
Figure 1: Different types of air cylinder.
1. Installation of Air Cylinder
Since the piston in the cylinder barrel makes a linear reciprocating motion, the installation form of the cylinder should be determined in accordance with the direction of the load movement.
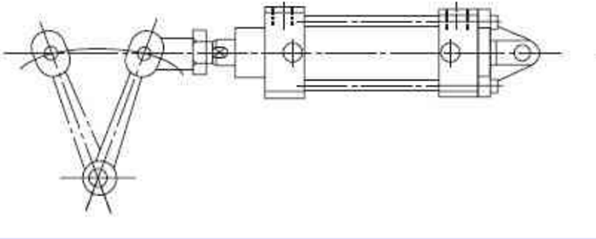
Figure 2: The installation demonstration of air cylinder.
When the direction of load movement is not parallel to the axis of piston rod, the rod or cylinder may become dislocated, causing sintering or breakage. Therefore, the axis of the piston rod must be aligned with the direction of load movement. If it really can't be adjusted, please use a cardan joint.
When the direction of load movement of the load changes with the motions, please use a swing cylinder (earring type, pin roll type) that can rotate a certain angle by itself. In addition, during installation, the metal connector (connector) at the front of the piston rod should also move in the same direction as the movement direction of the air cylinder.
1.1 Types of Installation
There are many ways to install the cylinder. According to whether the air cylinder can be moved after installation, it can be briefly divided into fixed type and swing type. Generally speaking, the same cylinder has multiple installation forms. Taking SC standard air cylinder as an example, there are free type, flange type, tripod type, earring type and middle swing type.
The earring type installation, divided into single ear type and double ear type, means that the cylinder end cover and the earring type installation accessories are fixed together with screws at the rear end cover of the SC standard cylinder series, and the vertical direction of the piston rod axis is provided with air cylinder with a shaft pin, and the load and the cylinder can swing around the shaft pin. During fast action, the larger the swing angle, the greater the lateral load on the piston rod.
Free type installation means fixed installation in which the threads in the cylinder body are screwed into the machine body without using installation accessories; Or the cylinder is fixed on the machine with nuts by using the threads outside the cylinder body; It can also be fixed on the machine with screws through the screw hole of the end cover.
Tripod type installation, expressed in LB, refers to refers to using a L-shaped mounting tripod with the screw holes at front end cover to install and fix with screws. The mounting tripod can bear large overturning moment and can be used in occasions where the direction of load movement is aligned with the axis of the piston rod.
The middle-swing type installation is to install the TC middle-swing in the middle of the cylinder to complete the installation and fixation of the cylinder. The cylinder under this installation method can swing around the middle trunnion and is suitable for long cylinders.
Flange type installation can be divided into front flange and rear flange.The former uses flanges and screws to fix the cylinder at the front end cover, while the latter uses flange and screws tic the cylinder at the rear end cover. It is also suitable for the occasions where the load movement direction is aligned with the axis of the piston rod.

Figure 3: There are five installation types of air cylinder shown in the figure.
2. How to Identify Whether the Air Cylinder Is Broken

Figure 4: Check whether the air cylinder is in good conddition by blocking the hole.
2.1 Air Cylinder in Good Condition
Block the air hole tightly, and then pull the piston shaft with your hand. There is a great reverse force when pulling, and the piston will automatically spring back to its original position when it is released; there is a large reverse force as well, when pressing push rod with your hands, and pull out the push rod, and then block the air hole. The piston will automatically spring back to its original position when it is released.
2.2 Air Cylinder in Bad Condition
There is no resistance or very little force when pulled. The piston has no movement or is weak and slow when released. There is a reverse force when pulled out but gradually decreases when pulled continuously. There is no pressure or very little pressure when pressed, or there is pressure, but the more you press, the little the pressure is.
3. Maintenance of Air Cylinder
The cylinder is a pneumatic actuator and a vulnerable component. When it is used for a period of time, there will be different faults such as air leakage, cylinder biting, buffer failure, etc. In order to address such problems, it is particularly important to maintain the air cylinder.
3.1 Piston Maintenance
The piston of air cylinder generates thrust under the action of air pressure and slides in the cylinder barrel, and therefore it is required that the piston have good sliding characteristics and good sealing between the piston and cylinder barrel. The sealing between the piston and the cylinder barrel is realized through the Yx sealing ring. And therefore, the Yx sealing ring is a vulnerable part.
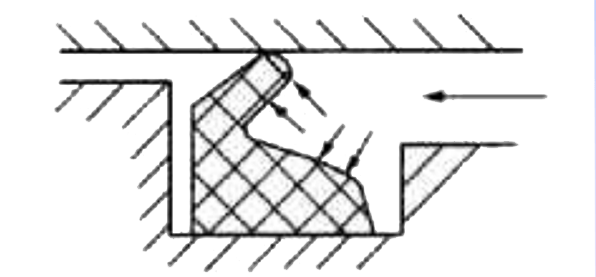
Figure 5: The structure of Yx sealing ring.
The section of the Yx-shaped sealing ring has two lips of unequal foot length. The sealing ring is installed in the groove of the piston in which when the right side is subjected to air pressure, the lip of the sealing ring opens under the action of air pressure and closely adheres to the cylinder wall, achieving sealing. After the cylinder disassembly, please pay attention to observation. If it is found that the lips of the Yx-shaped sealing ring have been worn down, it should be removed from the piston, replaced with a new one, and greased. The buffer plunger is in frequent friction with the cylinder head and it is necessary be greased.
3.2 Cylinder Head Maintenance
When the cylinder is working, the piston will hit the cylinder head, and the buffer sealing ring of the cylinder head is a vulnerable part. If the buffer sealing ring is seriously damaged, the buffer plunger and the buffer sealing ring will not be well sealed before the end of the cylinder stroke, thereby losing the buffering effect. If the cylinder is used for a long run, the sealing ring shall be replaced and greased at the same time. The cylinder head buffer is an easily forgotten corner. Here, when unscrewing the buffer throttle valve, carefully clean the buffer exhaust hole with a thin wire (be careful not to damage the throttle valve thread). Otherwise, the buffer exhaust hole will be blocked, which may cause the piston rod not to be in its original place.
3.3 Cylinder Barrel Maintenance
Apply grease on the inner wall of the cylinder barrel, install the piston rod, and push and pull several times by hand to ensure the lubrication and sealing performance between the cylinder barrel and the piston.

Figure 6: Different types and models of air cylinder barrel.
4. Notices for Air Cylinder Maintenance
After disassembly, the first thing to do is to rinse the cylinder barrel, the piston, the piston rod, and cylinder head to remove rust, dirt, and ash on the surface.
Applied grease ingredients have little solid additives.
The sealing material are contingent on the working conditions, preferably PTFE (plastic king), which has a small friction coefficient (about 0.04), is corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant, and can work within the temperature range of -80°C to +200°C.

Figure 7: The PTEF material for cylinder piston sealing ring.
Take heed of the direction when installing Yx-shaped sealing ring.
Related Info
Types and Characteristics of Common Air CylindersWorking Principle of Butterfly Valve and Emergence of New Butterfly Valve
Classification of Butterfly Valve
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Butterfly Valve and Its Installation and Maintenance
Common Problems and Causes of Gearboxes


