
Figure 1: The cutaway view of the gear pump.
Gear oil pump can be used as oil transfer pump, lubricating pump, booster pump, and fuel pump, suitable for hydraulic systems of machine tools, hydraulic machinery, construction machinery, and can also be used in metallurgy, mining, petroleum, chemical, textile machinery and other equipment.
In daily use, there may be some problems with gear oil pumps. By reading the following content, you will be able to understand in advance what causes hydraulic gear pump failure or some symptoms of a certain problem with the gear oil pump, and take corresponding measures to solve the problem or send it to the repair shop for repair in time.
1. Fault: Failure to Discharge Oil or Insufficient Flow After Starting
Reason 1: A sufficient suction vacuum cannot be established.
The seal ring is damaged or the seal is poor, resulting in excessive clearance and serious internal leakage, so that the gear pump cannot establish a sufficient suction vacuum.
The surface of the new pump or the overhauled pump gears is not oiled, which causes serious wear of gears, making it difficult for the pump to achieve self-priming.
The gear oil pump speed is too low (generally when the speed below 200~300r/min, it cannot work properly), the pump is reversed or blocked, the suction pipe is leaking, damaged or worn, or the suction oil level is too low, so that the pump cannot establish large enough suction vacuum.
The reasons why there is a large suction vacuum and the gear oil pump cannot inhale normally are:
The suction height is too large. The suction height of the hydraulic pump is generally not more than 500mm).
The oil temperature is too low, and the viscosity is too large, resulting in too large suction vacuum and too much gas sucked out, which reduces the volume efficiency of the gear oil pump.
The suction pipe is blocked, damaged or worn, the suction filter is dirty, the nominal flow rate is too small, or the suction valve is not opened.
Too high oil temperature or too many air bubbles in the sucked oil can lead to increased leakage from the pump, resulting in "cavitation".

Figure 2: External gear pump.
Reason 2: Problems with the discharge pipe
The discharge pipe is leaking, damaged or seriously worn. The spring of the bypass safety valve of the discharge pipe is too loose, so that the safety valve cannot return to its original position in time, resulting in abnormal operation of the gear oil pump.
The discharge valve is not open or damaged or the discharge pipe filter is blocked, which causes the pressure in the pump body to be too high, so that the safety valve is forced to open and the pump displacement is insufficient.
Other reasons: the direction of electric motor is reversed, etc.
1.1 Measures
Check the rotation direction. If the rotation direction is wrong, stop the electric motor immediately, change the direction of the electric motor, and restart it.
Check the seals, replace the damaged seals, and tighten the relevant threaded connections.
Check the pressure gauge, and the pressure should be regulated in time if the pressure is too high or too low.
Check the actual speed of the pump shaft.
Add oil to make the liquid level rise to the specified height.
Select the oil with the appropriate viscosity, check and diagnose the fault of excessive temperature rise, and prevent the oil viscosity from changing too much.
Check whether the oil filter or oil suction pipeline is blocked, disassemble and clean them or replace the oil.
Check whether the suction valve and discharge valve are open. If the valve is closed, it should be opened in time. If the opening degree is too small, it should be opened to a larger degree in time.

Figure 3: Normal hydraulic oil and emulsified hydraulic oil.
2. Fault: Too Large Working Noise
Liquid Noise:
It may be caused by air leakage or cavitation. If the oil temperature is high, the viscosity will decrease, which will increase the leakage of the gear oil pump and increase the noise of the liquid; if the oil temperature is too low, the viscosity of the oil will be too large, so that the suction vacuum will be too large, and the suction gas will increase, resulting in "cavitation".
In short, if the suction height is too high, the oil temperature is too low or too high, the viscosity is too high, the suction pipe is blocked, or there are too many air bubbles in the suction oil, all will make the pump liquid noise increase.
Mechanical Noise:
It may be that the pump and the prime mover are not concentric, resulting in damage or loosening of the rolling bearing, increasing the mechanical noise.
The gears are seriously worn and the meshing is poor, the keys of the gears on the shaft are loose, the pump shaft is bent or poor processing and installation causes mechanical friction in the pump.

