VVT, CVVT, DVVT, VVT-i, and VVT-iW are often seen on many automobile engines. What do these logos mean? These logos reflect some of the unique technologies of automobile engines. Today let’s talk about the meaning and differences of these engine-specific technologies.
First, let’s learn more about VVT technology.
1. VVT Technology
VVT refers to variable valve timing. In order to optimize the amount of air entering the cylinder and improve combustion efficiency, it adjusts the amount of air intake (exhaust), as well as the valve opening and closing time, angle, etc. according to the operating conditions of the engine.
Role of VVT
1. Improving fuel economy and idling stability.
2. Reducing the emissions of NOx (nitrogen oxides) and HC (hydrocarbons).
3. Increasing the torque at low speed.
4. Increasing the power at high speed.
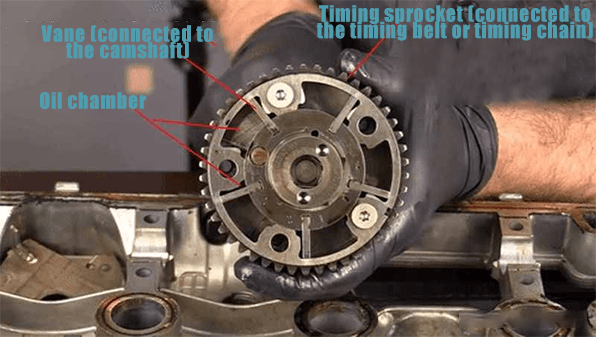
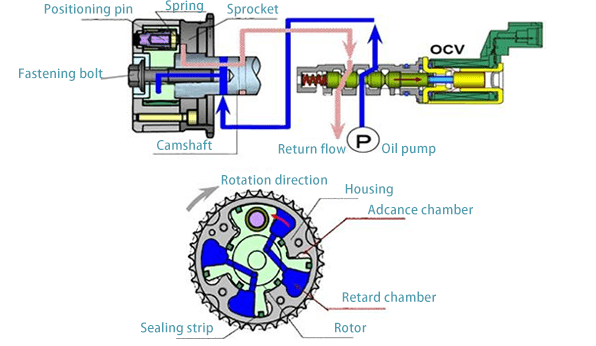
VVT System Structure
The VVT system structure mainly consists of VVT solenoid, engine control computer (controller), VVT phaser (actuator), sensors (CKP, CMP, MAP, THA, THW, etc.), oil channel, etc.
2. Features of Different "VVT" Engine Technologies
VVT refers to the control of the engine's intake and exhaust valves. Simply put, the control of the automobile engine valvetrain is achieved through mechanical structure or electronic control. The control is divided into two parts. One is to control the timing of the valve; the other is to control the lift of the valve.
CVVT, DVVT, VVT-i, VVT-iW, and i-VTEC are all extensions of VVT technology. So what are the uniquenesses of these technologies?
|
Name |
Manufacturer |
Name |
Manufacturer |
|
AVSC, AVLS |
Subaru |
VANOS |
BMW |
|
CPS |
Proton |
VALVETRONIC |
BMW, PSA |
|
VVL, N-VCT, VVEL, CVTCS |
Nissan |
Variatore di fase |
Alfa Romeo |
|
CVVT |
Hyundai, Kia, Geely, Iran Khodro, Volvo |
VarioCam |
Porsche |
|
DCVCP |
General Motors |
VTEC, i-VTEC |
Honda, ACURA |
|
DVT |
Ducati |
VTi |
Peugeot, Citroën, BMW |
|
DVVT |
Daihatsu, Perodua, Wuling |
VVC |
MG Rover |
|
MIVEC |
Mitsubishi |
Valvelift |
Audi |
|
MultiAir |
Fiat |
VVA |
Yamaha |
|
S-VT |
Fiat |
VVT |
Chrysler, General Motors, Proton, Suzuki, Isuzu, Volkswagen Group, Toyota |
|
Ti-VCT |
Ford |
VVT-i, VVTL-i |
Toyota |
2.1 CVVT
CVVT (Continue Variable Valve Timing) is a continuously variable valve timing mechanism. It is a very common technology in Korean and French cars.
It uses electro-hydraulic technology to control the opening and closing time of the camshaft, and then controls the valve overlap angle. To put it simply, under low load conditions of the car, the system delays the opening of the valve and reduces the amount of air intake. In the same way, when the car climbs a hill or accelerates rapidly, the engine load increases, and the system controls the valve to open in advance to increase the air intake to meet the increased load conditions.
2.2 DVVT
DVVT (Dual Variable Valve Timing) refers to controlling the timing of the intake and exhaust valves and changing the valve phase of the valvetrain through a set of hydraulic technology with a relatively simple structure.
The biggest feature of the DVVT system is the dual control of the intake and exhaust valves. DVVT has the characteristics of large torque at low speed and high efficiency at high speed. So far, compared with engines of the same level, the parameters of those equipped with DVVT technology are relatively good.
2.3 VVT-i
VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-intelligent) is an "intelligent variable valve timing system" developed by Toyota. It controls the timing of the air intake side valve through a computer (ECM). The ECM module collects and sorts signals from various sensors in the engine and outputs instructions to control the work of the actuator (solenoid valve) to complete the control of valve timing under different working conditions.
VVT-i has a great effect on engine power improvement and exhaust gas emissions.
2.4 VVT-iW
VVT-iW (Variable Valve Timing - intelligent Wide) is Toyota's upgrade of the VVT-i, which means an ultra-wide-angle valve variable timing system. It expands the valve timing control range of the original VVT-i to meet the wider needs of engine operating conditions.
Therefore, VVT-iW can meet the control of valve timing of larger displacement engines. VVT-i is more common on many Toyota's low-displacement naturally aspirated engines, while VVT-iW is the inherent technology used on the familiar D-4 ST 2.0T engine. Toyota has now expanded the use scope of the VVT-iW dual cycle engine.
2.5 i-VTEC
i-VTEC (Intelligent Variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control) is an engine technology developed by Honda to control valve lift. It is an upgrade based on Honda's original VTEC technology.
VTEC mechanically controls the valve lift. It adds a mechanical shaft in the middle of the DOHC (double overhead camshaft) to control the valve lift through mechanical movement. i-VTEC uses a microcomputer control unit and motor to realize electronic control of the valve lift, making the valve lift control range wider and the control more accurate.
3. Conclusion
VVT, CVVT, DVVT, VVT-i, VVT-iW and i-VTEC are all unique technologies developed based on VVT technology. They control the engine's valvetrain in different ways to achieve energy saving and high efficiency of the engine.


