
The solenoid valve is an industrial pneumatic component that we often use. It can control the reciprocating movement of the air cylinder, thereby driving the movement of the mechanism to achieve the desired function. It can control not only air, but also some media such as water and oil. According to its function, there are many different models to choose from. Now solenoid valves are also developing towards centralized intelligence.
The rated voltages of the solenoid valve coil include: DC12V, DC24V, AC24V (50/60Hz), AC110V (50/60Hz), AC220V (50/60Hz), AC380V (50/60Hz). Generally, DC24V is used in electrical design, which is a commonly used safe voltage and the switching power supply or solenoid valve coil is easy to repair and replace.
The failure frequency of this component is also relatively high. How to clearly judge and troubleshoot these failures is of great significance to maintain the stability of production efficiency. The following introduces the common faults of solenoid valves, their solutions and how to judge whether the solenoid valve is good or bad.
1. Troubleshoot Solenoid Valve Faults
1.1 Solenoid Coil Short Circuit or Open Circuit
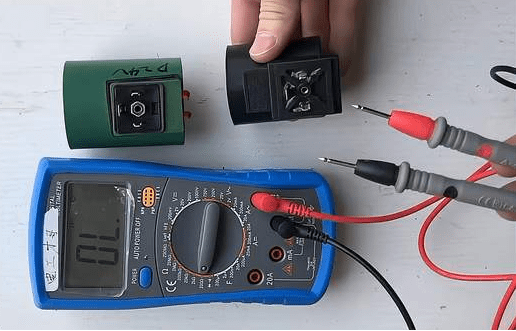
Check method: First use a multimeter to measure the coil. If the resistance approaches zero or infinity, it means the coil is short-circuited or open-circuited. If the measured resistance value is normal (probably tens of ohms), it does not mean that the coil is good. Please perform the following final test.
Find a small screwdriver and place it near the metal rod that goes through the solenoid valve coil, and then energize the solenoid valve. If you feel there is magnetism around the screwdriver, the solenoid valve coil is good, otherwise it is bad.
Solution: If a problem with the coil is detected, replace the solenoid valve coil.
1.2 Problem with Solenoid Coil Connector/Plug
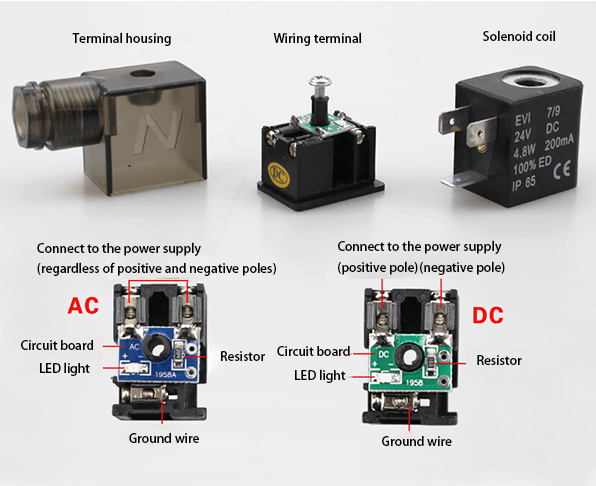
Fault content: When the solenoid valve is equipped with a connector, you may encounter problems such as damage to the metal reed of the connector, incorrect connector wiring (such as misconnecting the power cord to the ground wire), resulting in the failure of power transmission to the coil.
If the connector of the solenoid valve coil is equipped with a LED power indicator light, the wiring must be correct when the solenoid valve is driven by DC power, otherwise the indicator light will not light up.
In addition, it is forbidden to use connectors with LED power indicators of different voltage levels interchangeably, otherwise it may cause the LED to burn out, the power supply is short-circuited, or the LED light is very weak.
For solenoid valve coils without power indicator lights, there is no need to distinguish polarities.
Solution: Check and correct wiring errors, repair or replace damaged plugs and connectors.
1.3 Valve Core Problem
Check method 1: When the pressure of the medium passed through the solenoid valve is normal, press the red button of the solenoid valve, but the solenoid valve does not respond at all (there is no opening or closing change of the solenoid valve), indicating that the valve core must be bad.
Solution: Check whether there are problems with the medium, such as whether there is a lot of water in the compressed air and whether there are many impurities in the liquid medium passing through the solenoid valve. Sometimes the oil-water separator does not play a great role. Especially when the pipeline design is poor, there will be a lot of water in the compressed air flowing through the solenoid valve.
If a problem is detected with the media, then clear the water or impurities in the solenoid valve and pipelines. If it still doesn't work, please clean the system, and repair or replace the valve core, or simply replace the entire solenoid valve.
Check method 2: After inspection, it is found that the coil is the original coil and the magnetism of it is normal when it is energized, but the solenoid valve still does not operate (at this time, the function of the solenoid valve button may be normal), indicating that the valve core is broken.
Solution: Please repair or replace the valve core, or simply replace the entire solenoid valve.

1.4 Solenoid Valve Not Working after Being Energized
Failure causes and solutions:
1. Poor power wiring → Rewire and reconnect the connector.
2. The power supply voltage is not within the normal working range → Adjust the power supply voltage to the normal working range.
3. Coil desoldered → Re-solder it.
4. The coil is short-circuited → Replace the coil.
5. The working pressure difference is inappropriate → Adjust the pressure difference or replace the solenoid valve with an appropriate one.
6. Too high fluid temperature→ Replace with a suitable solenoid valve.
7. Impurities in the system make the main valve core and moving iron core of the solenoid valve stuck → Clean the system. If the seal is damaged, replace the seal and install a filter.

1.5 Solenoid Valve Unable to Be Closed
Failure causes and solutions:
1. The seal of the main valve core or the moving iron core is damaged → Replace the seal.
2. The fluid temperature and viscosity are too high → Replace with the appropriate solenoid valve.
3. Impurities enter the solenoid valve core or moving iron core → Clean the solenoid valve.
4. The spring life has expired or is deformed → Replace it.
5. The orifice / balance hole is clogged → Clean it in time.
6. The working frequency of the solenoid valve is too high or the lifespan has expired→Change the solenoid valve.
1.6 Other Faults of Solenoid Valves
Failure causes and solutions:
1. Internal leakage of the solenoid valve→ Check whether the seal is damaged and whether the spring is poorly assembled.
2. External leakage of the solenoid valve→The connection is loose or the seal is broken→Tighten the screws or replace the seal.
3. Solenoid valve noise when energized → If the fasteners are loose, tighten them. If the voltage fluctuation is not within the allowed range, adjust the voltage.


