
Figure 1: Pneumatic, Electric and Hydraulic Actuators.
The actuator used in the control valve are nothing more than pneumatic, electric, and hydraulic (electro-hydraulic) type. They have their own advantages and disadvantages in application, which are described below.
1. Pneumatic Actuators
Most of the actuators used in industrial control applications today are pneumatic actuators. Using the air source as power, pneumatic actuators are more economical than electric and hydraulic ones. Besides, their simple structure makes them easy to master and maintain.
1.1 Advantages
As for maintenance, pneumatic actuators are easier to operate and calibrate than other types of actuators. And they can also be easily interchanged in directions on the spot. Their biggest advantage is safety, so they are ideal for flammable and explosive environments. In the chemical industry, pneumatic control valves still occupy an absolute market advantage.
1.2 Disadvantages
The main disadvantages of pneumatic actuators are: slow response, poor control accuracy, and poor anti-deviation performance.
This is because of the compressibility of gas, especially when using large pneumatic actuators — it takes time for the air to fill the cylinder and to empty it. But this is probably not a problem, since many working conditions do not require a high degree of control accuracy, extremely fast response or anti-deviation performance.
2. Electric Actuators
Electric actuators are mainly used in power plants or nuclear power plants.

Figure 2: An electric actuator..
2.1 Advantages
The main advantages of electric actuators are a high degree of stability and constant thrust that can be applied by the user. The maximum thrust generated by the electric actuator can be as high as 225000kgf. However, only hydraulic actuators can achieve such a large thrust, but the cost of hydraulic actuators is much higher than that of electric ones.
The anti-deviation performance of electric actuators is very good, and the output thrust and the torque are basically constant. This can well overcome the unbalanced force of the medium and achieve accurate control of the process parameters. Thus, the control accuracy is higher than that of pneumatic actuators.
If the electric actuator is equipped with a servo amplifier, the exchange of positive and negative actions can be easily realized. And the valve position can be easily set (hold/fully open/fully closed) when the signal is off. Even when a fault occurs, the electric actuator is definitely still in place, which is impossible for a pneumatic actuator, because it needs a combined protection system to maintain its position.
2.2 Disadvantages
The main disadvantages of electric actuators are: the structure is more complex and more prone to failure. And because of its complexity, there are relatively higher technical requirements for on-site maintenance personnel. What’s more, the motor generates heat when running. Thus, if the adjustment is too frequent, it is easy to cause the motor to overheat, resulting in thermal protection, and at the same time, it will increase the abrasion of the reduction gear.
In addition, the operation of electric actuators is slow. It takes a long time from the regulator’s output of a signal to the control valve’s response and movement to the corresponding position. This is where electric actuators cannot hold a candle to pneumatic and hydraulic actuators.
3. Hydraulic Actuators
Electro-hydraulic actuators integrate the motor, oil pump, and electro-hydraulic servo valve. They work as long as the power supply and control signal are connected to them. Hydraulic actuators are similar to cylinders, but they can withstand higher pressure than cylinders. Their operation requires an external hydraulic system, so they need to be equipped with hydraulic stations and oil pipelines when used in factories. In contrast, electro-hydraulic actuators are more convenient than hydraulic actuators.
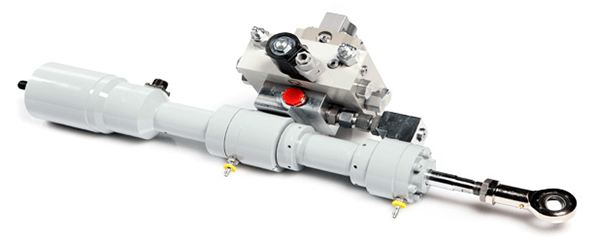
Figure 3: A hydraulic actuator.
3.1 Advantages
Hydraulic or electro-hydraulic actuators are often chosen for the requirement of outstanding anti-deviation performance, high thrust, and fast formation speed. Due to the incompressibility of liquids, one of the advantages of using hydraulic actuators is their great anti-deviation performance. This is important for regulating conditions, since throttling conditions are unstable when the regulating component is close to the valve seat, and the greater the differential pressure is, the severer the situation is. In addition, hydraulic actuators operate very smoothly and respond quickly, so they can achieve high-accuracy control.
3.2 Disadvantages
The main disadvantages of hydraulic actuators are that they are expensive, bulky, particularly complex and that they require special engineering. Therefore, they are mainly used in some special occasions such as power plants and petrochemicals.
| Types Advantages Disadvantages Applications | ||||
| Pneumatic | Safety, low cost, simple structure, easy to master and maintain |
Slow respond,poor cont o accuracy poor anti-deviation performance |
Most control chemical etc. |
industrial occasions, industry, |
| Electric | Stable, great anti- deviation performance, high controlaccuracy |
Complex structure, prone to failure and overheating of the motor, run slowly |
Power plants or nuclear power plants, medical technology, etc. |
|
| Hydraulic | Great anti-deviation performance, high thrust, constant operation, fast respondence, high contoaccuracy |
High cost, hulky size | Power plants, petrochemicals and other special occasions |
|
Figure 4: Ultrasonic level sensor for water/fuel/oil/powder, 0-60M, ATO-LEVS-DP.
Related Info
How to Reduce Gear Noise?6 Types of Commonly Used Gear Reducers
What is a worm gear reducer
What is an Actuator?
What is Gear Ratio?


