
Variable Valve Timing (VVT) technology has revolutionized the way modern internal combustion engines operate, providing a balance between performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. At the heart of this innovation lies the Variable Valve Timing (VVT) solenoid, a critical component that plays a pivotal role in optimizing engine performance. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into everything you need to know about the VVT solenoid, from its functionality to its location within the engine.
1. What is Engine Variable Valve Timing (VVT) Solenoid?
Before understanding the intricacies of a VVT solenoid, it's essential to grasp the concept of Variable Valve Timing (VVT) itself. Traditional internal combustion engines employ a fixed valve timing mechanism, where the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves are determined by the camshaft profile. However, VVT technology introduces dynamic adjustability to this process, allowing for optimal valve timing based on various driving conditions.
The VVT solenoid is a vital component within the Variable Valve Timing system. It serves as the control unit responsible for regulating the flow of oil to the VVT actuator, which, in turn, adjusts the position of the camshaft. By altering the camshaft's timing relative to the crankshaft, the VVT solenoid enables precise control over valve timing, optimizing engine performance across a wide range of operating conditions.
2. How Does a VVT Solenoid Work?
The operation of a VVT solenoid is contingent upon a complex interplay of mechanical and electrical systems within the engine. Here's a breakdown of how it works:
Electronic Control: The VVT solenoid is electronically controlled by the Engine Control Module (ECM) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM), which continuously monitors various sensor inputs such as engine speed, load, and throttle position.
Oil Flow Regulation: The VVT solenoid governs the flow of engine oil to the VVT actuator, which is typically located near the camshaft. By controlling the flow of oil, the solenoid can advance or retard the position of the camshaft, thereby adjusting valve timing.
Timing Adjustment: Depending on driving conditions, the ECM or PCM sends signals to the VVT solenoid, instructing it to either advance or retard the camshaft timing. Advancing the timing results in earlier valve opening and closing, enhancing low-end torque and responsiveness. Conversely, retarding the timing optimizes high-end power output.
Optimized Performance: Through precise control over valve timing, the VVT solenoid ensures that the engine operates at peak efficiency across a spectrum of driving scenarios. Whether it's cruising on the highway or accelerating from a standstill, the VVT system adjusts valve timing to deliver optimal performance and fuel economy.
 solenoid-min.png)
3. What Does a Variable Valve Timing Solenoid Do?
The Variable Valve Timing solenoid fulfills several critical functions within the engine, contributing to its overall performance and efficiency. Here are some key roles of the VVT solenoid:
Optimizing Valve Timing: The primary function of the VVT solenoid is to regulate the timing of valve operation by adjusting the position of the camshaft. By optimizing valve timing, the solenoid ensures that the engine operates efficiently across varying load and speed conditions.
Enhancing Performance: By dynamically adjusting valve timing, the VVT solenoid enhances engine performance by maximizing power output and torque delivery. Whether it's accelerating from a stoplight or towing heavy loads, the VVT system optimizes valve timing to meet the demands of the driver.
Improving Fuel Efficiency: Efficient valve timing not only boosts performance but also improves fuel efficiency. By optimizing the combustion process, the VVT solenoid helps reduce fuel consumption, leading to savings at the pump and lower emissions.
Reducing Emissions: In addition to improving performance and fuel efficiency, the VVT solenoid also plays a role in reducing harmful emissions. By ensuring that the engine operates at its most efficient state, the VVT system helps minimize the production of pollutants such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
4. Where is the Variable Valve Timing Solenoid Located? Variable Valve Timing Solenoid Location
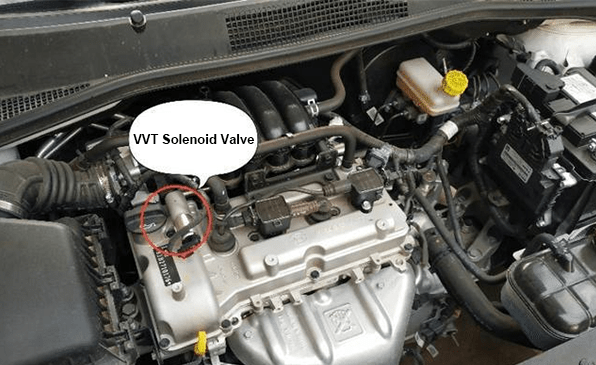
The location of the Variable Valve Timing solenoid varies depending on the engine's design and configuration. However, it is typically situated near the camshaft or cylinder head, in close proximity to the VVT actuator. In most modern engines, the VVT solenoid can be found either on the cylinder head itself or adjacent to the camshaft housing.
Accessing the VVT solenoid for inspection or replacement may require removing certain engine components, such as the intake manifold or valve cover. It's essential to consult the vehicle's service manual or seek professional assistance when performing maintenance tasks involving the VVT solenoid.
5. Conclusion
The Variable Valve Timing (VVT) solenoid is a crucial component within modern internal combustion engines, facilitating dynamic control over valve timing for optimized performance and efficiency. By regulating the flow of oil to the VVT actuator, the solenoid enables precise adjustments to the camshaft position, ensuring that the engine operates at its peak across a spectrum of driving conditions.
Understanding the role and functionality of the VVT solenoid is essential for maintaining and maximizing the performance of today's advanced automotive engines.


