Figure 1: Refrigerated compressed air dryers.
If you work in an industry that requires compressed air, you know that moisture is a common problem. When compressed air is cooled, it can condense, leading to water droplets that can damage equipment, cause corrosion, and affect the quality of the final product. That's where refrigerated air dryers come in.
In this article, we'll explore everything you need to know about refrigerated air dryers, including how they work, their advantages and disadvantages, and how to choose the right one for your application.
1. What is a Refrigerated Air Dryer?
A refrigerated air dryer (refrigerated compressed air dryer, refrigerant dryer) is a device that removes moisture from compressed air by cooling it. The compressed air enters the dryer and passes through a heat exchanger, where it is cooled to a temperature where water vapor condenses into liquid water. The liquid water is then removed from the compressed air stream through a drain valve, leaving dry compressed air that can be used in a variety of applications.

Figure 2: A dryer in a compressed air system.
1.1 Components of Refrigerated Air Dryer
The refrigerated air dryer is referred to as the refrigerated dryer, and its refrigeration system belongs to compression refrigeration, which is composed of four basic components such as a refrigeration compressor, a condenser, an evaporator, and an expansion valve. They are connected in turn by pipes to form a sealed system, and the refrigerant circulates continuously in the system, changes state and exchanges heat with compressed air and cooling medium.
In order to achieve the purpose of compressed air drying and the goal of energy saving, a typical refrigerated air dryer has other components besides the refrigeration system, specifically:
1. Freezing and cooling part. It includes a precooler (an air to air heat exchanger), and an evaporator (an air to refrigerant liquid heat exchanger).
2. Gas-water separation and discharge part. It includes a gas-water separator and an automatic drain valve.
3. Refrigeration part. It includes a refrigeration compressor, condenser, evaporator, expansion valve, energy (cooling capacity) regulating valve, solenoid valve, pressure switch, pressure controller (moisture regulating valves), liquid storage tank, filter dryer, stop valve, etc.
4. Electrical part. It includes an operation switch, electromagnetic contactor, relay, compressor crankcase heater, control board, etc.
5. Instrument part. It includes inlet and outlet air pressure gauges, refrigerant pressure gauges, etc.
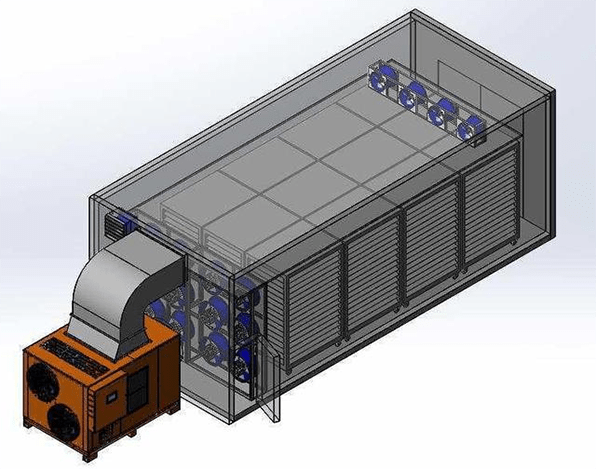
Figure 3: Refrigerated air dryer structure-min
2. How Does a Refrigerated Air Dryer Work?
Refrigerated air dryers work on the principle of cooling the compressed air to a temperature where water vapor condenses into liquid water. The compressed air enters the dryer and passes through a heat exchanger, where it is cooled by the refrigerant.
The cooled compressed air then enters a separator, where the liquid water is removed from the compressed air stream through a drain valve. After the liquid water is removed, the compressed air is reheated and exits the dryer as dry compressed air.
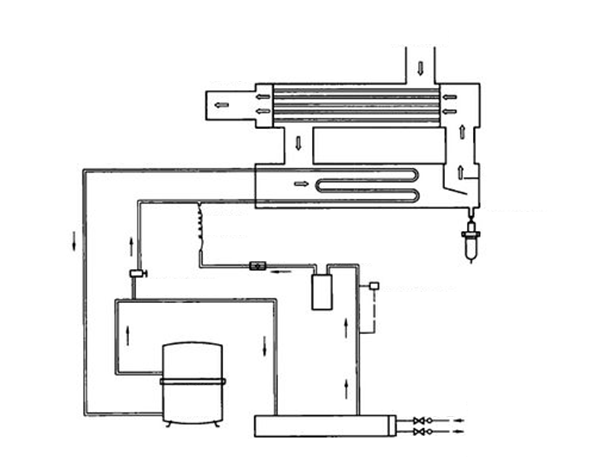
Figure 4: Working flow chart of refrigerated air dryer.
3. Refrigerated Air Dryer Pros and Cons
3.1 Advantages of Refrigerated Air Dryers
There are several advantages to using refrigerated air dryers in compressed air systems. Some of these advantages include:
1. Cost-effective: Refrigerated air dryers are generally less expensive than other types of air dryers, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications.
2. Easy to install and maintain: Refrigerated air dryers are relatively easy to install and maintain, making them a popular choice for many industries.
3. High efficiency: Refrigerated air dryers can remove up to 90% of the moisture in compressed air, making them a highly efficient solution for many applications.
4. Low energy consumption: Refrigerated air dryers use less energy than other types of air dryers, making them a more energy-efficient solution for many applications.

