Figure 1: Air source heat pump.
An inverter heat pump is a type of HVAC system that uses advanced technology to provide efficient heating and cooling for residential and commercial spaces. Unlike traditional HVAC systems, which operate at a fixed speed, inverter heat pumps can vary their output to match the exact requirements of your space.
In this article, we'll explore the ins and outs of inverter heat pumps, how they work, and the benefits they offer.
1. What is an Inverter Heat Pump?
An inverter heat pump is a type of heating and cooling system that utilizes an inverter to control the compressor's speed to regulate the temperature in your home or business.
Unlike traditional heat pumps, which use a fixed speed compressor that turns on and off as needed, inverter heat pumps are designed to operate continuously at varying speeds. This means that they can adjust their output to match the heating or cooling needs of your home, rather than simply turning on and off in response to temperature changes.
1.1 Heat Pump Inverter Technology
The key technology behind an inverter heat pump is the heat pump inverter. This is a device that converts the incoming AC power to DC power, and then back to AC power at a variable frequency and voltage.
The inverter controls the speed of the compressor motor by varying the frequency and voltage of the AC power. By doing so, the inverter can adjust the output of the heat pump to match the heating or cooling needs of the space.
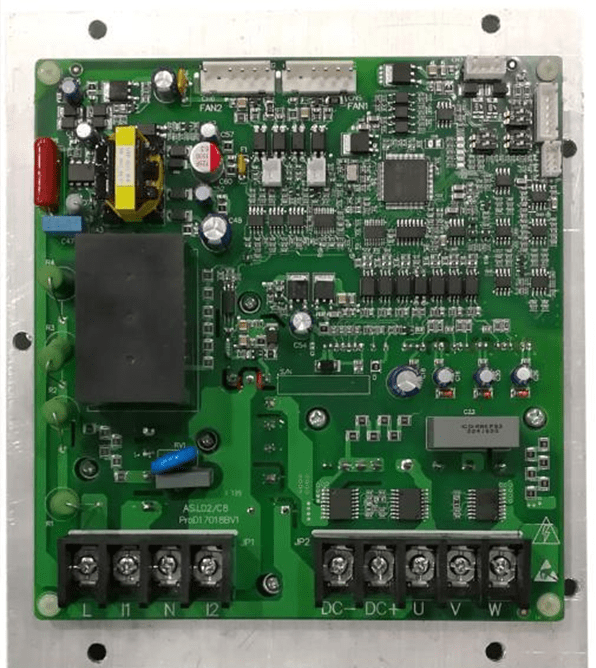
Figure 2: Driver board.
1.2 Inverter Heat Pump System
An inverter heat pump system consists of several components, including the inverter, compressor, heat exchanger, expansion valve, and refrigerant.
The compressor is responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas to increase its temperature. It operates at a variable speed controlled by an inverter to match the heating or cooling needs of your space.
The heat exchanger transfers heat between the indoor and outdoor environments.
The expansion valve controls the flow of refrigerant through the system. It is responsible for reducing the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant as it moves through the evaporator.
The refrigerant is a substance that absorbs and releases heat as it moves through the system. It is compressed and expanded as it moves through the compressor and the expansion valve, and it undergoes phase changes as it moves between the indoor and outdoor environments.
Together, these components work to provide precise temperature control and energy efficiency in an inverter heat pump system.
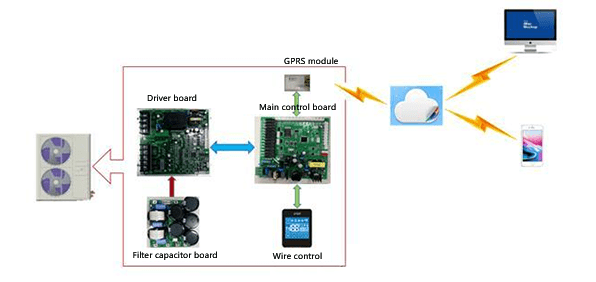
Figure 3: Heat pump inverter electric control assembly system block diagram.