Figure 4: Gear pump and electric motor connected together.
2.1 Measures
Measures to deal with too large liquid noise:
The suction height should be appropriately reduced. If the suction height is too high, too much air will leak into the gear oil pump, and the probability of cavitation will increase.
Appropriately increase the oil temperature and reduce the viscosity of the oil when the oil temperature is too low.
Check whether the suction line is dirty and blocked. If it is blocked, clean or replace the suction line.
Measures to deal with too large mechanical noise:
Adjust the coaxiality between the pump body and the electric motor, and the error should not exceed 0.01mm.
Replacing rolling bearings. Excessive wear or long-term use of rolling bearings will also produce a lot of mechanical noise.
Check the safety valve. The failure of the safety valve will also produce mechanical noise.
Replace the main precision gear and ensure that the axes of the two gears are parallel.
Replace the sealing ring. The damage or wear of the sealing ring will cause the gear pump to leak, resulting in greater mechanical noise.
3. Fault: Insufficient Pump Pressure
The main reasons are:
1.The radial clearance and axial clearance of the gear pump are too large, resulting in increased leakage in the pump.
2.There are cracks in the pump body, which increases the leakage of the pump.
3.If the viscosity of the oil is too high, the suction vacuum will be too large.
4.The power of the electric motor does not match the gear oil pump, and the too high or too low speed will seriously affect the normal operation of the pump.
5.The oil filter is blocked, resulting in the inability to effectively filter out impurities.
6.The pressure adjustment of the relief valve is too low or malfunctioning.
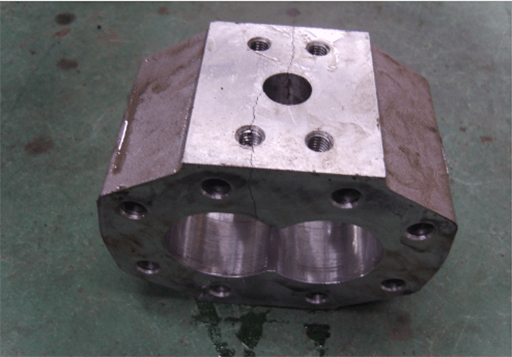
Figure 5: A crack on the gear pump body.
3.1 Measures
The main measures are:
If the pump body is severely worn, it will cause increased leakage, so replace the pump body.
Fasten the connecting parts. And if the pump body cracks, you should replace it.
Check whether the oil temperature is normal. If the temperature is too high, install a cooling device.
Select the matching motor.
Clean the oil filter.
Readjust the pressure or replace the relief valve.
4. Fault: Pump Does not Operate Normally or Seizes Up
Possible Reasons:
1.The axial clearance and radial clearance of the pump body are too small, which aggravates the wear of the pump gears, thereby shortening the working life of the pump.
2.Inflexible rotation or excessive wear of the needle roller bearing will seriously affect the normal operation of the pump.
3.The concentricity between the pump and the motor shaft coupling is insufficient, resulting in serious wear of gears or other components.
4.Excessive spring force of the pressure valve causes the pressure valve not to open correctly. Too little spring force of the pressure valve causes the safety valve not to return to its original position immediately, thus making the pump work abnormally.
5.Impurities in the pump will increase the wear of the pump gears, thereby reducing the working life of the pump.

Figure 6: Needle roller bearing.
4.1 Measures
Adjust the axial or radial clearance. If the axial or radial clearance is too large, the pump cannot establish effective pressure. If the axial or radial clearance is too small, the wear of the pump will increase.
Replace worn needle roller bearings.
Check whether the pump and the shaft are concentric and check whether the solid bolts are loose.
Replace the damaged spring, and at the same time, remove the dirt in the small hole of the valve body or replace the spool valve in time.
Use a fine silk screen to filter the oil to remove the dirt. If the pump oil is too dirty, replace it.
Check whether the electric motor is reversed.
5. Fault: Pump Stops Suddenly
Possible Reasons:
1.Abnormal meshing in the pump, such as gear jamming.
2.The shaft and the bearing are stuck, and the pump cannot operate normally.
3.Power supply wiring error or power supply failure.
4.Motor overload protection, motor reverse rotation or motor failure.
5.Damaged coupling, poor connection between the pump and the electric motor, poor alignment between pump and shaft.
5.1 Measures
Stop the gear oil pump to check the problem, clean the dirt and replace the corresponding wear parts.
Check the power supply to see if it is turned on or faulty.
Check the wiring of the motor.
Check whether the motor is reversed.
Open the safety cover and turn the gear by hand to check. If the gear does not rotate smoothly, the problem should be further investigated in time.
Check the interlock system of the instrument. If the instrument is damaged, it will mislead the user.
6. Failure: Oil Leakage
The main reasons are:
1.The sealing of the pump cover is not tight enough, resulting in increased oil leakage in the gear oil pump.
2.The sealing surface of the shaft is scratched.

Figure 7: Seals.
6.1 Measures
The main treatment measures are:
Adjust the gap between the pump cover and the sealing ring. If the gap is too large or too small, it will seriously affect the normal operation of the pump.
Replace damaged seals, because poor sealing will increase the leakage of the pump and cannot establish effective pressure.
Related Info
How Does a Hydraulic Pump Work?How to Select a Hydraulic Pump
Hydraulic Pumps: Common Faults and Troubleshooting Methods
Gear Pumps: Working Principle, Types, Pros&Cons and Applications
Hydraulic Pumps:Types and Pros & Cons