Figure 5: Refrigerated air dryer unit.
3.2 Disadvantages of Refrigerated Air Dryers
While there are many advantages to using refrigerated air dryers, there are also some disadvantages to consider. These disadvantages include:
1. Limited capacity: Refrigerated air dryers are typically limited in their capacity and may not be suitable for larger compressed air systems.
2. Temperature limitations: Refrigerated air dryers require a certain ambient temperature range to operate effectively, which may limit their use in some applications.
3. Limited dew point control: Refrigerated air dryers are not able to achieve the same low dew points as other types of air dryers, which may limit their use in some applications.
4. Choosing the Right Refrigerated Air Dryer
When choosing a refrigerated air dryer, there are several factors to consider, including:
1. Required dew point: Consider the dew point required for your application and make sure the refrigerated air dryer you choose is capable of achieving that dew point.
2. Capacity: Consider the capacity of your compressed air system and make sure the refrigerated air dryer you choose is suitable for your needs.
3. Ambient temperature range: Consider the ambient temperature range in which the refrigerated air dryer will be operating and make sure it is suitable for your application.
4. Maintenance requirements: Consider the maintenance requirements of the refrigerated air dryer and make sure they are feasible for your facility.
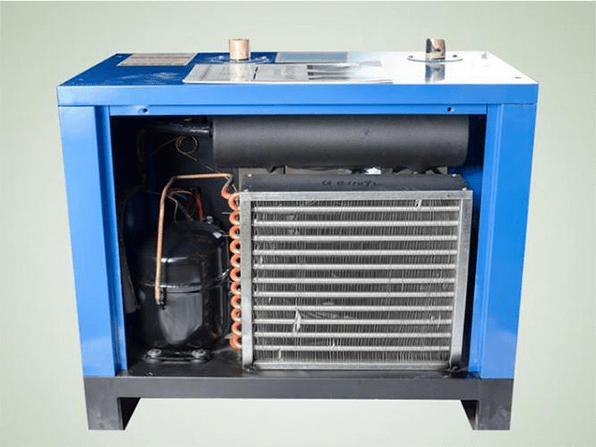
Figure 6: Cutaway view of refrigerated air dryer.
5. FAQs
5.1 What is a Refrigerated Air Dryer Used for?
A refrigerated air dryer is a device used to remove moisture from compressed air by cooling it to a temperature where the water vapor condenses into liquid form and can be removed from the air stream. This process is important because moisture in compressed air can cause damage to equipment and compromise the quality of the end product.
Refrigerated air dryers are commonly used in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and electronics manufacturing, where dry air is required for production processes. They are also used in compressed air systems for pneumatic tools and equipment to prevent corrosion and rust.
5.2 How Does a Compressed Air Dryer Work?
There are different types of compressed air dryers, including refrigerated, desiccant, and membrane dryers, each using different methods to achieve the same goal of removing moisture from compressed air. Refrigerated dryers use a refrigeration system to cool the air, while desiccant dryers use a material that absorbs moisture from the air, and membrane dryers use a selective permeation process to separate water vapor from the air.

Figure 7: Desiccant dryer.
5.3 How to Install Air Dryer for Compressed Air?
Installing an air dryer for compressed air (taking the refrigerated air dryer as an example) involves a few key steps:
1. Choose the right type of air dryer for your application based on factors such as the required flow rate, pressure, and dew point.
2. Install the dryer as close to the point of use as possible to minimize the length of the compressed air line and reduce the potential for moisture to re-enter the air stream.
3. Install a pre-filter before the air dryer to remove any large particles or contaminants that could damage the dryer.
4. Install a drain valve after the air dryer to remove any condensed moisture from the air stream.
5. Connect the air dryer to the compressed air system and ensure there are no leaks.
6. Turn on the compressed air system and verify that the air dryer is functioning properly and providing the required level of dew point.

Figure 8: Refrigerated air dryer connection system.
5.4 Why Does Compressed Air Require a Dryer?
Compressed air requires a dryer because the process of compressing air causes the moisture present in the air to condense. This moisture can cause corrosion, rust, and damage to equipment and products in various manufacturing processes. Moisture in compressed air can also lead to the growth of bacteria and other contaminants, which can be harmful to the end product or even cause health hazards.
A dryer removes the moisture from the compressed air by cooling it and condensing the water vapor, preventing these issues and ensuring the air is clean and dry for use in various applications.
6. Conclusion
Refrigerated air dryers are a cost-effective and efficient solution for removing moisture from compressed air. While they have some limitations, they are a popular choice for many industries due to their ease of installation and maintenance, high efficiency, and low energy consumption. When choosing a refrigerated air dryer, it is important to consider factors such as the required dew point, capacity, ambient temperature range, and maintenance requirements to ensure that you choose the right dryer for your application.
Related Info
Industrial Water Chiller Repair: Troubleshooting and Maintenance TipsWater Chiller for Ice Bath Explained: Working Principle, Pros and Cons, Application
Heat Pump Clothes Dryer: Everything You Need to Know
Dryer Heat Pump vs Condenser: Which One Should You Choose?
Industrial Heat Pump Dryer: Everything You Need to Know


