
Figure 1: The Assured Automation R-Series electric valve actuators.
An electric actuator is a drive device that provides linear or rotary motion. It uses a certain driving energy to work under the action of a certain control signal. There are three basic types of actuators: part-turn, multi-turn and linear.
Electric actuator has 3 control modes to realize its function: analog control, 4~20ma input and output current; switch type, divided into active and passive; protocol control mode.
The electric actuator has been widely applied in power plant, process control, and industrial automation. The followings will introduce it 5 main functions that qualify it for these applications
Torque Limiting
Excessive torque may lead to heat dissipation problems, aggravate device wear, and shorten the service life of the motor. The electric actuator can prevent excessive torque during operation, which protects both the valve and the actuator itself. The limiting value is set by the setting device.
Valve Position Control
When the electric actuator runs to the closing and opening limiting positions, it will automatically stop (related to the set working mode).
Phase Loss Protection
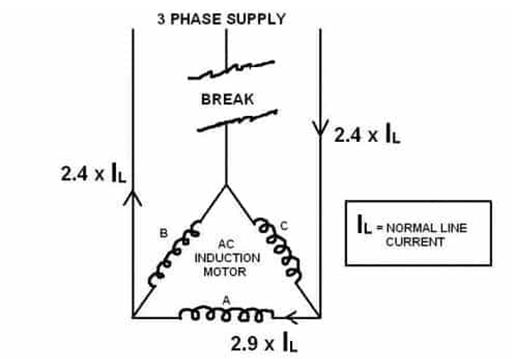
Figure 2: Phase loss of a three-phase motor.
The electric actuator has a very complete phase loss protection function. It combines the monitoring of voltage and current to detect phase loss phenomena that occur both when the motor is stationary and when it is running. Thus, it can prevent overheat of the motor caused by phase loss. But an important fact is that most phase loss phenomena occur when the motor is running.
Automatic Phase Sequence Correction
The electric actuator automatically detects the phase sequence of the three-phase power connected to the power terminal. Through appropriate logic operations, it determines which AC contactor is energized when the actuator operates to ensure that the phases are connected to the motor in correct sequence.
Without automatic phase sequence correction, it is possible to damage the valve due to wrong wiring phase sequence. Due to this function, the wiring of the actuator power supply can be performed regardless of the phase sequence.
Instantaneous Reverse Polarity Protection
When the electric actuator receives a command to move in the opposite direction, a time delay is automatically added to prevent unnecessary wear on the valve shaft and gearbox.
Related Info
Some Common Questions about Motor TorqueSpeed-Torque Curve of Stepper Motors and FAQs
Ways to Increase Stepper Motor Torque and Select Stepper Motor
What is a Pneumatic Actuator?
Torque Motor: Structure, Features, Types, Application


