
Figure 1: SAMSR NEMA 23 standard hybrid stepper motor.
1. What is a Stepper Motor
Stepper motor uses electronic circuits to convert direct current into a multi-phase sequence-controlled current, and to supply power to coils at different times. With this current to supply power, the stepper motor can work normally. The function of a stepper motor driver is to provide a time-sharing power supply and multi-phase sequential control for the stepper motor. Let's see how stepper motors are classified according to different standards.
1. According to Rotor Characteristics
According to the differences in rotor structure and materials, there are three main types of stepper motors: reactive step motor(VR type), permanent magnet step motor(PM type), and hybrid step motor (HB type).

Figure 2: Three types of stepper motors.
1.1 Variable Reluctance Stepper Motor
The variable reluctance stepper motor (VR), i.e. reactive stepper motor, is a traditional stepping motor with windings on the stator, and the windings are composed of soft magnetic materials. It features simple structure, low cost, small step angle, up to 1.2 degrees, but it also brings poor dynamic performance, low efficiency, high heat generation, and its reliability is difficult to ensure.
1.2 Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor
The rotor of the permanent magnet stepper motor (PM) is made of permanent magnet material, and the number of poles of the rotor is the same as that of the stator. It is characterized by good dynamic performance and large output torque, but this motor has a large step angle (usually 7.5 degrees or 15 degrees).
The stator of the stepper motor can be a coil, and the rotor can be a permanent magnet; or the stator can be a permanent magnet, and the rotor can be a coil.
1.3 Hybrid Stepper Motor
The hybrid stepper motor (HB) combines the advantages of reactive and permanent magnet stepper motors, with multi-phase windings on the stator, permanent magnet materials on the rotor, and multiple small teeth on both the rotor and stator to improve step accuracy. It is characterized by large output torque, good dynamic performance and small step angle. It is the stepper motor with the highest performance at present, but its structure is complex and the cost is relatively high.
The hybrid stepper motor is divided into two-phase, three-phase and five-phase: the two-phase step angle is generally 1.8 degrees, and the five-phase step angle is generally 0.72 degrees. As the number of phases (energized windings) increases, the step angle of the stepper motor decreases, and the accuracy improves. Hybrid stepper motors are the kind of stepper motor most widely used.
The performance of the hybrid stepper motor:
a. Control accuracy: the more phases and beats of a stepper motor, the higher its accuracy.
b. Low frequency: The stepper motor is prone to low frequency vibration at low speed. When it works at low speed, damping technology or micro step technology is generally used to overcome the low frequency vibration phenomenon.
c. Torque: the output torque of the stepper motor decreases with the increase of the speed, and it drops sharply at high speed.
d. Overload capability: Stepper motors do not have overload capability.
e. Running performance: The control of the stepper motor is open-loop control. If the starting frequency is too high or the load is too large, it is easy to lose steps or have a locked-rotor phenomenon. When the speed is too high, it is easy to cause overshoot.
f. Speed response: It takes hundreds of milliseconds for the stepper motor to accelerate from standstill to working speed.
|
Comparison |
VR Motor |
PM Motor |
HB motor |
|
Price |
Medium |
Relatively cheap |
Relatively expensive |
|
Structure design |
Simple |
Moderate difficulty |
Relatively complex |
|
Resolution |
Step angle: 1.8°, 0.9° or less |
Step angle: 3°~30° |
Step angle: 1.8, 0.9° or less |
|
Torque frequency curve |
No obvious torque drop at high speed |
High torque at low speed, obvious torque drop at high speed |
High torque at low speed, obvious torque drop at high speed |
|
Noise |
High noise |
Low noise |
High noise (using microstepping for better results) |
|
Heating |
High temperature rise (heat sink required) |
Low temperature rise |
Low temperature rise |
|
Operating modes |
Generally only full-step operation |
Full step, half step, micro step |
Full step, half step, micro step |
|
Rotor material |
Silicon steel sheet (no permanent magnet material) |
Ferrite or NdFeB permanent magnet material |
NdFeB permanent magnet material |
|
Rotor surface |
Multi-tooth structure
|
Toothless |
multi-tooth structure |
|
Magnetic torque |
Only producing attractive torque |
Both attractive and repulsive torques during operation |
Both attractive and repulsive torques during operation |
Table 1: Comparison of three types of stepper motors.
