
Figure 1: 57 Motor torque frequency curve.
1. What is Torque in Motor
Motor torque is simply the amount of force used to turn a Stepper motor. Torque is a kind of moment, and the definition of torque in physics is: torque = force X force arm. The force arm here can be regarded as the turning radius of the object driven by the motor. If the motor torque is too small, it will not be able to carry the object, that is, the "power" of the motor is not strong enough.
Generally speaking, the power of the motor to drive the mechanical rotation is the torque of the motor. The torque of the motor equals the force of the pulley to drag the belt X the radius of the pulley.
However, the torque of the motor is proportional to the strength of the rotating magnetic field and the current in the rotor, and it is also proportional to the square of the power supply voltage, so the torque is determined by factors such as current and voltage.

Figure 2: Example of typical torque for securing a nut with a wrench.
1.1 Introduction to Terms Related to Motor Torque
The torque of the motor is divided into starting torque, maximum torque, rated torque and stall torque.
The starting torque is a torque 1.7-2.2 times larger than the rated torque, generated at the time of motor starting. This starting torque can overcome the static friction of the rotor and the resistance of the load driven by the motor.
The maximum torque is a parameter for the motor to self-regulate under overload conditions. In layman's terms, it is the maximum load that can be driven. In fact, there is also a performance index of minimum torque, that is, the minimum load that can be driven. Beyond these performance indicators, the motor cannot run normally: the motor has the risk of burning after exceeding the maximum torque, and the motor is in a state of high energy consumption and low output when lowering than the minimum torque.
The rated torque refers to the torque generated by the motor under rated current (which can be understood as rated power), which is the best working condition of the motor with highest efficiency.
Stall torque, also known as short-circuit torque, refers to the torque when the rated voltage is applied to the motor, but the motor cannot be forced to rotate by external force, which directly reflects the starting performance of the motor.
In general, the larger the stall torque, the better, but if the stall torque is too large, the starting current will increase at the same time, which will cause an impact on the power grid. Therefore, in some national standards, there is a minimum limit on the stall torque and a maximum limit on the starting current.

Figure 3: A variable frequency motor torque curve.
2. How to Calculate Torque of Motor
The torque output by the motor is related to the speed and power of the motor. The "torque" unit of the motor is Nm, and the motor torque calculation formula is T=9550* P/n .
Where, P is the rated (output) power of the motor in kilowatts (Kw).
The denominator is the rated speed n, and the unit is revolutions per minute (r/min).
P and n can be found directly from the motor nameplate.
The origin of the constant 9550: The work done by T is also the work output by the motor.
Power=Force*Speed, that is: P=F*V
Torque=Force*action radius, namely: T=F*R
Then F=T/R
Speed=2πR*revolutions per second (revolution/second)
Convert seconds to minutes: Speed = 2πR*n (revolutions per minute)/60
So: P=F*V=(T/R)*(2πR*n/60)=2πTn/60=Tπn/30
Here, P: power unit W, T: torque unit Nm, n: rpm unit (rev/min)
If the unit of P is changed to KW, then it is the following formula:
P*1000=Tπn/30 ;
P*1000*30/π=Tn;
(30000/3.1415926)*P=T*n;
9549.297*P=T*n,
So T=9550P/n
Note: It should be noted that if the torque is calculated by the reducer, the factor of gear transmission efficiency loss should be considered.

Figure 4: Torque curve of stepper motor in theory.
2.1 Motor Torque Unit and Conversion
The motor torque is the output torque of the motor, which is one of the basic parameters of the motor. The commonly used unit is Nm (N*m), and others include: mN*m, KN*m, Oz*In, kg*cm, Gr* cm, Lb*Ft, Lb*In, Oz*Ft.
100 Oz*In = 0.706 N*m
1Lb=0.4536kg
1Ft=0.3048m
1Ft=12In
1Lb*Ft=0.13826kg*m
1Lb*In=0.1129N*m
3. Factors Affecting the Maximum Torque of Motor
Torque is the basic form of load on the drive shaft of various working machines, and is closely related to factors such as working capacity, energy consumption, efficiency, operating life and safety performance of power machinery. There are three different but interrelated limiting factors when it comes to the maximum torque rating of a motor.
3.1 Mechanical Properties of Materials
The first factor should be considered is the mechanical properties of the materials, and different servo models are a good example of this design consideration.
Cheaper, lower torque servos use plastic gears, usually made of nylon. Plastic gears are inexpensive to produce, making nylon gear servos cheaper to manufacture and buy. Nylon gears are also lightweight compared to metal type, which is an important consideration when designing robots or aircraft. However, if too much torque is applied to these nylon gears, they will break.
Servos with higher torque ratings have metal gears so they can deliver higher torque without breaking. The materials used in the construction of the motor play an important role in determining how much torque the motor can deliver.

Figure 5: Metal gears and nylon gears.
Electric motors are manufactured from a variety of materials, but generally those made of metal have higher torque ratings than those made of nylon or other plastics.
3.2 Maximum Voltage of Motor
The second factor that affects the maximum torque of a motor is the maximum voltage that the motor is designed to accept. If you look at any servo spec page, you will find torque ratings for different voltages. Higher voltage makes the motor have more power to provide higher torque. However, the motor and its drive circuit can only accept so much voltage before it overheats and burns out. The motor reaches its maximum torque rating when it accepts the maximum voltage without a failure factor.
The maximum voltage of the motor is given in the specifications provided by the manufacturer.
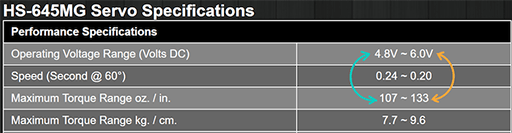
Figure 6: HS-645MG servo specifications.
3.3 Heat Generated by Motor
This is the ultimate limiting factor in achieving the maximum torque of the motor. When electric motors work, they generate waste heat. The harder the motor works, the more heat it generates.
For most motors used in hobby projects, from DC motors, servo motors, to stepper motors, the waste heat can simply radiate into the air. There's no active cooling. Therefore, it is important to know the range of torque (and speed) the motor can be without the risk of thermal failure.
4. Is Higher Motor Torque Better?
In theory, the bigger the torque, the better, as more torque gives more power and faster speed. Take a car engine as an example, such as a family car, the greater the torque, the better the acceleration; the greater the torque of the truck, the greater the weight that it can drive; the greater the torque of the off-road vehicle, the greater the climbing degree will be.
The larger the torque, the better the response of the car running. Compared with the same type of engine car, the larger the torque output, the larger the bearing capacity, the better the acceleration performance, the stronger the climbing force, the less the number of shifts, and the less wear and tear on the car. Especially when the car starts at zero speed, it shows the superiority of the one with the higher torque to increase the speed faster.
An important data for evaluating a car is the acceleration time of the car at 0-100 km/h, and this acceleration time depends on the torque of the car engine.
The greater the torque, the greater the power and the more power consumption. Therefore, choose the torque size according to your needs. If there is no need to use a higher torque motor, you can buy a smaller one to save costs.
Okmarts can provide you with all kinds of electric motors, such as high torque electric motor, evike high torque motor, 12v dc motor high torque, etc.
Related Info
AC Motor: Types, Speed Control, Features & UsesStepper Motor: Working Principle, Operating Modes & Application
Types of Stepper Motors: Three Methods to Classify
Servo Motor vs Stepper Motor: Comparison from 9 Aspects
Torque Motor: Structure, Features, Types, Application


