
Figure 1: Red Brushless motor with cables.
The following article introduces some differences between brushed motors and brushless motors in terms of working principle and performance, hoping to deepen your understanding of them.
1. What is a Brushed Motor
The main structure of a brushed motor is the stator, rotor windings, and brushes. The stator magnetic field can be generated by permanent magnets or by stator windings. A brushed motor is a rotating motor that contains brushes to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy (electric motor) or mechanical energy into electrical energy (generator). The role of the brushes in the brushed motor is to energize the coils in the rotor through the commutator, that is, to be used for the incoming and outgoing of voltage and current.
2. What is a Brushless Motor
The brushless motor consists of a permanent magnet rotor, a multi-pole winding stator, and a position sensor. A brushless motor means that there are no "brushes" in the motor, so how does a motor without brushes energize the coils in the rotor? A brushless motor uses permanent magnets as the rotor. There is no coil in the rotor, so there is no need for a commutator and brushes for energization. Instead, the coil is used as the stator.
The permanent magnets of small and medium-capacity brushless DC motors are now mostly made of rare earth NdFeB materials with high magnetic energy levels.

Figure 2: Types of motor.
3. Difference between Working Principle of Brushless Motor and Brushed Motor
3.1 How Does a Brushed Motor Work
As the picture below shows, the main structure of the brushed motor is the magnet stator + rotor + brush, which obtains the rotational torque through the rotating magnetic field, thereby outputting kinetic energy. During the rotation, the brushes are in constant contact and friction with the commutator to conduct electricity and change direction.
The brushed motor adopts mechanical commutation, the magnetic pole does not move, and the coil rotates. When the motor is working, the coil and commutator rotate, but the magnetic steel and carbon brush do not rotate. The alternation of the coil current direction is accomplished by the contact of the commutator and brushes.
As the motor rotates, different coils or different two poles of the same coil are energized at different times, so that the N-S pole of the magnetic field generated by the coil and the N-S pole of the closest permanent magnet stator have a suitable angle difference. In magnetic fields, the opposite poles will attract one another, but the like poles will repel one another, generating force that drives the motor to rotate.
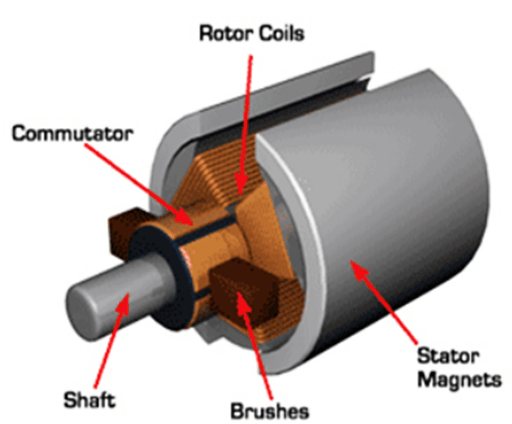
Figure 3: Structure of brushed motor.
3.2 How Does a Brushless Motor Work
In the brushless motor, the commutation work is completed by the control circuit in the controller (generally Hall sensor + controller, more advanced technology to take magnetic encoder).
The brushless motor adopts electronic commutation, the coil does not move, and the magnetic pole rotates. Brushless motors use a set of electronics to sense the position of the permanent magnet's poles through a Hall element. Based on this, an electronic circuit is used to switch the direction of the current in the coil at the right time, ensuring that the magnetic force in the correct direction is generated to drive the motor.
These circuits are the motor controllers. The controller of the brushless motor can also realize some functions that the brushed motor cannot, such as adjusting the power switching angle, braking the motor, reversing the motor, locking the motor, and using the brake signal to stop the power supply to the motor.

Figure 4: Brushless motor vs brushed motor.
4. Comparison of the Pros and Cons of Brushless Motors and Brushed Motors
4.1 Pros and Cons of Brushed DC Motors
Advantage:
1. Simple structure
The brushed motor has a simple structure, easy production and processing, convenient maintenance and easy control.
2. Fast response speed and large starting torque
The DC brush motor has fast starting response speed, large starting torque, stable speed change, almost no vibration from zero to maximum speed, and can drive a larger load when starting.
The brushless motor has a large starting resistance (inductive reactance), so the power factor is small, and the starting torque is relatively small. Besides, there is a humming sound when starting, accompanied by strong vibration, and the driving load is small when starting.
3. Smooth operation, good starting and braking effect
The brushed motor adjusts the speed through voltage regulation, so the starting and braking are stable, and the constant speed operation is also stable.
Brushless motors are usually digital frequency conversion control, which first converts AC into DC, and then DC into AC. The speed is controlled by frequency changes, so the brushless motor runs unevenly during starting and braking, and the vibration is large. It is stable only when the speed is constant.
4. High precision of direct motor control
The DC brush motor is usually used together with the reduction box and the decoder, which makes the output power of the motor larger and the control accuracy higher. The control accuracy can reach o.o1 mm, and the moving parts can be stopped almost anywhere you want.
Because the brushless motor is not stable when starting and braking, the moving parts will stop to different positions each time, and the positioning pins or limiters must be used to stop at the desired position.