In addition to the above classification methods, stepper motors can also be classified in the following ways.
2. According to Connection Method of Stator Winding
Stepper motors have two types of windings: bipolar and unipolar type.
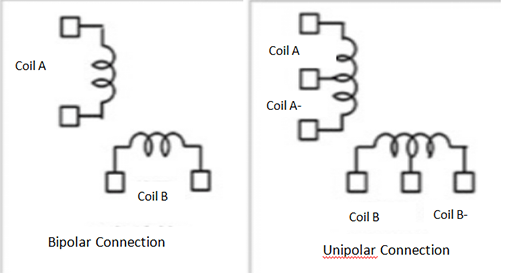
Figure 3: Comparison between bipolar and unipolar stepper motor.
Take a two-phase stepper motor as an example. There is only one winding coil on each phase of the bipolar stepper motor. When the motor rotates continuously, the current needs to change the direction of excitation in the same coil in turn. The drive circuit design requires eight electronic switches for sequential switching.
There are two winding coils with opposite polarities on each phase of a unipolar stepper motor. To make the motor rotate continuously, it is only necessary to alternately energize and excite the two winding coils on the same phase. The drive circuit design requires only four electronic switches.
In bipolar drive mode, because the winding coils of each phase are 100% excited, the output torque of the motor in bipolar drive mode is about 40% higher than that in unipolar drive mode.
Under the conditions of the same current and the same torque output, the unipolar stepper motor has twice as many coils as the bipolar stepper motor, so its cost is higher, and the structures of their control circuits are also different. Bipolar stepper motors are more popular on the market.
|
Bipolar Stepper Motor |
Unipolar Stepper Motor |
|
Current flows bidirectionally in one winding (bipolar drive). |
Current flows in one winding always in a fixed direction (unipolar drive). |
|
Simple structure, but complicated drive circuit |
Complex structure, but simple drive circuit |
|
Good winding utilization rate. Fine control can be performed, so the stepper motor can obtain high output torque. |
Poor winding utilization. The stepper motor can only obtain about - half the output torque compared with the bipolar connection. |
|
The counter-electromotive force (counter EMF, CEMF, back EMF) generated in the coil can be reduced, so a motor driver with a low withstand voltage can be used. |
Since a high back EMF is generated in the coil, a high withstand voltage motor driver is required. |
Table 2: Bipolar connection vs unipolar connection.
3. According to Phase Number of Stator Coils
Classified according to the phase number of windings on the stator, there are two-phase, three-phase and five-phase stepper motors.
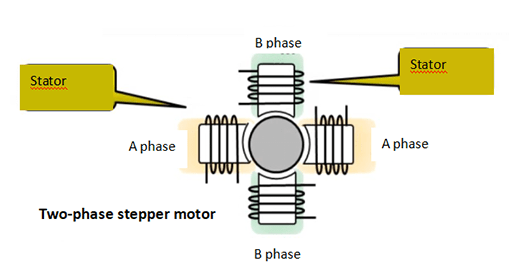
Figure 4: Diagram of two phase stepper motor.
At present, the most popular is the two-phase hybrid stepper motor, which accounts for more than 97% of the market share. It has high cost performance and after being equipped with a microstep driver features good effectiveness.
The basic step angle of this type of motor is 1.8 degrees/step. When equipped with a half-step driver, the step angle is reduced to 0.9 degrees. With a microstep driver, the step angle can be subdivided up to 256 times (0.007 degrees / micro-step). Due to friction force and manufacturing accuracy, the actual control accuracy is slightly lower. The same stepper motor can be equipped with different microstep drivers to change the precision effect.
Our company, Okmarts, has established long cooperations with many stepper motor manufacturers, we can provide a broad series of stepper motors from NEMA 6 (14 mm) to NEMA 42 (110 mm), such as NEMA 17 stepper motor, and NEMA 23 stepper motor. We can also offer stepper motor drivers well-matched with stepper motors. If you are looking for China NEMA 23 stepper motor manufacturers or 5V stepper motor manufacturers, please pay attention that we can provide the product you need.
Related Info
AC Motor: Types, Speed Control, Features & UsesStepper Motor: Working Principle, Operating Modes & Application
What is DC Motor and How Does It Work?
Types of DC Motors
Permanent Magnet DC Motor: Types, Application, Selection Principle (1)


