
Figure 1: Heat pump dryer.
Clothes dryers are a convenient appliance that saves time and effort when it comes to doing laundry. However, traditional clothes dryers can be not very energy-efficient. A heat pump clothes dryer (heat pump dryer) is an innovative solution that offers several benefits over conventional dryers. In this article, we will explain how a heat pump dryer works, its pros and cons, and more.
1. What is a Heat Pump Dryer?
A heat pump clothes dryer is a type of clothes dryer that uses a heat pump to remove moisture from clothes. The heat pump system in a clothes dryer is similar to that of an air conditioner or refrigerator. The system consists of an evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve.
The refrigerant is circulated through these components to remove moisture from the air inside the dryer drum. The moisture is then condensed and collected in a drain, while the dry, warm air is circulated back into the drum to continue the drying process.

Figure 2: Perspective view of heat pump dryer.
2. How Does a Heat Pump Dryer Work?
The drying process is mainly composed of refrigerant circulation and air circulation.
Refrigerant cycle:
1. The compressor compresses the refrigerant into a high-temperature, high-pressure gaseous state. The gaseous refrigerant is condensed into a low-temperature, high-pressure liquid state through the condenser, and at the same time releases heat, and then reduces the pressure through the throttling element.
2. The low-temperature, low-pressure liquid refrigerant absorbs heat through the evaporator, becomes a gaseous refrigerant, and returns to the compressor for pressurization. Then the next cycle begins.
Air circulation:
1. The condenser heats the air, and the fan blows dry hot air into the drum from the back of the clothes dryer.
2. The dry hot air absorbs the moisture of the clothes, turns into humid air, passes through the filter, and returns to the heat pump evaporator. The evaporator absorbs heat and dehumidifies, so that the humid air cools down and condenses. Condensate drops to the bottom container and is pumped to the top condensate box (or the condensate water can be directly drained).
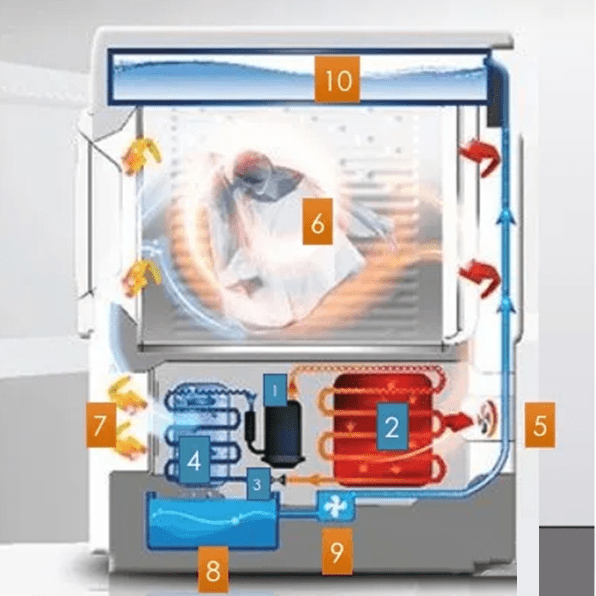
Figure 3: Working principle diagram of the heat pump dryer.
1-4 Refrigerant circulation, 5-10 Clothes drying
1. Compressor 2. Condenser 3. Capillary tube 4. Evaporator 5. Drying fan 6. Drying drum 7. Filter 8. Drain pan 9. Drain pump 10. Water tank
3. Heat Pump Dryer Pros and Cons
3.1 Pros of Using a Heat Pump Clothes Dryer
There are several benefits to using a heat pump clothes dryer, including:
1. Energy Efficiency
Heat pump clothes dryers are more energy-efficient than traditional clothes dryers. They use less energy to dry clothes, which can help to reduce your energy bills and lower your carbon footprint.
2. Cost Savings
Although heat pump clothes dryers may have a higher initial cost than traditional dryers, they can save you money in the long run. The energy savings can help to offset the initial cost of the dryer over time.
3. Improved Drying Performance
Heat pump clothes dryers are designed to dry clothes more gently and effectively than traditional dryers. They use lower temperatures and longer drying times, which can help to prevent shrinkage, color fading, and damage to delicate fabrics.
4. Reduced Wear and Tear on Clothes
Heat pump clothes dryers use lower temperatures and longer drying times, which can help to reduce wear and tear on clothes. This can help to extend the life of your clothes and reduce the need for frequent replacement.
5. Quieter Operation
Heat pump clothes dryers are typically quieter than traditional dryers, which can be a benefit for households where noise is a concern.
6. Environmentally Friendly
By using less energy, heat pump clothes dryers are more environmentally friendly than traditional dryers. They also produce less heat and moisture, which can help to reduce your home's humidity levels.

