
Figure 1: Car radiator set.
No matter if it is a desktop computer or a notebook computer, they all have fans. The fan plays the role of heat dissipation. The higher the
temperature of the computer CPU, the faster the rotation speed, which can improve the heat dissipation efficiency of
the computer CPU and ensure the normal operation of the CPU.
So how is the fan speed regulation achieved? This starts with the wiring of the fan. From the beginning to the
present, computer CPU fans have gone through two-wire, three-wire and today's four-wire. So what's the difference
between them?
1. Working Principle of Two-Wire CPU Fan
The early fans only had two wires, usually represented by red wire and black wire. The red wire represents the
positive power supply, and the black wire represents the negative power supply. That is to say, as long as the
appropriate voltage is connected to, the fan will rotate at full speed and the speed cannot be adjusted.
Although this fan is easy to control, it has no speed feedback. The CPU of the computer does not know whether the
fan is running or not, and what the speed of the fan is. Even if the fan is broken, the CPU of the computer cannot
detect it, and a closed loop cannot be formed between the temperature and the speed. It can also be said that the
state of the fan is uncontrollable, and there is a hidden danger of heat dissipation.

Figure 2: NMB-MAT 2-wire fan.
In view of the above shortcomings of the two-wire fan, in order to improve the heat dissipation efficiency, a three-wire fan appeared later.
2. Working Principle of Three-Wire CPU Fan
Three-wire fans have three wires, which are represented by red, black and yellow (blue, or white). Red and black are the power lines, and yellow is the feedback line of the fan speed. Through this line, the computer CPU can detect the fan speed in real time. After the fan is turned on, the CPU can know whether the fan is working, forming a simple closed loop.

Figure 3: 3-wire fan.
When the computer needs to dissipate heat, the CPU detects that the fan speed is zero, so it can judge that the fan
is broken or missing, and can prompt the user with a fault message.
The disadvantage of the above two fans is that they cannot adjust the speed according to the actual temperature
conditions, and only run at full speed, resulting in a lot of noise. In order to improve this situation, a four-wire
fan appears.
3. Working Principle of Four-Wire CPU Fan
The four-wire CPU fan has an additional speed control line on the basis of the three-wire type. The CPU can not only detect the fan speed in real time, but also control the fan speed according to the current CPU temperature, realizing the closed-loop control of the temperature and fan speed, improving heat dissipation efficiency, reducing power consumption of the host, and also reducing noise when the fan rotates. The advantages are obvious, so at present, four-wire fans are mostly used.
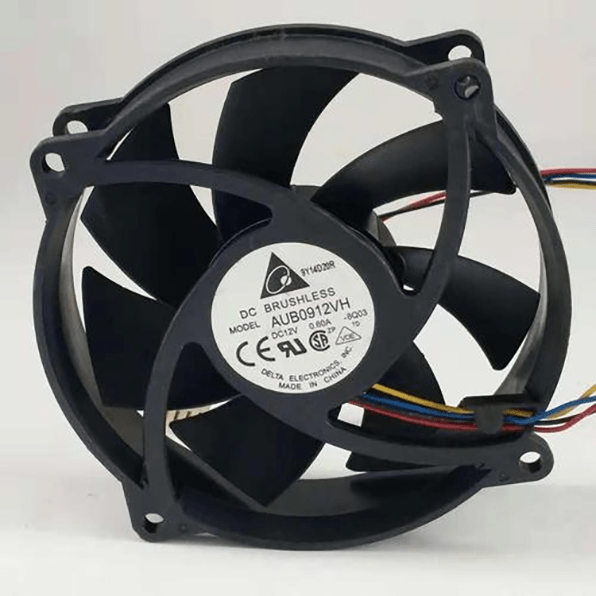
Figure 4: Delta 4-wire fan.
From the previous comparison, we can see that the three-wire fan has speed measurement function compared to the two-wire fan, and the four-wire fan has speed regulation function than the three-wire fan. The comparison is shown in the table below.

Table 1: The comparison between 2, 3, and 4 pin fans.
So how does the PWM adjust the speed of the fan?
4. How the PWM Adjusts the Fan Speed
After connecting a fan to a suitable rated voltage, the fan will run at full speed. If the voltage is lowered a little, the fan speed will also be reduced accordingly. When the voltage is reduced to zero, the fan will stop slowly. It can be found that the speed adjustment can be realized only by changing the voltage at both ends of the fan. So how to adjust the fan voltage? It uses PWM.
4.1 Principle of PWM Speed Regulation
The so-called PWM is pulse width modulation, and a square wave of a certain frequency is composed of high level and low level. Assuming that the duration of the high level is T1 and the duration of the low level is T2, then the period T=T1+T2.

Figure 5: PWM square wave.
By changing the duration of the high level, the average voltage of the square wave can be changed. The proportion of
the high level in one cycle is called the duty cycle. The calculation formula is: D=T1/T.
The relationship between duty cycle and average voltage:
The larger the duty cycle, the higher the average voltage; the lower the duty cycle, the smaller the average
voltage.
●The duty cycle is 100%, then the average voltage across the fan is 12V, and the fan rotates at full speed;
●The duty cycle is 50%, then the average voltage across the fan is 6V, and the fan rotates at half speed;
●If the duty cycle is 0%, then the average voltage across the fan is 0V, and the fan does not rotate.
The calculation relationship between the duty cycle and the average voltage is shown in the figure below.

Figure 6: Calculation method of the average voltage.
4.2 Design of the Circuit Diagram of PWM Speed Regulation
Therefore, the CPU can control the speed of the fan as long as it outputs square waves with different duty ratios, and the duty ratio is related to the temperature. The higher the temperature, the larger the duty cycle, and the faster the fan speed; the lower the temperature, the smaller the duty cycle, and the smaller the fan speed. The circuit schematic diagram of the PWM controlling the fan speed adjustment is shown in the figure below.
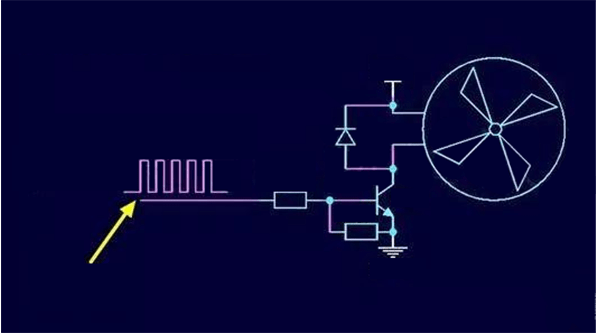
Figure 7: Circuit diagram of PWM speed regulation.
In the figure above, a triode is used as the fan driver, and other power devices such as MOSFETs can also be used. The duty cycle of the square wave is controlled by the CPU temperature. Theoretically speaking, the higher the frequency, the smoother the fan rotation, but the higher the response speed requirements for the power switching device, so the frequency of the square wave is generally controlled between 10K-30KHz.
5. Conclusion
Using PWM speed control to control the cooling fan can provide the advantages of precise speed control, energy saving, low noise and so on. When using PWM speed regulation, you need to select the appropriate PWM fan controller, PWM signal frequency and duty cycle range, and pay attention to factors such as the minimum speed of the fan.


