
Figure 1: Cross section of Industrial electric motor.
The Three-phase induction motor consists of two basic parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator is the fixed part of the motor and is used to generate a rotating magnetic field. It is mainly composed of the stator core, the stator winding and the base. The rotor is the rotating part of the motor, which consists of rotor core, rotor winding and rotating shaft. Its function is to obtain rotational torque under the action of a rotating magnetic field.
The most common three-phase induction motors in daily work are squirrel-cage motors and wound rotor motors (also known as slip ring-rotor motors, slip ring induction motors). This is classified according to their rotor structure. The stator of the squirrel cage motor and the wound rotor motor are basically the same, and the difference lies in the rotor part.
1. Different Rotor Structure
1.1 Three-phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor
In the cage rotor winding, metal bars are placed in the small slots of the rotor iron core, and then end rings are used to connect the bars at both ends of the iron core. In this way, any one bar and its corresponding bar form a closed winding through the end rings at both ends. If the iron core is removed, the remaining winding is shaped like a squirrel cage, so it is called squirrel cage winding.
There are two types of cage rotor windings: copper bar rotor winding and cast aluminum rotor winding. The copper bar rotor winding is to put copper bars in the small slots of the rotor core, and then weld them together with metal end rings at both ends. Cast aluminum rotor winding is to cast aluminum bars, end rings and fan blades on the iron core by casting method.
To increase the starting torque, can use a deep-slotted cage rotor winding (with long and narrow cage bar cross-section), or a double-cage rotor winding (two squirrel cages on the upper and lower layers connected with high-resistance materials).

Figure 2: Two types of cage rotor windings.
1.2 Three-phase Wound Rotor Induction Motor
The structure of the wound rotor winding is shown in the figure 4 below. It is to embed windings made of insulated wires in the rotor core according to certain rules, and then connect the windings in a delta or star connection, most of which are connected in a star (as shown in Figure 3) .

Figure 3: Wound rotor windings connected in star.
After the windings are connected, 3 phase wires are drawn out. Connected them to the 3 copper collector rings (also known as slip rings) of the rotating shaft through the inner hole of the rotating shaft. The collector rings run with the rotating shaft, and are in frictional contact with the stationary brushes. The brushes are connected to the varistor through wires, so that the current generated by the rotor winding forms a loop through the collector ring, the brushes, and the varistor. The slip rings are insulated from each other, as well as between the slip rings and the shaft.
Adjusting the varistor can change the resistance of the rotor winding circuit, thereby changing the current of the winding to adjust the speed of the rotor. When the three wires of the rotor winding are short-circuited, it can be used as a squirrel cage motor.

Figure 4: Structure of the wound rotor motor.
2. Other Differences
2.1 Slip Ring
From the appearance, the most obvious difference between them is that the wound rotor motor has a rotor slip ring, and the squirrel cage motor does not.
Squirrel-cage motor rotor windings are short-circuited windings. A conductor is placed in each slot of the rotor, which is longer than the iron core. And the conductors are short-circuited with two end rings at both ends of the iron core to form a short-circuit winding.
Wound rotor type motor: The rotor is a coil wound made of copper wire, and the end of the coil is led to the starting control device through a slip ring.
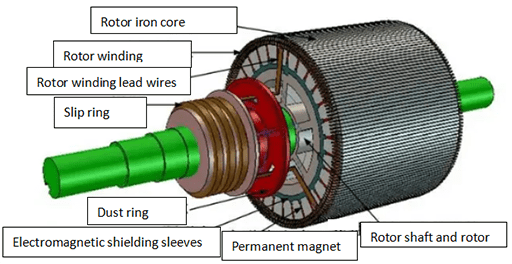
Figure 5: Structure of the wound rotor motor.
2.2 Starting Method
Common starting methods for squirrel-cage induction motors: direct start, step-down start, variable frequency start, or soft starter start.
Common starting methods for wound rotor induction motors: Direct start, rotor resistance starting, or frequency-sensitive rheostat starting is usually used when starting a wound induction motor. There is no need to start the wound rotor induction motor with a frequency converter or soft starter.
2.3 Phase Number Calculation Method
The number of rotor phases of a squirrel-cage induction motor is the number of bars on the squirrel-cage rotor. The number of turns per phase is equal to 1/2 turn. The number of rotor pole pairs is obtained asynchronously by the magnetomotive force of the stator winding, so it is always equal to the number of pole pairs of the stator winding, and has nothing to do with the number of bars of the squirrel-cage rotor.
The number of phases and pole pairs of the rotor winding of the wound rotor induction motor is always the same as that of the stator. The number of turns in each phase is relatively high, and the induced potential is relatively large.
2.4 Insulation to Ground
The rotor windings of squirrel-cage induction motors do not need to be insulated from ground.
The rotor winding of the wound induction motor needs to be insulated from the ground.
3. Advantages and Disadvantages

Figure 6: All kinds of coils.
3.1 Squirrel Cage Induction Motor
Advantages: simple structure, easy to start, reliable operation, small size, sturdy and durable, easy to maintain, repair and install, low cost, etc.
Disadvantages: The starting torque is small, the power factor is low, the speed is not easy to adjust, and the starting current is large when starting directly. Under normal circumstances, the squirrel-cage motor should be started 2-3 times in a cold state, and the interval between each time should not be less than 5 minutes. In the hot state, the motor is started once. When the squirrel-cage induction motor is started frequently, it is easy to cause the squirrel cage to break.
Applicable working conditions: squirrel cage induction motors are suitable for occasions where constant speed and hard characteristics are required.
3.2 Wound Rotor Induction Motor
Advantages: By adding resistance in series to the rotor circuit, the starting current and speed are reduced, and the starting torque is increased. It can improve the starting and speed regulation performance of the motor.
Disadvantages: complex structure, troublesome maintenance, poor operational reliability, and high price.
Applicable working conditions: Winding motors are suitable for occasions requiring soft speed regulation, such as cranes.
Related Info
What is Three Phase Induction Motor and How Does It WorkFANUC Spindle Amplifier Alarm Codes and Solutions (2)
FANUC Spindle Amplifier Alarm Codes and Solutions (3)
FANUC Spindle Amplifier Alarm Codes and Solutions (4)