Figure 4: Heat pump dryer.
3.2 Cons of Heat Pump Dryer
While heat pump clothes dryers offer many benefits, there are also some potential downsides to consider. Below are some of the possible downsides of using a heat pump clothes dryer:
1. Higher Initial Cost: Heat pump clothes dryers can have a higher initial cost compared to traditional clothes dryers, which may be a barrier for some consumers.
2. Longer Drying Time: Heat pump clothes dryers typically take longer to dry clothes compared to traditional clothes dryers. This may be an inconvenience for some users who need their clothes dried quickly.
3. Requires Regular Maintenance: Heat pump clothes dryers require regular maintenance to ensure proper operation. This may include cleaning the lint filter, checking the drain hose, and inspecting the heat exchanger.
4. Limited Capacity: Some heat pump clothes dryers may have a smaller capacity compared to traditional dryers, which may not be suitable for larger households or families.
5. May Not Be Suitable for All Fabrics: Heat pump clothes dryers use lower temperatures and longer drying times, which may not be suitable for all fabrics. Some fabrics may require higher temperatures for effective drying.
6. May Not Work Well in High Humidity Environments: Heat pump clothes dryers may not work well in high humidity environments, as the moisture in the air can affect the efficiency of the heat pump system.

Figure 5: Heat pump dryer filter.
4. How to Choose Heat Pump Dryer for Your Home
Choosing a heat pump clothes dryer for your home requires careful consideration of several factors. Here are some tips to help you choose the right heat pump clothes dryer for your needs:
1. Capacity: Consider the size of your household and the amount of laundry you typically do. Choose a heat pump clothes dryer with a capacity that can accommodate your laundry needs.
2. Energy Efficiency: Look for a heat pump clothes dryer with a high energy efficiency rating, such as Energy Star certification. This will help you save money on your energy bills and reduce your carbon footprint.
3. Price: Consider your budget when choosing a heat pump clothes dryer. While heat pump clothes dryers can be more expensive than traditional dryers, they can save you money in the long run through reduced energy costs.
4. Drying Time: Consider how quickly you need your laundry to be dried. Heat pump clothes dryers typically take longer to dry clothes compared to traditional dryers. Choose a dryer with a drying time that meets your needs.

Figure 6: Washer + heat pump dryer combination set.
5. Maintenance: Consider the maintenance requirements of the dryer. Look for a heat pump clothes dryer with easy-to-access filters and other parts that can be easily cleaned and maintained.
6. Features: Consider the features that are important to you, such as a delay start timer, wrinkle prevention, and anti-static options. Choose a heat pump clothes dryer with features that meet your specific needs.
7. Brand Reputation: Consider the reputation of the brand and the reliability of the dryer. Look for reviews from other customers and choose a heat pump clothes dryer with a good reputation for quality and performance.
By considering these factors, you can choose a heat pump clothes dryer that meets your specific needs and requirements. It is important to do your research and choose a dryer that will provide reliable performance and energy efficiency for years to come.
Related Info
Industrial Water Chiller Repair: Troubleshooting and Maintenance TipsWater Chiller for Ice Bath Explained: Working Principle, Pros and Cons, Application
Water-Cooled Chiller vs Air-Cooled Chiller: Which One is Better?
Chilled Water System: Basics, Working Principle Diagram, Types and More
Types of Water Chillers (Chiller Basics, Condenser Type and Compressor Type)


