
Figure 1: What is encoder?
1. Overview
An Encoder is a communication device that controls the motion of an operating device. Encoders can help determine the speed or position of a motor, or other moving equipment.
2. Function
As automation in many industries and applications spreads rapidly, encoders help to maintain speed and position in electromechanical equipment, a vital process when accuracy, repeatability and precise motion is necessary.
Encoders are used widely throughout many applications, including automotive, laboratory and medical equipment, robotics, factory automation and electric motors.
Traditionally, optical encoders were used most widely in motion control, but as the need for a more robust, rugged sensing solution increased, magnetic encoding technology has started to surpass optical encoders as a better solution for difficult environments.

Figure 2: Encoder is controlling an oprating device.
3. How Does an Encoder Work
Encoders use different types of technologies to create a signal, including: mechanical, magnetic, resistive and optical – optical being the most common. In optical sensing, the encoder provides feedback based on the interruption of light.
The graphic below outlines the basic construction of an incremental rotary encoder using optical technology. A beam of light emitted from an LED passes through the Code Disk, which is patterned with opaque lines (much like the spokes on a bike wheel). As the encoder shaft rotates, the light beam from the LED is interrupted by the opaque lines on the Code Disk before being picked up by the photodetector assembly. This produces a pulse signal: light = on; no light = off. The signal is sent to the counter or controller, which will then send the signal to produce the desired function.
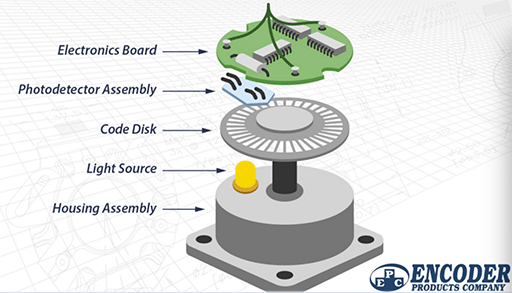
Figure 3: Structure of an encoder.
4. Application
• In a cut-to-length application, an encoder with a measuring wheel tells the control device how much material has been fed, so the control device knows when to cut.
• In an observatory, the encoders tell actuators what position a moveable mirror is in by providing positioning feedback.
• On railroad-car lifting jacks, precision-motion feedback is provided by encoders, so the jacks lift in unison.
• In a precision servo label application system, the encoder signal is used by the PLC to control the timing and speed of bottle rotation.
• In a printing application, feedback from the encoder activates a print head to create a mark at a specific location.
• With a large crane, encoders mounted to a motor shaft provide positioning feedback so the crane knows when to pick up or release its load.
• In an application where bottles or jars are being filled, feedback tells the filling machines the position of the containers.
• In an elevator, encoders tell the controller when the car has reached the correct floor, in the correct position. That is, encoder motion feedback to the elevator's controller ensures that elevator doors open level with the floor. Without encoders, you might find yourself climbing in or out of an elevator, rather than simply walking out onto a level floor.

Figure 4: An encoder used in an elevator.
• On automated assembly lines, encoders give motion feedback to robots. On an automotive assembly line, this might mean ensuring the robotic welding arms have the correct information to weld in the correct locations.
4. Difference Between Absolute and Incremental Encoders
Encoders may produce either incremental or absolute signals. Incremental signals do not indicate specific position, only that the position has changed. Absolute encoders, on the other hand, use a different “word" for each position, meaning that an absolute encoder provides both the indication that the position has changed and an indication of the absolute position of the encoder.
Related Info
How to Install a HMI and 4 Common Failures?What is a Transformer?
Classification and How Does a Transformer Work?
10 Common Types of Transformer?
What is an Encoder?


