
Figure 1: LG central AC compressor.
Do you know the working principles, advantages and disadvantages of piston compressors, rolling piston compressors, scroll compressors, screw compressors and centrifugal compressors for central air conditioning? This article will explain these 5 refrigeration compressors in detail.
1. Piston Compressor
1.1 Working Principle of Piston Compressor
When the crankshaft of the piston compressor (reciprocating compressor) rotates, the piston will reciprocate through the transmission of the connecting rod, and the working volume composed of the inner wall of the cylinder, the cylinder head and the top surface of the piston will change periodically.
When the piston starts to move from the cylinder head, the working volume in the cylinder gradually increases. At this time, the gas enters the cylinder along the intake pipe and pushes the intake valve until the working volume reaches the maximum. Then the intake valve will be closed.
When the piston moves in reverse, the working volume in the cylinder decreases and the gas pressure increases. When the pressure in the cylinder reaches and is slightly higher than the exhaust pressure, the exhaust valve opens and the gas is discharged from the cylinder until the piston moves to the limit position. Then the exhaust valve is closed.
In short, the crankshaft of the piston compressor rotates once, the piston reciprocates once, and the process of gas intake, compression, and exhaust is successively realized in the cylinder, that is, a working cycle is completed.
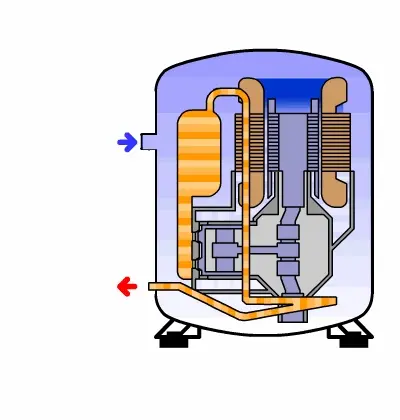
Figure 2: Piston compressor GIF.
1.2 Advantages of Piston Compressor
(1) Regardless of the flow rate, the required pressure can be obtained. The exhaust pressure range is wide, and the high pressure can reach 320MPa (industrial application), or even 700MPa, (laboratory application).
(2) In the general pressure range, the requirements for materials are low. Ordinary steel materials are mostly used, and they are easier to process and lower in cost.
(3) It can adapt to a wide pressure range and cooling capacity requirements.
(4) The gravity and characteristics of the gas have little effect on the working performance of the compressor, and the same compressor can be used for different gases.
(5) Piston compressors are relatively mature in technology and rich experience in production and use have been accumulated.
1.3 Disadvantages of Piston Compressor
(1) The structure is complex and heavy, with many wearing parts, large floor area, high investment, heavy maintenance workload, and short service life.
(2) The speed is not high, and the displacement of a single compressor is generally less than 500m³/min.
(3) There is vibration during the operation of the compressor.
(4) Discontinuous exhaust and pulsating gas flow can easily cause pipeline vibration. In severe cases, the pipe network or parts are often damaged due to air pulsation and resonance.
(5) The flow adjustment adopts an auxiliary volume or a bypass valve. Although it is simple, convenient and reliable, the power loss is large.
(6) For oil-lubricated compressors, the oil in the gas needs to be removed.
2. Rolling Piston Compressor
2.1 Working Principle of Rolling Piston Compressor

Figure 3: Rotary piston compressor.
The rolling piston compressor is a rotary compressor. The change of the working volume of the cylinder is realized by the rolling of an eccentrically placed cylindrical piston in the cylinder.
When the piston rotates once, it will complete the compression and exhaust process of the previous working cycle and the suction process of the next working cycle.
Because there is no intake valve, there is a strict corresponding relationship between the timing of the start of suction and the position of the suction hole on the cylinder, which does not change with the change of working conditions.
Because of the arrangement of the exhaust valve, the timing of the end of compression will vary with the pressure in the exhaust pipe.
2.2 Advantages of Rolling Piston Compressor
This type of compressor is also widely used in household refrigerators and air conditioners today. Its advantages are:
(1) Simple structure, small volume, and light weight. Compared with piston compressors, the size can be reduced by 40% to 50%, and the weight can also be reduced by 40% to 50%.
(2) There are few parts, especially less wearing parts, and at the same time, the friction loss between relative moving parts is small, so the reliability is high.
(3) Only the sliding vane has a small reciprocating inertial force, and the rotational inertial force can be completely balanced. The speed can be high, the vibration is small, and the operation is stable.
(4) There is no suction valve, the suction time is long, the clearance volume is small, and direct suction reduces the harmful overheating of suction, so its efficiency is high.

