
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve is a critical component in modern vehicle engines, playing a pivotal role in emissions control and engine performance. However, like any mechanical part, the EGR valve is susceptible to wear and failure over time.
Recognizing the symptoms of EGR valve failure is crucial for maintaining engine health and performance. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the various symptoms that indicate potential EGR valve issues and discuss the implications for engine operation.
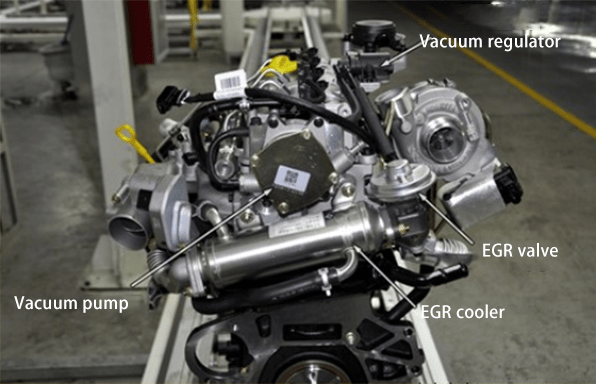
1. Understanding the EGR Valve
Before delving into the symptoms of EGR valve failure, it's essential to understand the role this component plays in engine function.
The EGR valve is responsible for recirculating a portion of exhaust gases back into the engine's combustion chambers. This process helps reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by lowering combustion temperatures. However, when the EGR valve malfunctions, it can lead to a host of engine performance issues.

2. Common Symptoms of EGR Valve Failure
2.1 Rough Idling
One of the earliest signs of EGR valve failure is rough idling. When the EGR valve fails to function properly, it can disrupt the air-fuel mixture entering the combustion chambers, resulting in uneven idling or engine hesitation.
2.2 Engine Stalling
A malfunctioning EGR valve can cause the engine to stall unexpectedly, especially during idle or low-speed driving. This occurs when the valve fails to regulate exhaust gas flow accurately, leading to disruptions in engine combustion.
2.3 Decreased Fuel Efficiency
Another common symptom of EGR valve failure is decreased fuel efficiency. When the valve is stuck open or closed, it can affect the engine's air-fuel ratio, leading to excessive fuel consumption. Drivers may notice a decrease in miles per gallon (MPG) or more frequent visits to the gas pump.
2.4 Check Engine Light (CEL) Illumination
A malfunctioning EGR valve can trigger the vehicle's onboard diagnostic system, causing the check engine light (CEL) to illuminate. The EGR system is monitored by various sensors, and any deviations from expected values can prompt the system to generate a fault code.
2.5 Increased Emissions
Since the primary function of the EGR valve is to reduce emissions, its failure can result in increased pollutant emissions. This can lead to a vehicle failing emissions tests or emitting visible smoke from the exhaust.
2.6 Engine Knocking or Pinging
In some cases, a faulty EGR valve can cause engine knocking or pinging sounds. This occurs when the improper combustion of fuel and air leads to abnormal pressure fluctuations within the engine cylinders.
2.7 Acceleration Issues
A malfunctioning EGR valve can also manifest as acceleration issues, such as hesitation or sluggishness when accelerating. This occurs when the valve fails to regulate exhaust gas flow properly, affecting engine performance under load.
3. Diagnosing EGR Valve Issues
Once the symptoms of EGR valve failure are identified, diagnosing the underlying cause requires a systematic approach. Automotive technicians may use a combination of visual inspections, electronic diagnostics, and functional tests to pinpoint the issue accurately. Common diagnostic procedures include:

3.1 Visual Inspection
Technicians visually inspect the EGR valve and associated components for signs of damage, corrosion, or carbon buildup. Any abnormalities observed during this inspection can provide valuable clues regarding the root cause of the issue.
3.2 Electronic Diagnostics
Using a diagnostic scan tool, technicians can retrieve fault codes stored in the vehicle's onboard computer system. These fault codes can provide insight into specific EGR system malfunctions, helping narrow down the diagnostic process.
3.3 Functional Testing
Functional tests involve manually operating the EGR valve and monitoring its response. Technicians may use a vacuum pump or electronic actuator to simulate engine operating conditions and verify proper EGR valve operation.
4. Addressing EGR Valve Failure
Once EGR valve failure is diagnosed, addressing the issue typically involves repair or replacement of the faulty component. Depending on the severity of the issue and the extent of damage, technicians may opt to clean, repair, or replace the EGR valve and associated components. Common repair strategies include:
4.1 Cleaning the EGR Valve
In cases where the EGR valve is obstructed by carbon buildup, cleaning the valve may restore proper function. Technicians use specialized cleaning solvents or tools to remove deposits and restore optimal airflow.

4.2 Replacing the EGR Valve
If the EGR valve is damaged beyond repair or cleaning, replacement may be necessary. Technicians install a new EGR valve and ensure proper calibration and sealing to prevent future issues.
EGR valve replacement cost
The cost of replacing an EGR valve can vary depending on several factors, including the make and model of the vehicle, labor costs in your area, and whether you choose to use an OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) part or an aftermarket part. Generally, EGR valve replacement costs can range from $150 to $500, including parts and labor. It's advisable to consult with a trusted mechanic or automotive service center for an accurate estimate tailored to your specific situation.

4.3 Addressing Underlying Issues
In addition to repairing or replacing the EGR valve, technicians may address underlying issues contributing to valve failure, such as vacuum leaks, sensor malfunctions, or exhaust system issues.
5. Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of EGR valve failure is essential for maintaining engine performance, emissions compliance, and overall vehicle reliability. By understanding the role of the EGR valve and its impact on engine operation, drivers can identify potential issues early and take proactive measures to address them. Whether it's rough idling, decreased fuel efficiency, or engine stalling, prompt diagnosis and repair of EGR valve issues are key to ensuring smooth and efficient vehicle operation. As automotive technology continues to evolve, vigilance and maintenance remain paramount in preserving engine health and performance for years to come.


