether the compressor is overheated. Today we will analyze the reasons for triggering compressor overheating.
1. 6 Reasons for Triggering Compressor Thermal Overload Protection
1.1 Insufficient Refrigerant
Lack of refrigerant will reduce the amount of refrigerant supplied to the evaporator, causing the evaporation temperature to rise and the compressor to suck "high-temperature" refrigerant vapor, that is, the superheat degree increases. It in turn causes the motor coil to overheat and triggers overheat protection.
Especially in hot summer, the ambient temperature is high. If the system refrigerant is only slightly insufficient, it is difficult to judge based on the compressor current and system pressure alone, but it is easy to cause overcharging. At this time, the compressor discharge pipe temperature can be measured to evaluate whether the system is lacking refrigerant.
Under normal circumstances, this temperature should be about 20℃ higher than the saturation temperature at the corresponding discharge pressure. If it is lower than this value, there may be too much refrigerant, and if it is higher than this value, there may be insufficient refrigerant.
You can also measure the temperature of the compressor suction pipe. Under normal circumstances, this temperature should be about 7℃ higher than the saturation temperature at the corresponding suction pressure. If it is too high, it indicates that the suction superheat is too large and the refrigerant is insufficient.
See the table below. For example, if the actual high pressure you measured is 1.83MPa and the discharge temperature is 85℃, and then, we can see from the following table that the condensation temperature is 50°C, 85>50+20. If the system dissipates heat well, it means that the system lacks refrigerant.
|
Evaporation temperature ℃ |
-10 |
-5 |
0 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
|
Evaporation pressure MPa |
0.26 |
0.32 |
0.4 |
0.48 |
0.58 |
0.688 |
|
Condensation temperature ℃ |
35 |
40 |
45 |
50 |
55 |
60 |
|
Condensation pressure MPa |
1.22 |
1.396 |
1.62 |
1.83 |
2.06 |
2.31 |
1.2 Excessive Refrigerant
Excessive refrigerant causes the evaporation pressure and evaporation temperature, the overall pressure, and the compressor load to increase. In addition, it is difficult to dissipate heat in a high temperature environment, the current increases, and overheating protection is easily triggered.
Typical symptoms include:
● The outdoor unit has a high air outlet temperature.
● The indoor unit has uniform condensation but insufficient cooling.
● The thin tube valve has no cooling, and the thick tube valve is slightly cold.
● In the morning and evening, the operation is normal, but the thermal protection is prone to occur at noon.
● The voltage is normal, and the filter and external heat exchanger are very clean.

1.3 Dirty Condenser
Similarly, if the condenser is dirty, it will cause poor heat dissipation. The heat can not be taken away, and it will cause the pressure and the current to increase, finally triggering thermal protection.
A case of poor heat dissipation of the condenser:
For example, the outdoor unit of the air conditioner in a high-rise apartment is placed in a small place, which is blocked by the louvers to affect the heat dissipation. After communicating with the user, the louvers were removed, and the condensed water flowing out of the indoor unit was directed to the external heat exchanger to assist in heat dissipation. Then the overheating protection was not triggered again after more than an hour of operation.

1.4 Throttle Mechanism or System Blockage
The throttle mechanism such as the capillary tube is slightly blocked, which is similar to the capillary being lengthened. If the throttling effect is too strong, the high pressure will be higher, and the low pressure will be lower. The air blown out by the external fan is very hot, which alone proves that the high pressure is too high. Incomplete condensation of the evaporator is a specific manifestation of low evaporation pressure.
Typical manifestations include:
●Poor cooling effect.
●Incomplete condensation of the evaporator.
●Too hot air from the external heat exchanger.
●Originally the machine could barely work, but after adding some refrigerant, the compressor did not work at all.
1.5 Low Power Supply Voltage
Practice has shown that when the power supply voltage drops below 190V (taking 220V as a normal working power supply as an example), there will be system pressure problems -- the high pressure can't go up and the low pressure can't go down. This is equivalent to compressor blowby, which increases the specific volume of the refrigerant gas sucked by the compressor, causing the return gas superheat to increase to trigger thermal protection.
A case of thermal protection caused by low voltage:
For example, thermal protection occurs in multiple air conditioners in a certain area. When the machine is turned on, the voltage seems normal (210V), but after turning on other electrical appliances, the voltage drops sharply to below 190V, causing the air conditioner to fail to operate normally, and the compressor cannot start and is seriously damaged.

1.6 Problems with the Compressor Itself
Lack of oil: Lack of oil in the compressor leads to poor lubrication of mechanical parts, which is easy to cause thermal protection.
In addition, the following factors may also cause compressor overheating protection:
● Four-way valve leak: The compressor relies on low-temperature return gas for cooling. If the four-way valve leaks, it will cause the compressor to suck hot gas instead of cold gas, which will not only cool, but also increase the temperature, so inevitably triggering thermal protection.
● The speed of the external fan is too low, which is mostly caused by the decrease in the capacity of the external fan starting capacitor. Just replace the capacitor.
● The installation location is poorly ventilated and the ambient temperature is too high.