Figure 5: Close-up of rotor in electric DC brushed motor.
5.Low cost of use
Because of the simple structure, low production cost, and relatively mature technology, DC brushed motors are widely used, such as factories, processing machine tools, and precision instruments. If the motor fails, you only need to replace the carbon brushes. Each carbon brush only costs a few dollars, very cheap.
The brushless motor technology is immature, the price is high, and the application range is limited. It should be mainly used on constant-speed equipment, such as inverter air conditioners, refrigerators, etc., and the brushless motor can only be replaced if it is damaged.
Shortcoming:
1. There is friction between the brush and the commutator, resulting in reduced efficiency, increased noise, and easy heat generation. The life of a brushed motor is several times shorter than that of a brushless motor.
2. Maintenance is troublesome, and the brushes need to be replaced constantly.
3. Because of the large resistance, low efficiency and low output power.
4. The friction between the brush and the commutator will cause sparks and cause great interference.
4.2 Pros and Cons of Brushless DC Motors
Advantage:
1. No brush, low interference
The brushless motor removes the brush, and the most direct change is that there is no electric spark generated when the brushed motor is running, which greatly reduces the interference of the electric spark to the remote control radio equipment. In addition, in some flammable and explosive occasions, brushless motors can also show their talents.
2. Low noise
The brushless motor has no brushes, the friction force is greatly reduced during operation, and the noise will be much lower. It can be used in quiet places such as hospitals, banks, airports, schools and so on.
3. High speed
Because of the use of magnetic field induction, there is no substantial contact, and the speed can be done faster.
4. Easy maintenance
Without the brush, the wear of the brushless motor is mainly on the bearing. From a mechanical point of view, the brushless motor is almost a maintenance-free motor. When necessary, only need to do some dust removal maintenance.
Shortcoming:
1. High cost
The cost of brushless motors and the controllers they are equipped with is high. The cost of brushed commutators and carbon brushes is much lower.
2. Cannot work in high magnetic field environment
If the application environment is a place with high a magnetic field or has been in contact with or very close to the high magnetic field, the motor will lose its function. Because the rotor part of the motor itself is made of magnets, the high magnetic field environment will change the magnetic field of the rotor or eliminate part of the magnetism, which will make the motor not work normally.

Figure 6: Transparent type DC motor with attached propeller to its shaft.
5. Different Speed Regulation Ways of Brushed Motor and Brushless Motor
In fact, the control of the two motors is voltage regulation, but because the brushless DC adopts electronic commutation, it can only be realized with digital control. The brushed DC is commutated through carbon brushes, and can be controlled by traditional analog circuits such as thyristors.
1. The speed regulation process of the brushed motor is to adjust the voltage of the motor power supply. The adjusted voltage and current through the commutator and the brush, change the strength of the magnetic field generated by the electrode, so as to achieve the purpose of changing the speed. This process is called variable voltage speed regulation.
2. In the process of brushless motor speed regulation, the voltage of the power supply of the motor remains unchanged. The control signal of the electronic speed governor is changed, and the switching rate of the high-power MOS tube is changed by the microprocessor to realize the change of the speed. This process is called variable frequency speed regulation.
6. Other Differences
1. Scope of application
Brushless motor equipment can be used in: dairy industry, brewing industry, meat processing industry, soy product processing industry, beverage processing industry, pastry processing industry, pharmaceutical industry, electronic precision factory and other dust-free workshops with higher requirements, etc.
Carbon brush motor: It can only be used in areas that are not too demanding, and cannot be used in dust-free workshops and explosion-proof workshops.
2. Service life
Brushless motor: It can work continuously for about 20,000 hours, and the conventional service life is 7-10 years.
Carbon brush motor: It can work continuously for about 5000 hours, and the normal service life is 2-3 years.
3. Use effect
Brushless motor: run at a high speed of 90-95m/s.
Carbon brush motor: The running speed is much lower than that of brushless motor.
4. Energy saving
Relatively speaking, the power consumption of a brushless motor is only 1/3 of that of a brushed motor.
5. Future maintenance
After the carbon brush motor is worn, not only replace the carbon brush, but also replace the accessories around the motor such as the rotating gear. The main thing is that the overall functionality will be affected.

Figure 7: Advantages and disadvantages of brushed and brushless motors.
In China, more and more high torque BLDC motor factories are flourishing whose brands originate from the whole world. OKmarts, as a trusted distributor for years, has deep cooperation with many Chinese BLDC motor manufacturers and can provide the type of electric motors you need.
Related Info
FANUC Spindle Amplifier Alarm Codes and Solutions (1)FANUC Spindle Amplifier Alarm Codes and Solutions (2)
FANUC Spindle Amplifier Alarm Codes and Solutions (3)
FANUC Spindle Amplifier Alarm Codes and Solutions (4)