2. How Does an Inverter Heat Pump Work?
The core component of an inverter heat pump is the inverter itself. When the inverter heat pump receives a signal from the thermostat indicating the need for heating or cooling, it activates the compressor. The inverter regulates the speed of the compressor motor by altering the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to the compressor.
When the temperature in your home or business is close to the desired temperature, the compressor operates at a lower speed. As the temperature deviates from the desired temperature, the compressor speeds up or slows down to adjust the output of the heat pump.

Figure 4: Ultra-low temperature inverter heat pump system.
3. Benefits of Inverter Heat Pumps
There are several benefits to choosing an inverter heat pump over other heating and cooling systems. Some of the most significant benefits include:
1. Energy Efficiency: Inverter heat pumps are much more energy-efficient than traditional heat pumps. Because they can adjust their output to match the heating or cooling needs of your space, they use less energy overall. This can translate into significant energy savings and lower utility bills over time.
2. Cost-Effectiveness: Although inverter heat pumps can be more expensive to purchase and install than traditional heat pumps, they can provide significant cost savings over time. Because they use less energy, they can help reduce your energy bills and pay for themselves over the lifespan of the system.
3. Enhanced Comfort: Inverter heat pumps provide more precise temperature control than other systems. This means that they can maintain a more consistent temperature throughout your space, even in extreme weather conditions. This can result in enhanced comfort and fewer hot or cold spots.
4. Quieter Operation: Inverter heat pumps operate more quietly than other systems. Because they do not need to turn on and off as frequently, they produce less noise overall. This can be especially important if you have a sensitive or noise-averse household.
5. Longer Lifespan: Inverter heat pumps are designed to operate continuously at varying speeds. This means that they experience less wear and tear than other systems, which can result in a longer lifespan overall. This can translate into lower maintenance costs and greater peace of mind.
6. Eco-Friendly Solution: Inverter heat pumps are considered environmentally friendly due to their energy-efficient performance. By consuming less electricity, these systems help reduce carbon emissions and contribute to a greener future.
Figure 5: Daikin heat pump.
4. Are Inverter Heat Pumps Better?
Inverter heat pumps are generally considered to be better than traditional heat pumps in terms of energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and comfort. Inverter heat pumps use a variable speed compressor that adjusts its output to match the heating or cooling needs of your space.
This results in more precise temperature control, greater energy efficiency, and improved comfort. While inverter heat pumps can be more expensive to purchase and install than traditional heat pumps, they can provide significant cost savings over time and a longer lifespan overall.
5. Is an Inverter Heat Pump Right for You?
Inverter heat pumps are an excellent choice for residential and commercial spaces seeking energy efficiency, enhanced comfort, and long-term cost savings. However, it's essential to consider certain factors before deciding if an inverter heat pump is right for your needs.
1. Climate: Inverter heat pumps perform exceptionally well in moderate climates. If you live in an area with extreme temperatures, such as very hot summers or extremely cold winters, it's important to consult with an HVAC professional who can assess whether an inverter heat pump can effectively meet your heating and cooling requirements.

Figure 6: Heat pump in winter.
2. Initial Investment: Inverter heat pumps typically have a higher upfront cost compared to traditional HVAC systems. However, the energy savings over time can offset this initial investment. Consider your long-term goals and budget when deciding if an inverter heat pump is a suitable option for you.
3. Existing Ductwork: If you already have ductwork in place, it may be more cost-effective to install an inverter heat pump as a replacement for your existing HVAC system. However, inverter heat pumps can also be installed in spaces without ductwork, utilizing a ductless mini-split system.
Related Info
Ducted Heat Pumps: Everything You Need to KnowHow Does a Ductless Heat Pump Work? A Comprehensive Guide
Ducted vs Ductless Heat Pump: Which One is Right for You?
Variable Speed Heat Pump: The Efficient Way to Heat and Cool Your Home
Heat Pump vs Conventional HVAC: Which is Better for Your Home?