Figure 4: Rolling piston compressor GIF.
2.3 Disadvantages of Rolling Piston Compressor
The main disadvantage of the rotary compressor is that the leakage, friction and wear between the sliding vane and the cylinder wall are large, which limits its working life and efficiency improvement. And this kind of compressor requires high machining accuracy.
Once this kind of compressor wears out on its bearing, main shaft, roller or slide vane, and the gap increases, it will immediately have a more obvious adverse effect on its performance, so it is usually used in refrigerators and air conditioners assembled in factories. Besides, the system also requires a high degree of cleanliness.
3. Scroll Compressor
3.1 Working Principle of Scroll Compressor
The main components in the scroll compressor are two involute scrolls with the same shape but staggered by 180° relative to each other. One is a fixed scroll, and the other is an orbiting scroll driven by an eccentric shaft, and its axis revolves around the fixed scroll axis.
During work, the two scrolls form multiple sealing lines tangentially, plus the proper sealing at the end faces of the two scrolls, and several crescent-shaped air cavities are formed.
The sealing lines at the common tangent point between the two scrolls are continuously shifted along the vortex curve as the orbiting scrolls orbit, so that the shape and size of these crescent-shaped air cavities are always changing.
As these peripheral crescent-shaped air chambers are closed and no longer communicated with the suction chamber, their closed volume is gradually transferred to the center of the fixed scroll and shrinks continuously, and the gas is continuously compressed and the pressure increases.

Figure 5: Scroll compressor GIF.
3.2 Advantages of Scroll Compressor
From the specific structure point of view, the scroll compressor has no suction and discharge valves, which greatly improves the reliability of high-speed operation. Taken together, the scroll compressor has the following main features:
(1) It belongs to the third generation compressor, and multiple compression chambers work at the same time. The gas pressure difference between adjacent compression chambers is small, the gas leakage is small, and the volumetric efficiency is high, up to 98%. Its efficiency is higher than that of the second generation compressor, rolling piston compressor is about 5% higher.
(2) The force change of moving parts such as the orbiting scroll and the main shaft is small, and the vibration of the whole machine is small.
(3) The scroll compressor operates reliably, and is especially suitable for variable speed movement and frequency conversion speed regulation technology.
(4) The noise of the scroll compressor is very low.
(5) The scroll compressor has reliable and effective sealing, so its refrigeration coefficient does not decrease with the increase of running time, but slightly increases.
(6) The scroll compressor has good working characteristics, and its performance is mainly affected by its own compression ratio and suction pressure. The discharge pressure range is wide, and it is suitable for various indoor and outdoor environments, ensuring that the compressor is always running at a high energy efficiency ratio, so as to ensure the energy efficiency ratio of the air conditioning unit.
(7) The moment of force change is small, the balance is high, the vibration is small, and the operation is stable, so the operation is simple and easy to realize automation.
(8) Because it has few moving parts and no reciprocating mechanism, it has simple structure, small size, light weight, few parts (especially less wearing parts), high reliability, and a service life of more than 20 years.

Figure 6: The fixed and orbiting scrolls.
3.3 Scroll Compressor Disadvantages
(1) The surface of its moving parts is mostly in the shape of a curved surface. The processing and inspection of these curved surfaces are more complicated. The manufacturing requires high-precision processing equipment and advanced aligning technology, so the manufacturing cost is relatively high.
(2) Between the moving parts or between the moving parts and the fixed parts, certain movement clearances are often maintained to achieve sealing, and the gas passing through the clearance will inevitably cause leakage, which limits the rotary compressor to achieve a high compression ratio. Therefore, most rotary compressors are mostly used in air-conditioning conditions.
4. Screw Compressor
4.1 Working Principle of Screw Compressor
The screw compressor sucks in the refrigerant through the tooth-shaped space formed by the meshing of the male rotor and the female rotor, and compresses the refrigerant to a predetermined pressure by reducing the tooth-shaped space. The working process of the screw compressor is as follows:

Figure 7: Twin screw compressor GIF.
Suction
The refrigerant is sucked in from the suction port. As the rotor rotates, the refrigerant is sucked into the tooth-shaped space.
Compression
The meshing of the tooth profile starts from the suction side of the tooth groove, and the sealing line gradually advances to the discharge side, and the tooth-shaped space is reduced and compressed.
The lubricating oil sucked together with the refrigerant forms an oil film seal in the rotor clearance and lubricates the rotor at the same time.
Discharge
When the tooth-shaped space is connected with the discharge port, the discharge stroke starts. This stroke continues until the refrigerant in the tooth-shaped space is completely discharged out.
4.2 Advantages of Screw Compressor
(1) Fewer parts and wearing parts, high reliability, easy operation and maintenance.
(2) There is no unbalanced inertial force. The operation is stable and safe, and the vibration is small.
(3) It has the characteristics of forced gas transmission, the displacement is almost not affected by the exhaust pressure, and the adaptability to working conditions is strong.
(4) The rotor tooth surface of the screw compressor actually has clearances. Therefore, it is not sensitive to wet strokes and can withstand liquid slugging.
(5) The exhaust temperature is low, and it can operate under the condition of higher pressure ratio.
(6) It adopts a slide valve mechanism, so that the cooling capacity can be adjusted steplessly from 15% to 100%, saving operating costs.
(7) It is easy to realize automation and remote communication.

Figure 8: Single screw compressor.
4.3 Disadvantages of Screw Compressor
(1) Compressor body components require high processing costs and precision.
(2) Since the volume between the teeth is periodically connected with the suction and exhaust ports, the noise of the compressor is high.
(3) Due to the limitation of rotor stiffness and bearing life, the inside of the compressor can only rely on the clearance seal, so the screw compressor can only be used in the medium and low pressure range, and cannot be used in high pressure occasions.
(4) Due to the large amount of oil injected by the oil-injected screw compressor and the complex oil treatment system, there are many auxiliary equipment for the unit.
5. Centrifugal Compressor
5.1 Working Principle of Centrifugal Compressor
The centrifugal compressor has a working wheel with blades. When the working wheel rotates, the blades drive the gas to move or give the gas kinetic energy, and then convert part of the kinetic energy into pressure energy to increase the pressure of the gas.
This type of compressor continuously sucks in the refrigerant vapor which is continuously discharged out along the radial direction at the same time when working.
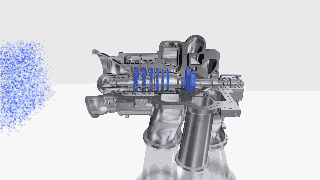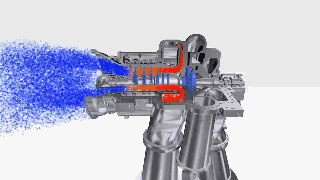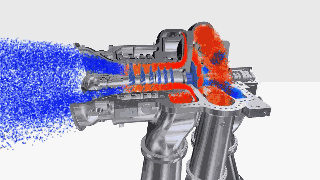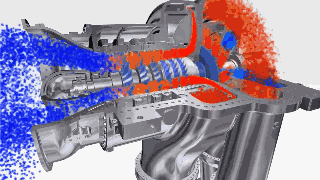
Figure 9: Centrifugal compressor GIF.
5.2 Advantages of Centrifugal Compressor
(1) The centrifugal compressor has a large air volume, simple and compact structure, light weight, small unit size, and small footprint. Compared with the piston compressor, when the cooling capacity is the same, its weight is 5 to 8 times lighter.
(2) Because it has no vulnerable parts such as air valves and piston rings, and no crank-link mechanism, it has balanced operation, reliable operation, high operating rate, and low maintenance costs.
(3) There is no friction between the working wheel and the casing, and no lubrication is required.
5.3 Disadvantages of Centrifugal Compressor
(1) Centrifugal compressors are currently not suitable for occasions where the gas volume is too small and the pressure ratio is too high, and because it is suitable to use refrigerants with relatively large molecular weights, it is only suitable for large cooling capacity, generally 250,000 to 300,000 kcal/h or more.
(2) The stable working area of the centrifugal compressor is narrow, and its gas volume adjustment is more convenient, but its economy is poor.
(3) At present, the efficiency of centrifugal compressors is generally lower than that of piston compressors.
(4) Generally, speed-increasing gears are used for transmission, the rotating speed is relatively high, and the requirements for shaft end sealing are high, which increase the difficulty of manufacture and the complexity of structure.
Related Info
Diagnosis and Troubleshooting of Refrigeration Compressor Failure13 Reasons Why Your Samsung Refrigerator Not Cooling (The Latest Version)
How Refrigerator Compressor Works (Structure Diagram, Working Principle Diagram)
How to Change Air Compressor Oil (5 Steps)
What are the 4 Main Components in a Central AC System


