
Figure 1: Solenoid Valve (Go to Okmarts and pick the solenoid valve you need.).
1. Working Principle of Direct Acting Solenoid Valve

Figure 2: Working principle of direct acting solenoid valve
When the power is on, the electromagnetic coil generates electromagnetic force to lift the closing part from the valve seat and open the valve; When the power is off, the electromagnetic force disappears, the spring presses the closing part on the valve seat, and the valve closes.
2. Working Principle of Distributed Direct Acting Solenoid Valve
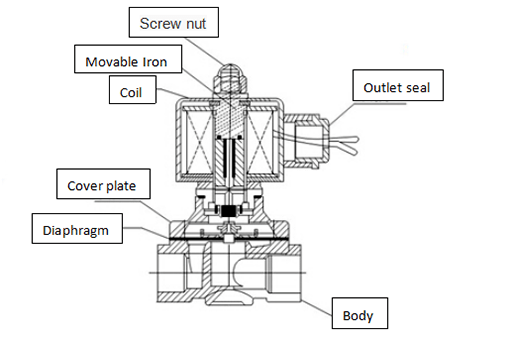
Figure 3: Working principle of distribured direct acting solenoid valve.
It is a combination of the working principle of direct acting solenoid valve and Pilot solenoid valve. When there is no pressure difference between the inlet and outlet, the electromagnetic force will directly open the pilot hole to connect with the main valve after power on. And the piston will lift up in turn and the valve will open; When the inlet and outlet reach the starting pressure difference, after power on, the electromagnetic force will first open the pilot hole, and the pressure in the upper chamber of the main valve piston will drop. So, it can use the pressure difference and electromagnetic force to pull the main piston and open the valve port; When the power is off, the pilot hole will be close by spring return, the upper chamber of the main piston will be pressurized, the main piston push downward, and the valve will be closed.
3. Working Principle of Pilot Solenoid Valve

Figure 4: Working principle of pilot solenoid valve.
When the power is on, the electromagnetic force will pull in the pilot hole spool, the pilot hole will open and the pressure in the upper chamber of the main valve piston will drop. Then, there is a high pressure between the upper chamber and the lower chamber of the main piston. The pressure in the lower chamber pushes the main piston to open the valve; When the power is off, the spring force returns and the pilot hole is closed, and the pressure in the upper chamber of the main piston increases. There is high and low pressure between the upper chamber and the lower chamber of the main piston. The medium pressure and spring force push the main piston and close the valve.
4. Working Principle of Diaphragm Solenoid Valve

Figure 5: Working principle of diaphragm solenoid valve.
When the power is on, the electromagnetic force opens the pilot hole. The pressure in the upper chamber drops rapidly forming a low and high differential pressure around the closing part. The fluid pressure pushes the closing part to move upward and the valve opens; When the power is off, the spring force closes the pilot hole, the inlet pressure quickly passes through the bypass hol, and the chamber forms a pressure difference between lower and upper around the valve closing part. The fluid pressure pushes the closing part to move downward to close the valve.
5. Working Principle of Piston Solenoid Valve

Figure 6: Working principle of piston solenoid valve.
After the iron core is energized, the auxiliary valve moves down due to the force of the iron core. The auxiliary valve is closed and the pressure in the main valve cup rises. When the pressure rises to a certain value, the difference between the upper and lower pressure of the main valve cup is the same. The action of electromagnetic force move the iron core to compress the main valve seat and close the valve. When the coil is powered off, the electromagnetic suction is zero. The auxiliary valve plug and supporting iron core are lifted upward due to the action of spring to open the auxiliary valve. The fluid on the main valve cup flows away through the auxiliary valve reducing the pressure acting on the main valve cup. When the pressure on the main valve cup decreases to a certain value, the differential pressure will push the main valve cup up openning the main valve.
Related Info
What is a contactorHow to test a contactor
How to judge the model of ac contactor


